Chapter 33 Plate Tectonics
... – The continents are slowly moving – All the continents has once been attached in a supercontinent and this was called Pangaea “all land” – Pangaea split and the continents moved apart – The boundary of each continent is not at the shoreline but the continental shelf ...
... – The continents are slowly moving – All the continents has once been attached in a supercontinent and this was called Pangaea “all land” – Pangaea split and the continents moved apart – The boundary of each continent is not at the shoreline but the continental shelf ...
Continental Drift through Plate Tectonics
... -10 million years ago, the continents began to slowly move apart from Pangaea and into their present locations. Wegener’s Evidence -Landforms- mountains matched across continents -Fossils- fossils matched across oceans -Climate- fossils and landforms created in climates that do not match today’s cli ...
... -10 million years ago, the continents began to slowly move apart from Pangaea and into their present locations. Wegener’s Evidence -Landforms- mountains matched across continents -Fossils- fossils matched across oceans -Climate- fossils and landforms created in climates that do not match today’s cli ...
Book F Chapter 3 Section 5
... The geologic column represents the 4.6 billion years that have passed since the first rocks formed on the Earth. • ...
... The geologic column represents the 4.6 billion years that have passed since the first rocks formed on the Earth. • ...
Contours Lesson Plan - Schmidt Ocean Institute
... area? What might the composition of the ocean floor be? What might have been going on in the rest of the world when this feature was formed? Do you think there was much life on or around this feature? Keywords/research topics include: volcanic activity, sea level, crust age, plate movement, landslid ...
... area? What might the composition of the ocean floor be? What might have been going on in the rest of the world when this feature was formed? Do you think there was much life on or around this feature? Keywords/research topics include: volcanic activity, sea level, crust age, plate movement, landslid ...
Power Point Presentation
... Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Understand the importance of asthenospheric thermal c ...
... Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Understand the importance of asthenospheric thermal c ...
Lecture #6 Causes of Ice Ages & Glacial
... begins to develop (think about feedback mechanisms again with ice development, ocean cooling). Cenozoic surface water temperature reconstruction (using planktonic foraminifera) of the Antarctic Ocean. The relative rapid adjustment of circulation systems that followed tectonic events is the likely ca ...
... begins to develop (think about feedback mechanisms again with ice development, ocean cooling). Cenozoic surface water temperature reconstruction (using planktonic foraminifera) of the Antarctic Ocean. The relative rapid adjustment of circulation systems that followed tectonic events is the likely ca ...
Marine Sediments - Rudy Marmolejo`s E
... Calcareous Ooze and the CCD Calcerous ooze contains at roughly about 30% of hard remains of calcerous-secreting organisms. The destruction of calcium carbonate varies with depth. The depth in the ocean at which the pressure is high enough and the amount of carbon dioxide is great enough to begin di ...
... Calcareous Ooze and the CCD Calcerous ooze contains at roughly about 30% of hard remains of calcerous-secreting organisms. The destruction of calcium carbonate varies with depth. The depth in the ocean at which the pressure is high enough and the amount of carbon dioxide is great enough to begin di ...
The Truth About Alfred Wegner
... intensified, thanks in large part to the newly-created U.S. Office of Naval Research. Within a few years, a curious terrain had emerged: vast, flat plains interrupted by ridges, or more precisely, vast mountain ranges. In the Atlantic Ocean, the “ridge” is about midway between the continents on eith ...
... intensified, thanks in large part to the newly-created U.S. Office of Naval Research. Within a few years, a curious terrain had emerged: vast, flat plains interrupted by ridges, or more precisely, vast mountain ranges. In the Atlantic Ocean, the “ridge” is about midway between the continents on eith ...
Work Package 3 Drifting Apart Story
... The process of ocean closure is not a straightforward one and over a period of 200 million years, the Iapetus Ocean slowly closed as Baltica and Avalonia (and the associated Ganderia terrane) moved northwards and collided with Laurentia, leading to the formation of the Rheic Ocean behind them. Ocean ...
... The process of ocean closure is not a straightforward one and over a period of 200 million years, the Iapetus Ocean slowly closed as Baltica and Avalonia (and the associated Ganderia terrane) moved northwards and collided with Laurentia, leading to the formation of the Rheic Ocean behind them. Ocean ...
8.3 – What is Seafloor Spreading?
... 1. Scientists think that the movement of tectonic plates is caused by a. conveyor belts b. heat in Earth’s core. c. pressure in Earth’s crust. d. convection currents. ...
... 1. Scientists think that the movement of tectonic plates is caused by a. conveyor belts b. heat in Earth’s core. c. pressure in Earth’s crust. d. convection currents. ...
Plate Tectonics
... were together. – Mountain ranges such as the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern U.S. are similar to those found in Greenland and western ...
... were together. – Mountain ranges such as the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern U.S. are similar to those found in Greenland and western ...
2 - Tectonic Plates - UTEP Geological Sciences
... - The concept of continental movement was first suggested when it was noticed that Africa and South America had coastlines which appeared to be counterparts of one another - This suggested they may once have been joined and drifted apart - He postulated that all landmasses were originally united int ...
... - The concept of continental movement was first suggested when it was noticed that Africa and South America had coastlines which appeared to be counterparts of one another - This suggested they may once have been joined and drifted apart - He postulated that all landmasses were originally united int ...
Study Guide Questions – Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics What
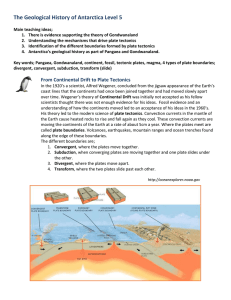
... ocean basins formed, evolved, and closed. This is summarized toward the end of Chapter 3. Review, and understand, Figure 3.37, which shows the stages in evolution of an ocean basin. Apply these processes to the breakup of Pangaea, which began about 250 million years ago, to produce the present confi ...
... ocean basins formed, evolved, and closed. This is summarized toward the end of Chapter 3. Review, and understand, Figure 3.37, which shows the stages in evolution of an ocean basin. Apply these processes to the breakup of Pangaea, which began about 250 million years ago, to produce the present confi ...
Word - LEARNZ
... Pangaea was a super continent that split into ____________________ and _________________ about 250 million years ago. The northern super continent of Laurasia later split into Europe, Asia and North America while the southern super continent of Gondwanaland would eventually split into Africa, India, ...
... Pangaea was a super continent that split into ____________________ and _________________ about 250 million years ago. The northern super continent of Laurasia later split into Europe, Asia and North America while the southern super continent of Gondwanaland would eventually split into Africa, India, ...
Ocean Basin Physiography
... morphology. 3. Abyssal plains are found near some "Atlantic" type continental margins where sediments from turbidity currents have flowed off the continental rise and spread out over the ocean floor producing extremely flat stretches of the ocean floor. Other features include seamounts (hills >1 km ...
... morphology. 3. Abyssal plains are found near some "Atlantic" type continental margins where sediments from turbidity currents have flowed off the continental rise and spread out over the ocean floor producing extremely flat stretches of the ocean floor. Other features include seamounts (hills >1 km ...
Chapter 18 – The Ocean Floor Outline (NOTE NEW CHAPTER TITLE)
... 2. Graded bedding – decrease in sediment grain size from bottom to top d. Continental rise 1. Found in regions where trenches are absent 2. Continental slope merges into a more gradual incline – the continental rise 3. Thick accumulation of sediment 4. At the base of the continental slope turbidity ...
... 2. Graded bedding – decrease in sediment grain size from bottom to top d. Continental rise 1. Found in regions where trenches are absent 2. Continental slope merges into a more gradual incline – the continental rise 3. Thick accumulation of sediment 4. At the base of the continental slope turbidity ...
KEY - UNIT 7 REVIEW 1. Describe Pangaea. When all continents
... 1. Describe Pangaea. When all continents were fused together into one super continent 2. Describe Continental Drift. When continents broke away from being one land mass and moved to where they are currently 3. Who is given credit for both Pangaea and Continental Drift? What evidence did he use to s ...
... 1. Describe Pangaea. When all continents were fused together into one super continent 2. Describe Continental Drift. When continents broke away from being one land mass and moved to where they are currently 3. Who is given credit for both Pangaea and Continental Drift? What evidence did he use to s ...
Pangaea
... In the convection current of a pot or beaker of boiling water, the cooler, denser fluid: ...
... In the convection current of a pot or beaker of boiling water, the cooler, denser fluid: ...
No Slide Title
... Georgia to Newfoundland includes – volcanic activity in the form of deep-sea lava flows, ...
... Georgia to Newfoundland includes – volcanic activity in the form of deep-sea lava flows, ...
The Structure and Origin of the Ocean Basins The water Planet
... North Sea, and South China Sea are examples of seas. Owing to their restricted connections with the open ocean, most marginal seas have unique oceanographic characteristics. For example, the presence of a shallow-water barrier, or sill (Gibraltar Sill), restricts exchange between the Mediterranean a ...
... North Sea, and South China Sea are examples of seas. Owing to their restricted connections with the open ocean, most marginal seas have unique oceanographic characteristics. For example, the presence of a shallow-water barrier, or sill (Gibraltar Sill), restricts exchange between the Mediterranean a ...
Ch.4 Notes
... • 2. If continental crust plates are even both crumple and go up (Himalayas) • 3. oceanic and oceanic crusts one is subducted • Deep trench and island arc of volcanoes ...
... • 2. If continental crust plates are even both crumple and go up (Himalayas) • 3. oceanic and oceanic crusts one is subducted • Deep trench and island arc of volcanoes ...
Chapter 14 - Mesozoic Geology
... – in the present-day Rocky Mountain areas – of New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming ...
... – in the present-day Rocky Mountain areas – of New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming ...
Plate Tectonic Test Use the pictures above to answer questions 1
... which of the points would represent the epicenter or where the surface waves begin? a. A c. C b. B ____10. In the diagram of the earthquake simulation, which point would experience the weakest surface ...
... which of the points would represent the epicenter or where the surface waves begin? a. A c. C b. B ____10. In the diagram of the earthquake simulation, which point would experience the weakest surface ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.