Why Doesn`t Your Brain Heal Like Your Skin?
... plasticity is driven and directed by activities that we perform. After a stroke or brain injury, patients usually improve to a certain extent doing some sort of physical therapy. The improvement is not so much due to growth of new neurons, as you learned above, but because these patients keep stimul ...
... plasticity is driven and directed by activities that we perform. After a stroke or brain injury, patients usually improve to a certain extent doing some sort of physical therapy. The improvement is not so much due to growth of new neurons, as you learned above, but because these patients keep stimul ...
Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord
... spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (motor vs. sensory), given either a model of the spinal cord or a microscope slide. (use the same tw ...
... spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (motor vs. sensory), given either a model of the spinal cord or a microscope slide. (use the same tw ...
General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal
... The idea that general anaesthetics might act on specific neuronal pathways is difficult to entertain without first accepting that anaesthetics act selectively at the molecular level. The old idea that anaesthetics act by disrupting lipid bilayers or by some other ‘nonspecific’ mechanism has been dis ...
... The idea that general anaesthetics might act on specific neuronal pathways is difficult to entertain without first accepting that anaesthetics act selectively at the molecular level. The old idea that anaesthetics act by disrupting lipid bilayers or by some other ‘nonspecific’ mechanism has been dis ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Glial cells are smaller and capable of mitosis. Glial cells do not transmit nerve impulses. Glial cells physically protect and help nourish neurons, and provide an organized, supporting framework for all the nervous tissue. Glial cells far outnumber neurons. Glial cells account for roughly half the ...
... Glial cells are smaller and capable of mitosis. Glial cells do not transmit nerve impulses. Glial cells physically protect and help nourish neurons, and provide an organized, supporting framework for all the nervous tissue. Glial cells far outnumber neurons. Glial cells account for roughly half the ...
30 - HistologyforMedStudents
... 11. In this schematic diagram the presynaptic terminal is shown releasing a neurotransmitter (yellow and orange spheres indicated with white arrows) into a space termed the _____. ...
... 11. In this schematic diagram the presynaptic terminal is shown releasing a neurotransmitter (yellow and orange spheres indicated with white arrows) into a space termed the _____. ...
11 - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... vesicles to release neurotransmitter by exocytosis 4 Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. ...
... vesicles to release neurotransmitter by exocytosis 4 Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. ...
Drug List - Grand Saline ISD
... • Targets benzodiazepine receptors with less effects on skeletal muscles and seizure threshold • Short-term treatment only – Should not be used for more than 10 days – Alert the pharmacist, but realize there are exceptions ...
... • Targets benzodiazepine receptors with less effects on skeletal muscles and seizure threshold • Short-term treatment only – Should not be used for more than 10 days – Alert the pharmacist, but realize there are exceptions ...
notes - Mrs. Blackmon`s Science Blackboard
... 1. astrocytes - control ionic environment, attach neurons to caps. (nutrients) 2. microglia - type of macrophage, engulf microorganisms 3. ependymal - form cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 4. oligodendrocytes - form myelin sheath, insulates nerve fibers 5. Schwann cells - form myelin sheath, act as phagocy ...
... 1. astrocytes - control ionic environment, attach neurons to caps. (nutrients) 2. microglia - type of macrophage, engulf microorganisms 3. ependymal - form cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 4. oligodendrocytes - form myelin sheath, insulates nerve fibers 5. Schwann cells - form myelin sheath, act as phagocy ...
Mechanism for Understanding and Imitating Actions
... Compulsive imitation observed in patients with Utilization behaviors (Lhermitte et al., 1986): a frontal lobe disorder in which the patient has difficulty resisting the impulse to operate or manipulate objects which are in their visual field and within reach. ...
... Compulsive imitation observed in patients with Utilization behaviors (Lhermitte et al., 1986): a frontal lobe disorder in which the patient has difficulty resisting the impulse to operate or manipulate objects which are in their visual field and within reach. ...
Link - thejabberwock
... restraints” across the U.S. At greatest risk: disadvantaged, poor children treated within state mental health systems ...
... restraints” across the U.S. At greatest risk: disadvantaged, poor children treated within state mental health systems ...
Respiratory Drug Agents
... 2. Dextromethorphan 0.125g 3. Ephedrine HCL 0.150g 4. Guaiphenesin 1g ...
... 2. Dextromethorphan 0.125g 3. Ephedrine HCL 0.150g 4. Guaiphenesin 1g ...
Document
... Epilepsy is caused by abnormalities in brain electrical activity. The brain in unable to stop or inhibit electrical impulses between neurons. When the electrical discarded happens the epileptic attack happens. Treatment for this disorder is VNS Pulse Therapy by Cybertronics. ...
... Epilepsy is caused by abnormalities in brain electrical activity. The brain in unable to stop or inhibit electrical impulses between neurons. When the electrical discarded happens the epileptic attack happens. Treatment for this disorder is VNS Pulse Therapy by Cybertronics. ...
Nervous System
... 2. enzyme deactivation – specific enzyme changes structure of neurotransmitter so it is not recognized by receptor 3. glia cells – astrocytes remove neurotransmitters from synaptic cleft 4. reuptake – whole neurotransmitter molecule is taken back into axon terminal that released it a. this is a comm ...
... 2. enzyme deactivation – specific enzyme changes structure of neurotransmitter so it is not recognized by receptor 3. glia cells – astrocytes remove neurotransmitters from synaptic cleft 4. reuptake – whole neurotransmitter molecule is taken back into axon terminal that released it a. this is a comm ...
Organization of Behavior
... oriented change in movement act on central pattern generators changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward ...
... oriented change in movement act on central pattern generators changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward ...
638969476616MyersMod_LG_04
... 4. Discuss the importance of the association areas, and describe how damage to several different cortical areas can impair language functioning. The association areas are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. Rather, they interpret, integrate, and act on information processed by the se ...
... 4. Discuss the importance of the association areas, and describe how damage to several different cortical areas can impair language functioning. The association areas are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. Rather, they interpret, integrate, and act on information processed by the se ...
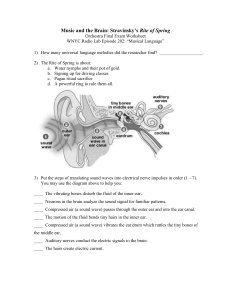
Music and the Brain: Stravinsky`s Rite of Spring
... b. irregular, jagged nerve impulse patterns c. loud impulse patterns d. euphoria 6) When auditory neurons struggle to make sense of a sound they release: a. the dogs b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. ...
... b. irregular, jagged nerve impulse patterns c. loud impulse patterns d. euphoria 6) When auditory neurons struggle to make sense of a sound they release: a. the dogs b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... • Sensory receptors may convey information to the cortex with awareness or perception and may lead to cerebrally controlled responses. • Sensory receptors also serve as afferent pathways for reflex action with or without conscious sensation. ...
... • Sensory receptors may convey information to the cortex with awareness or perception and may lead to cerebrally controlled responses. • Sensory receptors also serve as afferent pathways for reflex action with or without conscious sensation. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 25.1 Drawing of the auditory periphery
... superior olivary complex; SS, suprasylvian sulcus; VNLL, ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus. From Kiang and Peake (1988). FIGURE 25.17 Schematic of the main anatomical cell types of the cochlear nucleus and their corresponding poststimulus time (PST) histograms. (Left) An auditory nerve fiber ...
... superior olivary complex; SS, suprasylvian sulcus; VNLL, ventral nucleus of the lateral lemniscus. From Kiang and Peake (1988). FIGURE 25.17 Schematic of the main anatomical cell types of the cochlear nucleus and their corresponding poststimulus time (PST) histograms. (Left) An auditory nerve fiber ...
lecture 14 File
... location the neuron secretes a neurotransmitter at a synapse that crosses the synaptic gap and stimulates the next cell. ...
... location the neuron secretes a neurotransmitter at a synapse that crosses the synaptic gap and stimulates the next cell. ...
anticholinergic drugs
... • Scopolamine causes drowsiness, amnesia, fatigue, and dreamless sleep. It is effective in motion sickness • Both may be used to treat extrapyramidal side effects of antipsychotic drugs. • Toxic doses of both alkaloids produces CNS excitation- restlessness irritability, disorientation, hallucination ...
... • Scopolamine causes drowsiness, amnesia, fatigue, and dreamless sleep. It is effective in motion sickness • Both may be used to treat extrapyramidal side effects of antipsychotic drugs. • Toxic doses of both alkaloids produces CNS excitation- restlessness irritability, disorientation, hallucination ...
Neonatal rat organotypic brain slice culture and its effect on induced
... number 3 were labeled by CM-DiI for 20 minutes in dark and cultured for 3 to 4 days. The labeled cells were transplanted onto the organotypic slices in 2 weeks culture. The survival of transplanted NSCs was confirmed by visual CM-DiI labeled cells on the slices. The differentiation of transplanted N ...
... number 3 were labeled by CM-DiI for 20 minutes in dark and cultured for 3 to 4 days. The labeled cells were transplanted onto the organotypic slices in 2 weeks culture. The survival of transplanted NSCs was confirmed by visual CM-DiI labeled cells on the slices. The differentiation of transplanted N ...
ISTRUZIONI PER PREPARARE POSTER DA ESPORRE A …
... Assessment of the benefit-risk profile of drugs for non-responders to standard treatments. NB: this research topic is aimed at subgroups of patients who do not respond to standard therapies (e.g., because of the genetic modification of drug metabolism or targeting), and for whom a rationale for subs ...
... Assessment of the benefit-risk profile of drugs for non-responders to standard treatments. NB: this research topic is aimed at subgroups of patients who do not respond to standard therapies (e.g., because of the genetic modification of drug metabolism or targeting), and for whom a rationale for subs ...