... of addidefect in spore germination, in addition to its metabolic effects during the vegetative phase. tional studies on conidiol germination in this strain. In these studies, the scone strain grew as fast as o wild-type strain, RL3-8A, on minimal glucose agar and conidiated abundantly. On sorbore pl ...
DNA polymerase - yusronsugiarto
... DNA sequencing or genes expressed, e.g. comparing genes expressed by a diseased cell to genes expressed by an healthy cell. • Other uses include- Testing for hereditary disease, Evolutionary history of species, Screening e.g.food supply • Applications to synthetic biology - identification of various ...
... DNA sequencing or genes expressed, e.g. comparing genes expressed by a diseased cell to genes expressed by an healthy cell. • Other uses include- Testing for hereditary disease, Evolutionary history of species, Screening e.g.food supply • Applications to synthetic biology - identification of various ...
Ab initio gene prediction
... Note: intron length distributions in Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens (and most other species) are longer and broader. ...
... Note: intron length distributions in Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens (and most other species) are longer and broader. ...
Factsheet - Andrology Australia
... to any male child born through the use of sperm in IVF or ICSI procedures. However, for most men with presumed genetic causes of infertility, we don’t yet know whether their children will be affected. The investigation of men with unexplained low sperm counts (less than 10 million sperm/mL) should i ...
... to any male child born through the use of sperm in IVF or ICSI procedures. However, for most men with presumed genetic causes of infertility, we don’t yet know whether their children will be affected. The investigation of men with unexplained low sperm counts (less than 10 million sperm/mL) should i ...
Chem 410 Chapter 11: Polyprotic Acids and Bases Part 1 How
... shown in the figure on the right. The result is a dipolar compound ( one + and one – charge) which is overall a neutral compound. This type of compound is called a zwitterion. But these amino acid zwitterions are salts, actually internal salts. So they will have many physical properties in common wi ...
... shown in the figure on the right. The result is a dipolar compound ( one + and one – charge) which is overall a neutral compound. This type of compound is called a zwitterion. But these amino acid zwitterions are salts, actually internal salts. So they will have many physical properties in common wi ...
KEY Exam 2 ID
... initiate mitosis. Cyclin B degrades quickly, inactivating cdc2. This degradation limits mitotic events, which do not resume until cyclin B has been resupplied. In cleavage-stage embryos, cyclin B mRNA is supplied in maternally-derived stores; therefore, the cell cycle can continue without G phases, ...
... initiate mitosis. Cyclin B degrades quickly, inactivating cdc2. This degradation limits mitotic events, which do not resume until cyclin B has been resupplied. In cleavage-stage embryos, cyclin B mRNA is supplied in maternally-derived stores; therefore, the cell cycle can continue without G phases, ...
1. Which genetic concept was proposed by Mendel?
... red in color. Which statement most accurately describes why this change in the color of the bread mold occurs? A. ...
... red in color. Which statement most accurately describes why this change in the color of the bread mold occurs? A. ...
Chapter 15 The Techniques of Molecular Genetics
... samples of specific segments of chromosomes. Gel electrophoresis procedures able to resolve DNA fragments differing in length by a single nucleotide. Gene-cloning techniques allowing preparation of large quantities of a DNA molecule. Sanger sequencing Technique is used to determine ...
... samples of specific segments of chromosomes. Gel electrophoresis procedures able to resolve DNA fragments differing in length by a single nucleotide. Gene-cloning techniques allowing preparation of large quantities of a DNA molecule. Sanger sequencing Technique is used to determine ...
Practice exam (2012)
... 1 (21 pt) In your own words, define or describe each of the following: 1-a) Hetroplasmy (as it pertains to organelle genetics) ...
... 1 (21 pt) In your own words, define or describe each of the following: 1-a) Hetroplasmy (as it pertains to organelle genetics) ...
Human_lecture3
... • Usually parents are heterozygous carriers • Affected individuals are usually born to unaffected parents • Affected children are homozygous for mutant gene • In most autosomal recessive diseases males and females are equally likely to be affected • Carrier couple has a 1 in 4 chance of having affec ...
... • Usually parents are heterozygous carriers • Affected individuals are usually born to unaffected parents • Affected children are homozygous for mutant gene • In most autosomal recessive diseases males and females are equally likely to be affected • Carrier couple has a 1 in 4 chance of having affec ...
QuASI: Question Answering using Statistics, Semantics, and
... expand the original set, and increase recall. • Some rules with lower confidence get a lower weight in the ranking step. ...
... expand the original set, and increase recall. • Some rules with lower confidence get a lower weight in the ranking step. ...
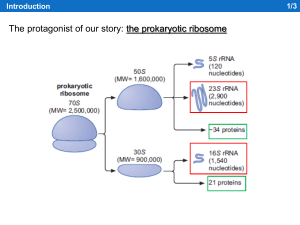
RiboT
... RiboT is a fantastic molecule: a ribosome with tethered subunits, that is able to substain the expression of an entire genome! That’s incredible! So, what now? ...
... RiboT is a fantastic molecule: a ribosome with tethered subunits, that is able to substain the expression of an entire genome! That’s incredible! So, what now? ...
doc SchoenMidtermPractise
... exclude null hypotheses when the probability of acceptance is less than 1/20). In other words, the probability that a Bb black parent produces all brown progeny when crossed with a brown parent is considered reasonably high (one out of eight, which is well within the margin of chance alone being res ...
... exclude null hypotheses when the probability of acceptance is less than 1/20). In other words, the probability that a Bb black parent produces all brown progeny when crossed with a brown parent is considered reasonably high (one out of eight, which is well within the margin of chance alone being res ...
Cloning, Characterization, and Chromosomal Mapping of Human
... Congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI) is a rare inherited disorder characterized by renal unresponsiveness to vasopressin. Most cases of NDI appear to have an X-linked recessive pattern of inheritance. Very recently several mutations in vasopressin V2 receptor gene, which is located in chr ...
... Congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI) is a rare inherited disorder characterized by renal unresponsiveness to vasopressin. Most cases of NDI appear to have an X-linked recessive pattern of inheritance. Very recently several mutations in vasopressin V2 receptor gene, which is located in chr ...
Epilepsy Advanced Sequencing Evaluation
... Determining the cause of epilepsy can help avoid diagnostic uncertainty and aid in selecting appropriate therapy.2 Known causes of epilepsy include stroke, head trauma, infections, and genetic disorders. Once physical causes of epilepsy have been ruled out, a genetic cause or predisposition can reas ...
... Determining the cause of epilepsy can help avoid diagnostic uncertainty and aid in selecting appropriate therapy.2 Known causes of epilepsy include stroke, head trauma, infections, and genetic disorders. Once physical causes of epilepsy have been ruled out, a genetic cause or predisposition can reas ...
ascendant cerebral 5-hydroxytryptamine
... Dowdall, R. M. Facino & V. P. Whittaker, unpublished work) that the vesicles contain not more than four main protein components, three in the membrane and the fourth, accounting for over 50 % of the total protein, in the core. After dialysis and freeze-drying, the core protein (vesiculin) is recover ...
... Dowdall, R. M. Facino & V. P. Whittaker, unpublished work) that the vesicles contain not more than four main protein components, three in the membrane and the fourth, accounting for over 50 % of the total protein, in the core. After dialysis and freeze-drying, the core protein (vesiculin) is recover ...
How Genes and the Environment Influence Our Health
... genetics in the first two chapters of this manual, our emphasis was necessarily on the importance of genes in the living world. But now it is time to begin striking the balance referred to above. In this chapter, we will introduce the students to some of the paradoxical features of genes and a few o ...
... genetics in the first two chapters of this manual, our emphasis was necessarily on the importance of genes in the living world. But now it is time to begin striking the balance referred to above. In this chapter, we will introduce the students to some of the paradoxical features of genes and a few o ...
doc Schoen Midterm
... probability of acceptance is less than 1/20). In other words, the probability that a Bb black parent produces all brown progeny when crossed with a brown parent is considered reasonably high (one out of eight, which is well within the margin of chance alone being responsible for the outcome when the ...
... probability of acceptance is less than 1/20). In other words, the probability that a Bb black parent produces all brown progeny when crossed with a brown parent is considered reasonably high (one out of eight, which is well within the margin of chance alone being responsible for the outcome when the ...
Chapter 5 - macromolecules
... • secondary structure: 3-D shape in local regions of peptide chain • Caused by hydrogen bonds between parts of the polypeptide backbone • Typical secondary structures are a coil called an helix and a folded structure called a ...
... • secondary structure: 3-D shape in local regions of peptide chain • Caused by hydrogen bonds between parts of the polypeptide backbone • Typical secondary structures are a coil called an helix and a folded structure called a ...
Answers questions chapter 15
... c. Describe the structural and sequence elements that are common to all tRNA molecules, addressing the function of each of the elements. What forces stabilize the tRNAs' structural features? Suggested Answer: tRNAs all share a secondary structure that resembles a cloverleaf, including a stem, three ...
... c. Describe the structural and sequence elements that are common to all tRNA molecules, addressing the function of each of the elements. What forces stabilize the tRNAs' structural features? Suggested Answer: tRNAs all share a secondary structure that resembles a cloverleaf, including a stem, three ...
Chapter 5 – Extensions and Modifications of Basic Principles
... – Some extra digits are fully functional; others are just small skin tags ...
... – Some extra digits are fully functional; others are just small skin tags ...
Breaking Down Cell-Cycle Barriers in the Adult Heart
... interact with Rb and p107 and promote G1 exit of nonproliferating cells presumably by displacing E2F proteins.15 Expression of E1A proteins was found to reactivate cell-cycle progression and DNA synthesis in postnatal ventricular myocytes.9 Similarly, expression of E2F-1 proteins in cardiac muscle w ...
... interact with Rb and p107 and promote G1 exit of nonproliferating cells presumably by displacing E2F proteins.15 Expression of E1A proteins was found to reactivate cell-cycle progression and DNA synthesis in postnatal ventricular myocytes.9 Similarly, expression of E2F-1 proteins in cardiac muscle w ...
Transition bias and substitution models
... transversions because – Misincorporation during DNA replication occur more frequently between two purines or between two pyrimidines than between a purine and a pyrimidine – A purine is more likely to mutate chemically to another purine than to a pyrimidine (e.g., through spontaneous deamination) . ...
... transversions because – Misincorporation during DNA replication occur more frequently between two purines or between two pyrimidines than between a purine and a pyrimidine – A purine is more likely to mutate chemically to another purine than to a pyrimidine (e.g., through spontaneous deamination) . ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.