Chapter 3 - COSEE Florida
... such as seamounts exert more gravitational pull Differences affect sea level that can be detected by satellite Seismic reflection profiles looks at ocean structure beneath sea floor ...
... such as seamounts exert more gravitational pull Differences affect sea level that can be detected by satellite Seismic reflection profiles looks at ocean structure beneath sea floor ...
File
... 9. Fossils of the fern Glossopteris have been found in the continents of South America, Africa, Asia, and Antarctica. The seeds of this fern were too small to be dispersed by wind. Which is best indicated by the presence of Glossopteris fossils on these continents? a. The northern climate regions we ...
... 9. Fossils of the fern Glossopteris have been found in the continents of South America, Africa, Asia, and Antarctica. The seeds of this fern were too small to be dispersed by wind. Which is best indicated by the presence of Glossopteris fossils on these continents? a. The northern climate regions we ...
Ocean Depth through Deep Time
... can be accommodated by the ocean basins. Assuming that the oceanic volume of water has not changed, we can calculate the sea level from the assumed total volume of oceanic water and the amount of water that can be accommodated by oceanic basins. As a result, we establish a relationship between sea l ...
... can be accommodated by the ocean basins. Assuming that the oceanic volume of water has not changed, we can calculate the sea level from the assumed total volume of oceanic water and the amount of water that can be accommodated by oceanic basins. As a result, we establish a relationship between sea l ...
Supplemental Earth Science Review Questions
... B. Rock samples taken near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge are much younger than those taken near the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America. C. Stripes of rock from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge have alternating magnetic polarities. D. There is more sediment along the continental shelf than on th ...
... B. Rock samples taken near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge are much younger than those taken near the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America. C. Stripes of rock from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge have alternating magnetic polarities. D. There is more sediment along the continental shelf than on th ...
Ch 4 Sec 1,2
... All the continents once formed a large super continent that he called Pangaea which means “all lands” He said that there was one large ocean surrounding it called Panthalassa meaning “all seas” ...
... All the continents once formed a large super continent that he called Pangaea which means “all lands” He said that there was one large ocean surrounding it called Panthalassa meaning “all seas” ...
File
... had at one time all been joined together into one supercontinent. What was the name of this supercontinent? Pangaea (Greek for “all lands”). Pg.639 p2 3. What are glacial striations? Scrapes and gouges in the land surface (revealing the direction of ice flow) left by moving ice sheets and glaciers. ...
... had at one time all been joined together into one supercontinent. What was the name of this supercontinent? Pangaea (Greek for “all lands”). Pg.639 p2 3. What are glacial striations? Scrapes and gouges in the land surface (revealing the direction of ice flow) left by moving ice sheets and glaciers. ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... A trench is a steep-walled valley on the sea floor adjacent to a continental margin. For example, ocean crust formed at the East Pacific Rise, an oceanic ridge in the east Pacific, plunges into the trench adjacent to the Andes Mountains on the west side of the South American continent. In Hess' mode ...
... A trench is a steep-walled valley on the sea floor adjacent to a continental margin. For example, ocean crust formed at the East Pacific Rise, an oceanic ridge in the east Pacific, plunges into the trench adjacent to the Andes Mountains on the west side of the South American continent. In Hess' mode ...
Physical Geography - Brogranoni-GEO1
... As far back as 1620, Francis Bacon spotted that the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America looked as if they would fit together, like pieces of a jigsaw. Between then and 1912 other people identified further similarities between other continental coastlines, but it was only in 1912 ...
... As far back as 1620, Francis Bacon spotted that the west coast of Africa and the east coast of South America looked as if they would fit together, like pieces of a jigsaw. Between then and 1912 other people identified further similarities between other continental coastlines, but it was only in 1912 ...
1000
... Molten rock contains metal minerals that will align with the Earth’s magnetic field, then cool and stay as a record of that time ...
... Molten rock contains metal minerals that will align with the Earth’s magnetic field, then cool and stay as a record of that time ...
Plate Tectonic Theory
... Proposed that hot, less dense mantle material rises toward the mid-ocean ridges ...
... Proposed that hot, less dense mantle material rises toward the mid-ocean ridges ...
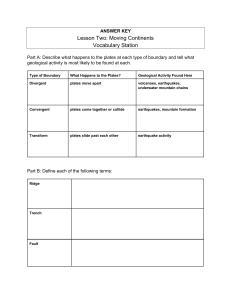
Lesson Two: Moving Continents Vocabulary Station
... According to the Continental Drift Theory, the continents once formed a giant landmass named Pangaea. It wasn’t until the 1950s and 1960s that scientists began to explain how the continents were able to move with their discovery of the midocean ridges and sea-floor spreading. According to this new t ...
... According to the Continental Drift Theory, the continents once formed a giant landmass named Pangaea. It wasn’t until the 1950s and 1960s that scientists began to explain how the continents were able to move with their discovery of the midocean ridges and sea-floor spreading. According to this new t ...
Structure of the Earth
... He thought that all the continents used to fit together in one big continent called Pangaea which broke apart about 200 million years ago into the continents that we now know. ...
... He thought that all the continents used to fit together in one big continent called Pangaea which broke apart about 200 million years ago into the continents that we now know. ...
lecture notes
... through the lithosphere and are defined by seismicity Plate edges are trenches, oceanic ridges and transform faults Seismicity and volcanism are concentrated along plate boundaries Movement of plates is caused by thermal convection of the “plastic” rocks of the asthenosphere which drag along t ...
... through the lithosphere and are defined by seismicity Plate edges are trenches, oceanic ridges and transform faults Seismicity and volcanism are concentrated along plate boundaries Movement of plates is caused by thermal convection of the “plastic” rocks of the asthenosphere which drag along t ...
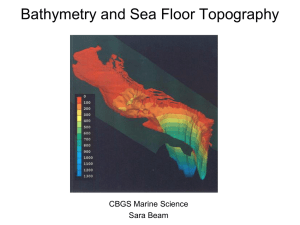
Bathymetry
... trench is easily seen here This is an area of intense subduction where the Nazca plate is being detroyed and is pushing up the Andes mountains in the process. Note the very narrow continental shelf at the active coastal margin, wide shelf at passive margin ...
... trench is easily seen here This is an area of intense subduction where the Nazca plate is being detroyed and is pushing up the Andes mountains in the process. Note the very narrow continental shelf at the active coastal margin, wide shelf at passive margin ...
Continental Drift - Monroe County Schools
... was relatively flat & featureless. •19th century measurements improved, discovery of underwater mountains in the mid Atlantic Ocean. •After World War I early sonar showed the ocean floor to be much more rugged than was previously thought. •In 1947 the survey ship Atlantis found that the sediment lay ...
... was relatively flat & featureless. •19th century measurements improved, discovery of underwater mountains in the mid Atlantic Ocean. •After World War I early sonar showed the ocean floor to be much more rugged than was previously thought. •In 1947 the survey ship Atlantis found that the sediment lay ...
1. Where is the triple junction?
... pattern of known impact craters on Earth? A. The Moon has protected the equatorial regions from Meteor impacts. B. The oceans, polar regions, and most tropical areas have not been explored for craters. C. The poles don’t get many impacts. D. Meteors are attracted to temperate areas – the “Goldilocks ...
... pattern of known impact craters on Earth? A. The Moon has protected the equatorial regions from Meteor impacts. B. The oceans, polar regions, and most tropical areas have not been explored for craters. C. The poles don’t get many impacts. D. Meteors are attracted to temperate areas – the “Goldilocks ...
1 Science 8 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2: Oceans
... The slow rise and fall of the ocean. The upper and lower edges of a beach are determined by the high- and lowtide mark. Tides are connected to the motion of the moon and the spinning of the Earth. The moon exerts a greater force of pull than the sun due to its closer proximity to Earth. ...
... The slow rise and fall of the ocean. The upper and lower edges of a beach are determined by the high- and lowtide mark. Tides are connected to the motion of the moon and the spinning of the Earth. The moon exerts a greater force of pull than the sun due to its closer proximity to Earth. ...
Plate Boundary
... Which is not something that was used to support Continental drift hypothesis? A. The fit of the continents B. The alignment of mountains C. The locations of fossils on various continents D. The arrangement of unique rocks on continents E. All of the above were used to support Continental Drift hypo ...
... Which is not something that was used to support Continental drift hypothesis? A. The fit of the continents B. The alignment of mountains C. The locations of fossils on various continents D. The arrangement of unique rocks on continents E. All of the above were used to support Continental Drift hypo ...
notes
... Principle of Superposition • In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rocks, the oldest rocks are on the bottom with the most recent on top. ...
... Principle of Superposition • In an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rocks, the oldest rocks are on the bottom with the most recent on top. ...
Plate Tectonics
... In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continents. For example, the discovery of fossils of tropical plants (in the form of coal deposits) in Antarctica l ...
... In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continents. For example, the discovery of fossils of tropical plants (in the form of coal deposits) in Antarctica l ...
Mapping the Ocean Floor
... Mid-Ocean Ridge a long, undersea mountain chain that usually extends down the middle of the ocean The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, for example, snakes down the middle of the Atlantic most of the way from the North Pole to Antarctica. ...
... Mid-Ocean Ridge a long, undersea mountain chain that usually extends down the middle of the ocean The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, for example, snakes down the middle of the Atlantic most of the way from the North Pole to Antarctica. ...
Mr. Lanik - Plate Tectonics 2 DO NOT MARK ANSWERS ON THIS
... 6. During which geologic period within the Mesozoic Era did the supercontinent Pangaea begin to break apart? 7. State the compass direction toward which North America has moved since Pangaea began to break apart. 8. State one form of evidence that supports the inference that Pangaea existed. 9. Base ...
... 6. During which geologic period within the Mesozoic Era did the supercontinent Pangaea begin to break apart? 7. State the compass direction toward which North America has moved since Pangaea began to break apart. 8. State one form of evidence that supports the inference that Pangaea existed. 9. Base ...
The evolution of Middle America and the Gulf of l\tfexico
... of Middle America and the Gulf of Mexico-Caribbean Sea region is presented. The model. which is based upon the existence of the Mojave-Sonora megashear, incorporates into the Triassic Pangea reconstruction three microplates between North and South America. thus avoiding the overlap of the Bullard fi ...
... of Middle America and the Gulf of Mexico-Caribbean Sea region is presented. The model. which is based upon the existence of the Mojave-Sonora megashear, incorporates into the Triassic Pangea reconstruction three microplates between North and South America. thus avoiding the overlap of the Bullard fi ...
Sea Floor Spreading The Mid-ocean Ridge
... Soon, scientists observed a large mountain chain running down the center of the Atlantic ocean. ...
... Soon, scientists observed a large mountain chain running down the center of the Atlantic ocean. ...
Now
... • By 1912, Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, suggested that long ago the continents were joined in a large landmass. • He called this landmass “PANGEA”. It appeared that Pangea split into what we now call continents. Once split, they slowly drifted to where they are today. ...
... • By 1912, Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, suggested that long ago the continents were joined in a large landmass. • He called this landmass “PANGEA”. It appeared that Pangea split into what we now call continents. Once split, they slowly drifted to where they are today. ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.