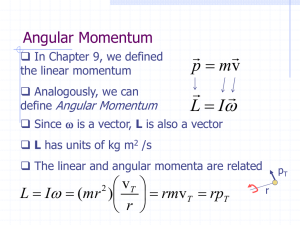
Gravitation and Rotational Motion
... For a given applied force, the change in angular velocity depends on the lever arm, which is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is exerted. ...
... For a given applied force, the change in angular velocity depends on the lever arm, which is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is exerted. ...
Mid Term Test 2012 Answers File
... b) A flywheel with a moment of inertia I = 5 kg m2 is mounted on a light axle. It is initially stationary. A torque of 100 N m is applied to the axle for 100 s. (i) Calculate the final angular velocity of the flywheel. v = u + at = u + F/m t, so f = I + t = 0 + /I t = 2000 rads–1. (ii) Calculate ...
... b) A flywheel with a moment of inertia I = 5 kg m2 is mounted on a light axle. It is initially stationary. A torque of 100 N m is applied to the axle for 100 s. (i) Calculate the final angular velocity of the flywheel. v = u + at = u + F/m t, so f = I + t = 0 + /I t = 2000 rads–1. (ii) Calculate ...
Quiz
... 5. What is the moment of inertia about its centre of gravity of a 7.5 kg thigh if the thigh’s length is 35 cm and its radius of gyration is 50% of the length? a) 0.230 kg.m2 b) 1.313 kg.m2 c) 2.63 kg.m2 d) 0.919 kg.m2 ...
... 5. What is the moment of inertia about its centre of gravity of a 7.5 kg thigh if the thigh’s length is 35 cm and its radius of gyration is 50% of the length? a) 0.230 kg.m2 b) 1.313 kg.m2 c) 2.63 kg.m2 d) 0.919 kg.m2 ...
T3 F2013 9 30
... 0.30 kg putty wad that sticks to the end of the rod. If the rod's angular speed just before collision is 2.4 rad/s, what is the angular speed of the rod–putty system immediately after collision? ...
... 0.30 kg putty wad that sticks to the end of the rod. If the rod's angular speed just before collision is 2.4 rad/s, what is the angular speed of the rod–putty system immediately after collision? ...
Section 8-2 Center of Mass
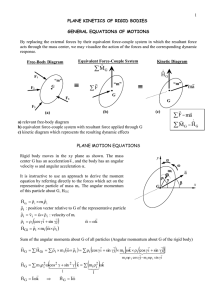
... Unit 6 Notes: Part 1 – Corresponds to Chapter 7 text - Chapter 7 Rotational Motion / Gravitation 1. Rotational Motion – motion of a body that spins about an axis a. Axis of rotation – line about which rotation occurs i. Perpendicular to motion ii. Through center of motion b. Linear equations will no ...
... Unit 6 Notes: Part 1 – Corresponds to Chapter 7 text - Chapter 7 Rotational Motion / Gravitation 1. Rotational Motion – motion of a body that spins about an axis a. Axis of rotation – line about which rotation occurs i. Perpendicular to motion ii. Through center of motion b. Linear equations will no ...
4 Types of Planetary Motion - Earth Science With Mrs. Locke
... BUT if gravity was all there was, we’d all fall into the sun So there is also INERTIA • It’s the tendency of an object in motion to keep moving in the SAME direction and speed unless something else acts on it, like gravity • when balanced with gravity it keeps planets orbiting ...
... BUT if gravity was all there was, we’d all fall into the sun So there is also INERTIA • It’s the tendency of an object in motion to keep moving in the SAME direction and speed unless something else acts on it, like gravity • when balanced with gravity it keeps planets orbiting ...
A moving object has a tendency to keep moving, this is momentum
... spinning merry-go-round, it will speed up. Neutron stars are formed by the collapse of a star's matter following a supernova. ...
... spinning merry-go-round, it will speed up. Neutron stars are formed by the collapse of a star's matter following a supernova. ...
Precession

Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, the axis of rotation of a precessing body itself rotates around another axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called nutation. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced.In astronomy, ""precession"" refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters, and especially to Earth's precession of the equinoxes. (See section Astronomy below.)