Slides for Chapters 9, 10, 11 and Review
... More generally a given rigid body can have both rotational motion (about some axis passing through center of mass) and translation motion (of the center of mass). ...
... More generally a given rigid body can have both rotational motion (about some axis passing through center of mass) and translation motion (of the center of mass). ...
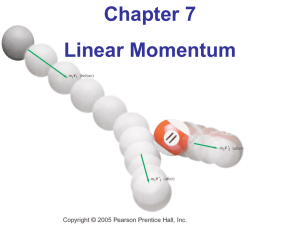
Chapter 7- Linear Momentum
... We have to make use of the concept of vector components. In the figure, considering the system isolated, the total momentum has to be conserved in both x and y directions. In this particular case, the reference system is taken such B is initially (before the collision) at rest and A moves in the x d ...
... We have to make use of the concept of vector components. In the figure, considering the system isolated, the total momentum has to be conserved in both x and y directions. In this particular case, the reference system is taken such B is initially (before the collision) at rest and A moves in the x d ...
Wednesday, April 2, 2008
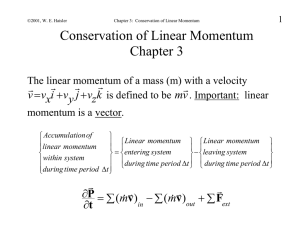
... The principle of energy conservation can be used to solve problems that are harder to solve just using Newton’s laws. It is used to describe motion of an object or a system of objects. A new concept of linear momentum can also be used to solve physical problems, especially the problems involving col ...
... The principle of energy conservation can be used to solve problems that are harder to solve just using Newton’s laws. It is used to describe motion of an object or a system of objects. A new concept of linear momentum can also be used to solve physical problems, especially the problems involving col ...
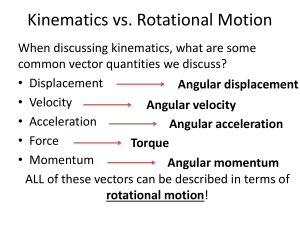
What is angular velocity? Angular speed
... sides 2a and 2b. The system rotates with angular speed ω about an axis in the plane of the figure through the center as shown. a) Find the KE of the entire object. b) Check your results individually by calculating the KE of each particle, and then finding their sum. ...
... sides 2a and 2b. The system rotates with angular speed ω about an axis in the plane of the figure through the center as shown. a) Find the KE of the entire object. b) Check your results individually by calculating the KE of each particle, and then finding their sum. ...