GENETIC CONTROL MECHANISMS AND …
... __________________ : arises when a change in the base sequence of DNA alters a codon, leading to a ______________ amino acid being placed in the protein sequence. Nonsense mutation: converts a codon specifying an amino acid to a _______ codon. Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell as prote ...
... __________________ : arises when a change in the base sequence of DNA alters a codon, leading to a ______________ amino acid being placed in the protein sequence. Nonsense mutation: converts a codon specifying an amino acid to a _______ codon. Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell as prote ...
Bill Nye: Genes - stephaniemcoggins
... 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell con ...
... 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell con ...
ws bubbles new 1213 with answers
... glu gly ser his blue eyes (pt mutation changed one letter in 2nd amino acid from gac to ggc) point mutation, substitution This protein used for: _____________________________________ blue eyes # 1 and #2 are different because of a point mutation ...
... glu gly ser his blue eyes (pt mutation changed one letter in 2nd amino acid from gac to ggc) point mutation, substitution This protein used for: _____________________________________ blue eyes # 1 and #2 are different because of a point mutation ...
קודים גנטיים, 2 שש"ס (שיעור), פרופ` אדוארד טריפונוב In addition to protein
... פרופ' אדוארד טריפונוב,) שש"ס (שיעור2 ,קודים גנטיים In addition to protein-coding message the nucleotide sequences carry instructions for DNA folding, transcription, translation framing, gene splicing, fast adaptation code, and many more. Every sequence element belongs simultaneously to severa ...
... פרופ' אדוארד טריפונוב,) שש"ס (שיעור2 ,קודים גנטיים In addition to protein-coding message the nucleotide sequences carry instructions for DNA folding, transcription, translation framing, gene splicing, fast adaptation code, and many more. Every sequence element belongs simultaneously to severa ...
Gene-and-Chromosome-Mutations
... Splice-site mutations • Remember: - before mRNA leaves the nucleus it is spliced • Splicing is controlled by specific nucleotide sequences at splice sites on the introns • If a mutation occurs at one of these splice sites, the codon may be affected and the intron will remain attached to the mRNA ...
... Splice-site mutations • Remember: - before mRNA leaves the nucleus it is spliced • Splicing is controlled by specific nucleotide sequences at splice sites on the introns • If a mutation occurs at one of these splice sites, the codon may be affected and the intron will remain attached to the mRNA ...
8.7 Mutations
... 2. Translocation results from the exchange of DNA segments between nonhomologous chromosomes. 3. Chromosomal mutations tend to have a bigger affect on the individual. ...
... 2. Translocation results from the exchange of DNA segments between nonhomologous chromosomes. 3. Chromosomal mutations tend to have a bigger affect on the individual. ...
Glossary of Genetic Terms
... Gene amplification -- any process by which specific DNA sequences are replicated disproportionately greater than their representation in the parent molecules; during development, some genes become amplified in specific tissues. Gene map -- the linear arrangement of mutable sites on a chromosome as d ...
... Gene amplification -- any process by which specific DNA sequences are replicated disproportionately greater than their representation in the parent molecules; during development, some genes become amplified in specific tissues. Gene map -- the linear arrangement of mutable sites on a chromosome as d ...
During the last years we have observed a rapid development of
... confirmed the high utility of HRM for mutation scanning of unknown variants, as well as genotyping of common variants. Concurrently, we have provided a list of methodical guidelines which could be applied for setting up HRM in other genetic laboratories and provided a diagnostic validation strategy ...
... confirmed the high utility of HRM for mutation scanning of unknown variants, as well as genotyping of common variants. Concurrently, we have provided a list of methodical guidelines which could be applied for setting up HRM in other genetic laboratories and provided a diagnostic validation strategy ...
DNA Replication Transcription translation [Read
... • Prokaryotic cells regulate gene expression with a set of genes called an operon (also located in some eukaryotes). • An operon is a group of closely linked genes that produces a single mRNA molecule in transcription and that consists of structural genes and regulating elements ...
... • Prokaryotic cells regulate gene expression with a set of genes called an operon (also located in some eukaryotes). • An operon is a group of closely linked genes that produces a single mRNA molecule in transcription and that consists of structural genes and regulating elements ...
asdfs - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Orientation in which the two complementary strands in a DNA molecule run in opposite directions Anti-parallel Sequence of DNA that can jump from one location to another which is thought to be involved in increasing mutations in cells Transposons or Jumping genes ...
... Orientation in which the two complementary strands in a DNA molecule run in opposite directions Anti-parallel Sequence of DNA that can jump from one location to another which is thought to be involved in increasing mutations in cells Transposons or Jumping genes ...
File - Wk 1-2
... Alters the subsequent reading frame by inserting or deleting one or more bases (within a set of three). This alters the reading frame (triplet grouping) of the genetic message, causing an entirely new series of AA’s to be coded after the site of the mutation. All nucleotides downstream of the mutati ...
... Alters the subsequent reading frame by inserting or deleting one or more bases (within a set of three). This alters the reading frame (triplet grouping) of the genetic message, causing an entirely new series of AA’s to be coded after the site of the mutation. All nucleotides downstream of the mutati ...
Gene Function
... • Archibald Garrod and William Bateson (1902) concluded alkaptonuria is genetically determined because: – Families with alkaptonuria often have several affected members. – Alkaptonuria is much more common in first cousin marriages than marriages with unrelated partners. ...
... • Archibald Garrod and William Bateson (1902) concluded alkaptonuria is genetically determined because: – Families with alkaptonuria often have several affected members. – Alkaptonuria is much more common in first cousin marriages than marriages with unrelated partners. ...
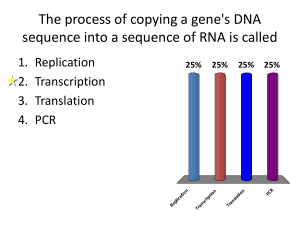
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly synthesized strand 2. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence 3. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming 4. Both RNA a ...
... Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly synthesized strand 2. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence 3. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming 4. Both RNA a ...
4 chapter_test_b 4 chapter_test_b
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
... attached oxygen atoms, which bonds to deoxyribose sugar in DNA. ...
... attached oxygen atoms, which bonds to deoxyribose sugar in DNA. ...
Fact Sheet 3 | GENE MUTATIONS Genes contain the instructions for
... The effect a mutation has on a person’s growth, development or health is determined by a number of factors including how it affects the gene product (the protein); which cells in the body carry the mutation; and when the mutation arose in that individual. TYPES OF MUTATIONS There are a number of dif ...
... The effect a mutation has on a person’s growth, development or health is determined by a number of factors including how it affects the gene product (the protein); which cells in the body carry the mutation; and when the mutation arose in that individual. TYPES OF MUTATIONS There are a number of dif ...
DNA & RNA - East Pennsboro High School
... Repeating sequence bases – signals where transcription should begin Immediately followed by start codon AUG ...
... Repeating sequence bases – signals where transcription should begin Immediately followed by start codon AUG ...
Document
... Mutations are the only way to introduce novel alleles into a species (good for evolution). The effects of mutation are usually bad or neutral - only sometimes are mutations beneficial. So, just like Goldilocks – not to hot, not too cold, just right – the optimal rate of new mutation is a balancing a ...
... Mutations are the only way to introduce novel alleles into a species (good for evolution). The effects of mutation are usually bad or neutral - only sometimes are mutations beneficial. So, just like Goldilocks – not to hot, not too cold, just right – the optimal rate of new mutation is a balancing a ...
BIO 304 Genetics
... d. chromosomes in a Metaphase II cell ___________7________________ 17. By freely substituting bases within a nine-nucleotide segment of RNA (three codons), how many different peptide sequences could be encoded?__203 = 8000 (or nonsense→fewer)_ 18. In mRNA, UUA codes for leucine. What anticodon seque ...
... d. chromosomes in a Metaphase II cell ___________7________________ 17. By freely substituting bases within a nine-nucleotide segment of RNA (three codons), how many different peptide sequences could be encoded?__203 = 8000 (or nonsense→fewer)_ 18. In mRNA, UUA codes for leucine. What anticodon seque ...
Lecture 6: Genome variation File
... – There are 2 types of nucleotides: purines (A,G) and pyrimidines (T,C) ...
... – There are 2 types of nucleotides: purines (A,G) and pyrimidines (T,C) ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.