Pathophysiologic Changes after Brain Death
... hemolysis, and leftward shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. Several endocrine disorders can be evidenced after brain death has occurred. The most important changes are hypothalamic-pituitary abnormalities and decreased thyroid function. These endocrine changes induce several hemodynamic a ...
... hemolysis, and leftward shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. Several endocrine disorders can be evidenced after brain death has occurred. The most important changes are hypothalamic-pituitary abnormalities and decreased thyroid function. These endocrine changes induce several hemodynamic a ...
Club drugs: review of the `rave` - Indian Council of Medical Research
... the release of serotonin and also blocks serotonin reuptake. These effects are thought to be related to the observed depression, anorexia, agitation, and marked feelings of empathy reported in association with use of the drug. Because MDMA depletes serotonin stores in neurons, subsequent doses produ ...
... the release of serotonin and also blocks serotonin reuptake. These effects are thought to be related to the observed depression, anorexia, agitation, and marked feelings of empathy reported in association with use of the drug. Because MDMA depletes serotonin stores in neurons, subsequent doses produ ...
M. Woodin
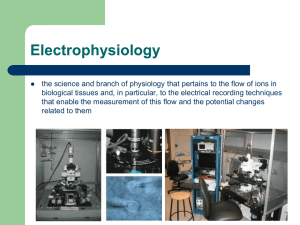
... that enable the measurement of this flow and the potential changes related to them ...
... that enable the measurement of this flow and the potential changes related to them ...
T 1/2
... 4 Excretion of drugs drugs are eliminated from the body either unchanged or as metablites. Excretory organs, the lung excluded, eliminate polar compounds more efficiently than substances with high lipid solubility. The kidney is the most important organ for elimination of drugs and their metaboli ...
... 4 Excretion of drugs drugs are eliminated from the body either unchanged or as metablites. Excretory organs, the lung excluded, eliminate polar compounds more efficiently than substances with high lipid solubility. The kidney is the most important organ for elimination of drugs and their metaboli ...
L.O- To learn about different types of illegal drugs
... • Usually smoked with tobacco or by itself but sometimes dried and cooked with food. • Naturally grown drug which contains a strong chemical known as THC. • Most commonly used illegal drug in Britain but only 1 in 6 16-24 year olds said they had tried it in 2010. ...
... • Usually smoked with tobacco or by itself but sometimes dried and cooked with food. • Naturally grown drug which contains a strong chemical known as THC. • Most commonly used illegal drug in Britain but only 1 in 6 16-24 year olds said they had tried it in 2010. ...
Advantages - pharmacist
... Mechanism is based on the physical phenomenon that “like charges repel and opposite charges attract”. The drugs are forced Across the skin by simple electronic repulsion of similar charges. Thus, anionic drugs Can cross the skin by using a negatively charged electrode. Similarly, cationic drugs ente ...
... Mechanism is based on the physical phenomenon that “like charges repel and opposite charges attract”. The drugs are forced Across the skin by simple electronic repulsion of similar charges. Thus, anionic drugs Can cross the skin by using a negatively charged electrode. Similarly, cationic drugs ente ...
Transcript
... memories, and our actions. I'm going to continue, pick up on some of these themes but in two slightly different ways. I'm going to look at the brain at a higher focus and I'm going to move backwards in time and ask about the origins of mind and the building blocks of behavior. In this lecture I'm go ...
... memories, and our actions. I'm going to continue, pick up on some of these themes but in two slightly different ways. I'm going to look at the brain at a higher focus and I'm going to move backwards in time and ask about the origins of mind and the building blocks of behavior. In this lecture I'm go ...
Full Text Article
... Displacement of a drug from binding sites in plasma or tissues transiently increases the concentration of free (unbound) drug, but this is followed by increased elimination so a new steady state results, in which total drug concentration in plasma is reduced but the free drug concentration is simi ...
... Displacement of a drug from binding sites in plasma or tissues transiently increases the concentration of free (unbound) drug, but this is followed by increased elimination so a new steady state results, in which total drug concentration in plasma is reduced but the free drug concentration is simi ...
- Lorentz Center
... by the intrinsic properties of the cell. The Fourier transform of the input (external + feedback) is given by Xi(). ...
... by the intrinsic properties of the cell. The Fourier transform of the input (external + feedback) is given by Xi(). ...
NADPH Oxidase 1, a novel molecular source of ROS in
... While oxidative stress has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the molecular mechanism underlying selective vulnerability of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway to oxidative damage remains unknown. Increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) result in a ...
... While oxidative stress has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the molecular mechanism underlying selective vulnerability of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway to oxidative damage remains unknown. Increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) result in a ...
(Pharmaceutics) Syllabus
... Systems and methods of molecular biology: Introduction to genetic engineering and biotechnology, genes and gene expression, bacteria, bacteriophage, yeasts, animal cells, use of mutants, genetic analysis of mutants, genetic recombination, complementation. 2. Gene cloning: Nucleic acid isolation clon ...
... Systems and methods of molecular biology: Introduction to genetic engineering and biotechnology, genes and gene expression, bacteria, bacteriophage, yeasts, animal cells, use of mutants, genetic analysis of mutants, genetic recombination, complementation. 2. Gene cloning: Nucleic acid isolation clon ...
ANTIDEPRESSANTS: MAOIs (p.1) 1. Mono
... MAOA – found in NE and 5HT axon terminals MAOB – found in DA axox terminals, GI tract, liver MAOIs block both enzymes --- beneficial main effects & neg. SEs 4. Non-Selective & Irreversible MAOIs non-selective = block both MAOA and B enzymes irreversible = the MAOI enzyme is permanently blocked only ...
... MAOA – found in NE and 5HT axon terminals MAOB – found in DA axox terminals, GI tract, liver MAOIs block both enzymes --- beneficial main effects & neg. SEs 4. Non-Selective & Irreversible MAOIs non-selective = block both MAOA and B enzymes irreversible = the MAOI enzyme is permanently blocked only ...
(off-label) and without (unlicensed)
... increase anxiety, and could result in the refusal of beneficial treatment.15 A recent UK survey of over 220 palliative medicine doctors showed that, when using a drug for a routine off-label indication, only 5% always mention this to their patients, and 31% never do. However, in situations where the ...
... increase anxiety, and could result in the refusal of beneficial treatment.15 A recent UK survey of over 220 palliative medicine doctors showed that, when using a drug for a routine off-label indication, only 5% always mention this to their patients, and 31% never do. However, in situations where the ...
CHAPTER 15 THE CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS
... sensitive to motion. b. The parvocellular (parvo = small) pathway originats in small ganglion cells with small receptive fields. Cells in the parvo pathway are sensitive to color. They are also sensitive to fine ...
... sensitive to motion. b. The parvocellular (parvo = small) pathway originats in small ganglion cells with small receptive fields. Cells in the parvo pathway are sensitive to color. They are also sensitive to fine ...
Neurons Excitatory vs Inhibitory Neurons The Neuron and its Ions
... 1. Biology of networks: the cortex 2. Excitation: • Unidirectional (transformations) • Bidirectional (pattern completion, amplification) 3. Inhibition: Controlling bidirectional excitation. 4. Constraint Satisfaction: Putting it all together. ...
... 1. Biology of networks: the cortex 2. Excitation: • Unidirectional (transformations) • Bidirectional (pattern completion, amplification) 3. Inhibition: Controlling bidirectional excitation. 4. Constraint Satisfaction: Putting it all together. ...
Frequently Asked Questions
... 11. I cannot find certain drugs listed on the PDL or RDL. What does this mean? New drug entities, including new generics and new drug product dosage forms of existing drug entities, are typically non-preferred initially and are not added to the PDL until after being reviewed by the P&T Committee for ...
... 11. I cannot find certain drugs listed on the PDL or RDL. What does this mean? New drug entities, including new generics and new drug product dosage forms of existing drug entities, are typically non-preferred initially and are not added to the PDL until after being reviewed by the P&T Committee for ...
5.4 Muscle Tissues
... – 2. Neuroglial Cells: Support and protect neurons • Parts of Neuroglial Cells: – Shwann Cells: produce myelin sheath around the PNS. – Synapse: gap between neurons ...
... – 2. Neuroglial Cells: Support and protect neurons • Parts of Neuroglial Cells: – Shwann Cells: produce myelin sheath around the PNS. – Synapse: gap between neurons ...
Slide 1
... • Pain is a subjective conscious experience. Pain does not exist without the brain • CNS inhibitory or facilitatory mechanisms are remarkable efficient in decreasing or amplifying the pain experience • Changes in CNS contributes to chronic pain (reorganization: biochemical, atrophy, functions) • A b ...
... • Pain is a subjective conscious experience. Pain does not exist without the brain • CNS inhibitory or facilitatory mechanisms are remarkable efficient in decreasing or amplifying the pain experience • Changes in CNS contributes to chronic pain (reorganization: biochemical, atrophy, functions) • A b ...
Anterior nuclei
... Posterior Hypothalamic Region : Temperature regulation function has been assigned. Responds to temperature changes, such as sweating. Lesion causes hypothermia Also, arousal, shift of attention; especially as a function of behavioral states mediated by hypothalamus Mammillary body: involved in limbi ...
... Posterior Hypothalamic Region : Temperature regulation function has been assigned. Responds to temperature changes, such as sweating. Lesion causes hypothermia Also, arousal, shift of attention; especially as a function of behavioral states mediated by hypothalamus Mammillary body: involved in limbi ...
PD233-Lecture6
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
The Cerebellum, Basal Ganglia and Overall Motor
... cerebellum contributes to the rapid turn-on signals for agonist muscles and turn-off of antagonist muscles at beginning of a motion then it times the opposite sequence at the end of the intended motion direct motor pathway via corticospinal tract is enhanced by cerebellum by additional signals to th ...
... cerebellum contributes to the rapid turn-on signals for agonist muscles and turn-off of antagonist muscles at beginning of a motion then it times the opposite sequence at the end of the intended motion direct motor pathway via corticospinal tract is enhanced by cerebellum by additional signals to th ...
12 The Central Nervous System Part A Central Nervous System
... Located posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex Integrates sensory information Forms comprehensive understanding of the stimulus Determines size, texture, and relationship of parts Visual Areas Primary visual (striate) cortex Seen on the extreme posterior tip of the occipital lobe Most of it i ...
... Located posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex Integrates sensory information Forms comprehensive understanding of the stimulus Determines size, texture, and relationship of parts Visual Areas Primary visual (striate) cortex Seen on the extreme posterior tip of the occipital lobe Most of it i ...
Tom`s JSNC2000 paper
... sufficient to produce changes in activity. Typically, studies producing effects such as LTP and LTD use prolonged pulse trains of stimulation (e.g., Jimbo et al. 1999) rather than a single pulse. In fact, the current arrangement essentially produces a situation analogous to an animal in a dark room ...
... sufficient to produce changes in activity. Typically, studies producing effects such as LTP and LTD use prolonged pulse trains of stimulation (e.g., Jimbo et al. 1999) rather than a single pulse. In fact, the current arrangement essentially produces a situation analogous to an animal in a dark room ...
Lesson 1 - SEL at Meigs
... New research shows how the brain works and what you can do to reach your full potential. In adolescence, you have a unique opportunity for rapid brain growth. Therefore, let’s learn about how the brain thinks thoughts and what you can do to shape your brain. Your brain thinks thoughts by sending e ...
... New research shows how the brain works and what you can do to reach your full potential. In adolescence, you have a unique opportunity for rapid brain growth. Therefore, let’s learn about how the brain thinks thoughts and what you can do to shape your brain. Your brain thinks thoughts by sending e ...