Lecture 9b (2/18/13) "How to Make Proteins"
... disease; make probability of reproducing less likely. Recall you’re diploid—have two copies of each gene. If have both SS, then you have anemia. ...
... disease; make probability of reproducing less likely. Recall you’re diploid—have two copies of each gene. If have both SS, then you have anemia. ...
Chapter 09 Lecture PowerPoint - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... greatly enhances binding between DNA and protein as the 2 protein subunits bind cooperatively • Multimeric DNA-binding proteins have an inherently higher affinity for binding sites on DNA than do multiple monomeric proteins that bind independently of one another ...
... greatly enhances binding between DNA and protein as the 2 protein subunits bind cooperatively • Multimeric DNA-binding proteins have an inherently higher affinity for binding sites on DNA than do multiple monomeric proteins that bind independently of one another ...
Recombination
... A. The sizes of DNA molecules can be determined by the position to which they migrate in a gel. B. Smaller DNA molecules move faster and farther than larger ones. C. Gels used for electrophoresis of DNA are made out of agarose. D. DNA molecules move through the gel towards the negative electrode. ...
... A. The sizes of DNA molecules can be determined by the position to which they migrate in a gel. B. Smaller DNA molecules move faster and farther than larger ones. C. Gels used for electrophoresis of DNA are made out of agarose. D. DNA molecules move through the gel towards the negative electrode. ...
Genetics Chapter 13 p258
... Genetic testing is defined as analysis of chromosomes, DNA, RNA, proteins, or other analytes to detect abnormalities that can cause a genetic disease. 1. Population Screening for Genetic Disease a. Designed to detect treatable disease early i. Pap smears, hypercholesterolemia b. Population screening ...
... Genetic testing is defined as analysis of chromosomes, DNA, RNA, proteins, or other analytes to detect abnormalities that can cause a genetic disease. 1. Population Screening for Genetic Disease a. Designed to detect treatable disease early i. Pap smears, hypercholesterolemia b. Population screening ...
Homework Assignment #5
... a) Which, if any, drug resistance phenotype is due to a mutation in a mitochondrial gene? Briefly explain your answer using the information on the phenotypic proportion of progeny. ...
... a) Which, if any, drug resistance phenotype is due to a mutation in a mitochondrial gene? Briefly explain your answer using the information on the phenotypic proportion of progeny. ...
DOC - SoulCare.ORG
... * Then he bred the F1 to F1 and the F2 were a mixture of traits (tall and short) Genes = factors that control traits. (Example: plant height) Alleles = different forms of a gene. (Examples: tall or short) * Dominant allele = one whose trait always shows up if it is in the genes. * Recessive allele = ...
... * Then he bred the F1 to F1 and the F2 were a mixture of traits (tall and short) Genes = factors that control traits. (Example: plant height) Alleles = different forms of a gene. (Examples: tall or short) * Dominant allele = one whose trait always shows up if it is in the genes. * Recessive allele = ...
Genetic Engineering
... enzymes that go on to make the traits of an entire body. Actually, the route from DNA sequence to protein is a bit more complicated. First the DNA sequence spells out a certain type of amino acid and that then helps produce a certain type of protein. ...
... enzymes that go on to make the traits of an entire body. Actually, the route from DNA sequence to protein is a bit more complicated. First the DNA sequence spells out a certain type of amino acid and that then helps produce a certain type of protein. ...
Chapter 9 Slide PDF
... defects or ―inborn errors of metabolism‖ 1941 George Beadle and Edward Tatum firmly established the link between genes, the proteins produced from those genes, and a visible phenotype (won the Nobel Prize in 1958) ...
... defects or ―inborn errors of metabolism‖ 1941 George Beadle and Edward Tatum firmly established the link between genes, the proteins produced from those genes, and a visible phenotype (won the Nobel Prize in 1958) ...
Herbicide resistance - Howard University > Plant Biotechnology
... ENGINEERING PLANTS WITH THEIR OWN GENES ...
... ENGINEERING PLANTS WITH THEIR OWN GENES ...
Information Flow
... peels off can form a “hairpin loop.” The hairpin structure is recognized by RNA polymerase and this causes it to dissociate from the DNA. ...
... peels off can form a “hairpin loop.” The hairpin structure is recognized by RNA polymerase and this causes it to dissociate from the DNA. ...
Proteins 101 - Virginia Tech
... of structure •NMR // “true” structure in solution. Can get hydrogens. Can trace some dynamics (e.g. in folding ). // expensive, slow. Large errors -> low reolution in many cases. Can’t get all atoms. No large structures. •Neutron Scattering // perfect for hydrogens. Dynamics. // proteins in powder s ...
... of structure •NMR // “true” structure in solution. Can get hydrogens. Can trace some dynamics (e.g. in folding ). // expensive, slow. Large errors -> low reolution in many cases. Can’t get all atoms. No large structures. •Neutron Scattering // perfect for hydrogens. Dynamics. // proteins in powder s ...
TECRL: connecting sequence to consequence for a new sudden
... Ackerman, 2010). Establishing an accurate genetic diagnosis can not only answer the parents’ question as to why did this happen to my child, but is invaluable for cascade screening of all family members to identify other individuals harbouring the same mutation and who therefore may be at risk of su ...
... Ackerman, 2010). Establishing an accurate genetic diagnosis can not only answer the parents’ question as to why did this happen to my child, but is invaluable for cascade screening of all family members to identify other individuals harbouring the same mutation and who therefore may be at risk of su ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... sequence, thereby increasing the amount of information that can be stored in the DNA. Conceptual Questions 1. List the components of the lac operon and explain the function of each. Answer: LacA, lacY and lacZ are structural genes that code for enzymes involved in the catabolism of lactose. The oper ...
... sequence, thereby increasing the amount of information that can be stored in the DNA. Conceptual Questions 1. List the components of the lac operon and explain the function of each. Answer: LacA, lacY and lacZ are structural genes that code for enzymes involved in the catabolism of lactose. The oper ...
problem set
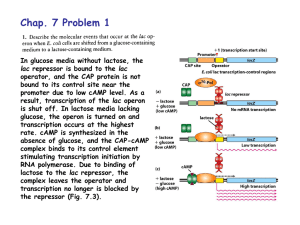
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
Biochemistry (Macromolecules)
... b. Primary Sequence is REALLY IMPORTANT; just look at the difference between Sickle-Cell Disease and normal red blood cells. Just changing the SIXTH amino acid in the primary sequence creates this horrible disease. The easy way to remember that it is the SIXTH amino acid that changed, remember the n ...
... b. Primary Sequence is REALLY IMPORTANT; just look at the difference between Sickle-Cell Disease and normal red blood cells. Just changing the SIXTH amino acid in the primary sequence creates this horrible disease. The easy way to remember that it is the SIXTH amino acid that changed, remember the n ...
01 - Denton ISD
... ii. The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the amino acids. It breaks the bond between the first amino acid and tRNA. iii. An exposed codon attracts a complementary tRNA bearing an amino acid. ...
... ii. The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the amino acids. It breaks the bond between the first amino acid and tRNA. iii. An exposed codon attracts a complementary tRNA bearing an amino acid. ...
KEY UNIT TWO TEST – STUDY GUIDE Define primer. A short piece
... 9. Define PCR (including what does it stand for)? Polymerase Chain Reaction A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short 10. Define SNP (including what does it stand for)? Single Nucleotide Polymorphism One base-pair variation in the genome sequ ...
... 9. Define PCR (including what does it stand for)? Polymerase Chain Reaction A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short 10. Define SNP (including what does it stand for)? Single Nucleotide Polymorphism One base-pair variation in the genome sequ ...
Genetics Syllabus.pages - Maranacook Area Schools
... be on student understanding of Mendelian Genetics, Punnett Squares, the Classification of Living Things, Heredity, the Inheritance of Traits, and the story that DNA tells us. Current events will also be discussed to include cloning and genetically altered foods. Essential Questions: 1. How do the tr ...
... be on student understanding of Mendelian Genetics, Punnett Squares, the Classification of Living Things, Heredity, the Inheritance of Traits, and the story that DNA tells us. Current events will also be discussed to include cloning and genetically altered foods. Essential Questions: 1. How do the tr ...
DNA.Protein.Synthesis Notes
... • Translation is defined as going from mRNA to protein – tRNA which have amino acids attached are going to the ribosome in the cytoplasm. • What are amino acids? monomers of proteins Amino acid attachment site • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold ...
... • Translation is defined as going from mRNA to protein – tRNA which have amino acids attached are going to the ribosome in the cytoplasm. • What are amino acids? monomers of proteins Amino acid attachment site • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold ...
A Bacterial Plasmid: What can you tell me about the plamid?
... • Remove plasmid from bacterial cell. • Use restriction enzyme (RE) open up the plasmid. • Use restriction enzyme to cut the gene out of on the organism’s DNA. Create sticky ends that are complementary to the plasmid’s sticky ends. • Insert the gene using ligase. How does one determine which RE’s to ...
... • Remove plasmid from bacterial cell. • Use restriction enzyme (RE) open up the plasmid. • Use restriction enzyme to cut the gene out of on the organism’s DNA. Create sticky ends that are complementary to the plasmid’s sticky ends. • Insert the gene using ligase. How does one determine which RE’s to ...
Genetics AIMS Review
... 27 Genetic engineering in corn allows genes from bacteria to be added to the genetic material of corn. In traditional breeding, genes of only closely related types of corn can be exchanged. What is one risk of genetically engineering corn plants? A decreases the amount of pesticide needed to grow c ...
... 27 Genetic engineering in corn allows genes from bacteria to be added to the genetic material of corn. In traditional breeding, genes of only closely related types of corn can be exchanged. What is one risk of genetically engineering corn plants? A decreases the amount of pesticide needed to grow c ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life
... o Include the roles of messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), codons, anticodons, ribosomes and amino acids. ...
... o Include the roles of messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), codons, anticodons, ribosomes and amino acids. ...
AA G
... asisDNA to “RNA gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human the mRNA key molecule molecule for has the about manufacture ...
... asisDNA to “RNA gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human the mRNA key molecule molecule for has the about manufacture ...
Leukaemia Section t(11;20)(q23;q11) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... MAPRE1 encoding EB1 which contains a microtubulebinding domain, a dynactin-binding domain (DBD), and an APC-binding domain that is overlapped to DBD; localized at cytoplasmic microtubule tips, centrosomes, and spindle microtubules, and interacts with APC or dynein/dynactin complex to regulate microt ...
... MAPRE1 encoding EB1 which contains a microtubulebinding domain, a dynactin-binding domain (DBD), and an APC-binding domain that is overlapped to DBD; localized at cytoplasmic microtubule tips, centrosomes, and spindle microtubules, and interacts with APC or dynein/dynactin complex to regulate microt ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.