Chapter 18
... • Primitive earth and formation of the ocean – early earth thought to be composed of silicon compounds, iron, magnesium oxide, and other elements – gradually, the earth heated, causing melting and separation of elements – water vapor locked within minerals released to the surface, where it cooled, c ...
... • Primitive earth and formation of the ocean – early earth thought to be composed of silicon compounds, iron, magnesium oxide, and other elements – gradually, the earth heated, causing melting and separation of elements – water vapor locked within minerals released to the surface, where it cooled, c ...
EGU2012-6051
... Continents slowly drift at the top of the mantle, undergoing episodic events like collision, aggregation or splitting. Continental drift and oceanic plate tectonics are surface expressions of mantle convection and closely linked to the thermal state of the mantle. In the present study we will presen ...
... Continents slowly drift at the top of the mantle, undergoing episodic events like collision, aggregation or splitting. Continental drift and oceanic plate tectonics are surface expressions of mantle convection and closely linked to the thermal state of the mantle. In the present study we will presen ...
Announcements
... – As new igneous rock forms, magnetic minerals will line up with Earth’s magnetic field. ...
... – As new igneous rock forms, magnetic minerals will line up with Earth’s magnetic field. ...
Instructions: Earth`s Layers Questions
... separated by great geographic distance. These organisms couldn't have travelled the long distance between these continents, supporting his theory that they were once joined. Evidence 4: Ice Age Explanation 4: Scientists found identical marks caused by the movement of glaciers along the coasts of Afr ...
... separated by great geographic distance. These organisms couldn't have travelled the long distance between these continents, supporting his theory that they were once joined. Evidence 4: Ice Age Explanation 4: Scientists found identical marks caused by the movement of glaciers along the coasts of Afr ...
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name
... separated by great geographic distance. These organisms couldn't have travelled the long distance between these continents, supporting his theory that they were once joined. Evidence 4: Ice Age Explanation 4: Scientists found identical marks caused by the movement of glaciers along the coasts of Afr ...
... separated by great geographic distance. These organisms couldn't have travelled the long distance between these continents, supporting his theory that they were once joined. Evidence 4: Ice Age Explanation 4: Scientists found identical marks caused by the movement of glaciers along the coasts of Afr ...
_____, meaning *all land,* is the name for the great landmass that
... know today had once been part of an earlier supercontinent. • He called this great landmass Pangaea. ...
... know today had once been part of an earlier supercontinent. • He called this great landmass Pangaea. ...
STATION 1: EARTH`S INTERIOR 1. Pressure occurs – remain here 2
... 1. Water washes away layers – go to MOUNTAINS 2. Sediments form – go to SOIL 3. Ice melts carrying rocks – remain here 4. Floodwater causes silt from river to be deposited on flood plain – go to SOIL 5. Silt washed into ocean – go to OCEAN 6. Sediments under pressure – go to EARTH’S INTERIOR ...
... 1. Water washes away layers – go to MOUNTAINS 2. Sediments form – go to SOIL 3. Ice melts carrying rocks – remain here 4. Floodwater causes silt from river to be deposited on flood plain – go to SOIL 5. Silt washed into ocean – go to OCEAN 6. Sediments under pressure – go to EARTH’S INTERIOR ...
Ocean Basins
... water depth – 4000-6000 m (only trenches are deeper) abyssal hills, include rough relief from volcanic formation abyssal plains, smooth surface due to burial by sediment Continental margins created by sediment from land that builds into ocean basins ...
... water depth – 4000-6000 m (only trenches are deeper) abyssal hills, include rough relief from volcanic formation abyssal plains, smooth surface due to burial by sediment Continental margins created by sediment from land that builds into ocean basins ...
Evidence for Plate Tectonics
... • Trenches: V-shaped valley on the ocean floor where old ocean floor is subducted; a convergent plate boundary ...
... • Trenches: V-shaped valley on the ocean floor where old ocean floor is subducted; a convergent plate boundary ...
Continents change position over time.
... like pieces in a puzzle. Were these continents joined at one time? In the late 1800s, German scientist Alfred Wegener (VAY-guh-nuhr) began studying this question. In 1912, he proposed a hypothesis known as continental drift. According to Wegener’s hypothesis, Earth’s continents were once joined in a ...
... like pieces in a puzzle. Were these continents joined at one time? In the late 1800s, German scientist Alfred Wegener (VAY-guh-nuhr) began studying this question. In 1912, he proposed a hypothesis known as continental drift. According to Wegener’s hypothesis, Earth’s continents were once joined in a ...
RELICS OF MOZAMBIQUE OCEAN IN EASTERN AFRICA OROGEN
... formation of which is related to the assembly of the Gondwana supercontinent. It is dominated by metabasic rocks, which have chemical compositions similar to those of recent basalts from a mid-ocean ridge, back-arc setting and island-arc setting. The age of formation of proto lith basalts has been d ...
... formation of which is related to the assembly of the Gondwana supercontinent. It is dominated by metabasic rocks, which have chemical compositions similar to those of recent basalts from a mid-ocean ridge, back-arc setting and island-arc setting. The age of formation of proto lith basalts has been d ...
Chapter 1 The Growth of Oceanography
... • Magnetometers detect and measure Earth’s magnetic field. • Moving across the ocean floor perpendicularly to the oceanic ridges, magneometers alternately record stronger (positive) and weaker (negative) magnetic fields (called magnetic anomalies) in response to the influence of the sea floor rocks. ...
... • Magnetometers detect and measure Earth’s magnetic field. • Moving across the ocean floor perpendicularly to the oceanic ridges, magneometers alternately record stronger (positive) and weaker (negative) magnetic fields (called magnetic anomalies) in response to the influence of the sea floor rocks. ...
Answer Key for Effects of Plate Tectonics Note-taking
... around the world, led to the development of a new unifying theory called the plate tectonic theory. The plate tectonic theory explains how earth works. Heat from Earth’s interior, creates convection currents which move the lithospheric plates around in different directions, at different ...
... around the world, led to the development of a new unifying theory called the plate tectonic theory. The plate tectonic theory explains how earth works. Heat from Earth’s interior, creates convection currents which move the lithospheric plates around in different directions, at different ...
North America - Solid Rock Virtual School
... located, it is also the world's third largest continent, with more than 450 million people living there. It includes 23 countries with dozens of small islands in the Caribbean. The major countries include the United States, Canada, Mexico and the world's largest island, Greenland. Central America is ...
... located, it is also the world's third largest continent, with more than 450 million people living there. It includes 23 countries with dozens of small islands in the Caribbean. The major countries include the United States, Canada, Mexico and the world's largest island, Greenland. Central America is ...
Plate Tectonics - Boone County Schools
... continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past. • Wegener’s proof was fossils of the same plant or animal found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Many of these species couldn’t make it across the ocean. • Continental drift also explained similar glacial patterns found on ...
... continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past. • Wegener’s proof was fossils of the same plant or animal found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Many of these species couldn’t make it across the ocean. • Continental drift also explained similar glacial patterns found on ...
File
... given off from the center of the Earth. That energy is what constantly heats the rocks and partially melts and deforms them. As they are heated they become less dense and rise. As they cool near the surface they sink forming loops that drive push and pull movements of the tectonic plates. Even think ...
... given off from the center of the Earth. That energy is what constantly heats the rocks and partially melts and deforms them. As they are heated they become less dense and rise. As they cool near the surface they sink forming loops that drive push and pull movements of the tectonic plates. Even think ...
Announcements - Western Washington University
... - Know the differences between active and passive margins - Know the structures and provinces of the ocean floor from the coast to the deep sea - Understand the origin and significance of turbidite deposits - Understand the processes that create hydrothermal vents ...
... - Know the differences between active and passive margins - Know the structures and provinces of the ocean floor from the coast to the deep sea - Understand the origin and significance of turbidite deposits - Understand the processes that create hydrothermal vents ...
GY 112 Lecture Notes
... Velikovsky’s book was published, the scientific community apparently jumped all over it. I suspect that it was because of the religious overtones (science and religion will never be totally comfortable with one another). Read the book yourself, then decide if it’s ideas are right or wrong. Here is t ...
... Velikovsky’s book was published, the scientific community apparently jumped all over it. I suspect that it was because of the religious overtones (science and religion will never be totally comfortable with one another). Read the book yourself, then decide if it’s ideas are right or wrong. Here is t ...
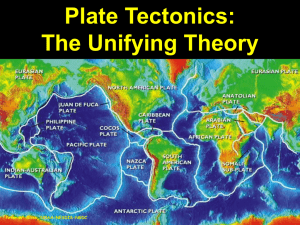
Plate Tectonics
... The Earth’s crust appears to be broken into pieces like a puzzle, which are called plates. These rigid plates are being moved by the convection currents in the hot, molten mantle. The plates spread apart, collide or slide past each other, causing earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains and ridges. The pl ...
... The Earth’s crust appears to be broken into pieces like a puzzle, which are called plates. These rigid plates are being moved by the convection currents in the hot, molten mantle. The plates spread apart, collide or slide past each other, causing earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains and ridges. The pl ...
sxES_G6_RNG_ch04-A_070-073.fm
... 19. Wegener’s idea that the continents slowly moved over Earth’s surface became known as 20. Circle the letter of each sentence that supports Wegener’s hypothesis. a. Some continents match up like jigsaw puzzle pieces. b. Different rock structures are found on different continents. c. Fossils of tro ...
... 19. Wegener’s idea that the continents slowly moved over Earth’s surface became known as 20. Circle the letter of each sentence that supports Wegener’s hypothesis. a. Some continents match up like jigsaw puzzle pieces. b. Different rock structures are found on different continents. c. Fossils of tro ...
Renaissance Practice Exam*Introduction and the Arts
... Reasons that Europe set out to explore the seas in the 1400s and 1500s? Which nation led the way? Columbus’s arguments to persuade Spain to finance his voyage across the Atlantic to Asia? Key goods in the Columbian Exchange ...
... Reasons that Europe set out to explore the seas in the 1400s and 1500s? Which nation led the way? Columbus’s arguments to persuade Spain to finance his voyage across the Atlantic to Asia? Key goods in the Columbian Exchange ...
Teaching_Strategies_files/EARTH PROJECT
... You will be creating a 2-sided poster/large piece of paper project depicting various geographical details of the planet Earth. The goal of this project is to introduce you to the physical features of the world in which you live. This will be an extended project that is made up of 3 important steps. ...
... You will be creating a 2-sided poster/large piece of paper project depicting various geographical details of the planet Earth. The goal of this project is to introduce you to the physical features of the world in which you live. This will be an extended project that is made up of 3 important steps. ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.