Tangential velocity Angular velocity
... • The point or line that is the center of the circle is the axis of rotation. • If the axis of rotation is inside the object, the object is rotating (spinning). • If the axis of rotation is outside the object, the object is revolving. ...
... • The point or line that is the center of the circle is the axis of rotation. • If the axis of rotation is inside the object, the object is rotating (spinning). • If the axis of rotation is outside the object, the object is revolving. ...
Ch33
... • to briefly understand the free symmetric top: letting the axis do its own thing: gyroscopic motion Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
... • to briefly understand the free symmetric top: letting the axis do its own thing: gyroscopic motion Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
H Ch 7 Notes - Angular Motion.notebook
... Similarly, (net) torque causes angular acceleration. Torque (τ) is a measure of how much a force causes an object to rotate. ...
... Similarly, (net) torque causes angular acceleration. Torque (τ) is a measure of how much a force causes an object to rotate. ...
Torque
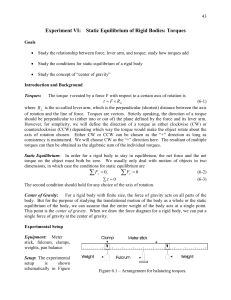
... in static equilibrium (balance) in a horizontal position. The position of the fulcrum is roughly the center of gravity of the meter stick. Note that this position is not necessarily in the middle of the stick (50 cm mark). 2. With a clamp, hang a 200-g mass on the stick 20 cm from the fulcrum. Hang ...
... in static equilibrium (balance) in a horizontal position. The position of the fulcrum is roughly the center of gravity of the meter stick. Note that this position is not necessarily in the middle of the stick (50 cm mark). 2. With a clamp, hang a 200-g mass on the stick 20 cm from the fulcrum. Hang ...
Rigid Body - Kinematics
... dr = d Φn × r = dΩ × r Sign opposite from last lecture because the rotation is CCW ...
... dr = d Φn × r = dΩ × r Sign opposite from last lecture because the rotation is CCW ...
Rotational Motion
... 2) explain what dependence the angular acceleration has upon the magnitude of the applied force 3) determine the moment of inertia of any rotating body Review of concepts: Moment of Inertia Just what in the world is a “moment of inertia”? That’s probably the most asked question in my lab. While it d ...
... 2) explain what dependence the angular acceleration has upon the magnitude of the applied force 3) determine the moment of inertia of any rotating body Review of concepts: Moment of Inertia Just what in the world is a “moment of inertia”? That’s probably the most asked question in my lab. While it d ...
Jeopardy
... Which ball has a greater inertia when released from the top of a 10 foot ladder; a 2N ball or a 3N ball? Be able to explain why! ...
... Which ball has a greater inertia when released from the top of a 10 foot ladder; a 2N ball or a 3N ball? Be able to explain why! ...
Precession

Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, the axis of rotation of a precessing body itself rotates around another axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called nutation. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced.In astronomy, ""precession"" refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters, and especially to Earth's precession of the equinoxes. (See section Astronomy below.)