Stone Walls: Stories from Minnesota`s Geologic Past
... Quarried in the Minnesota River valley, the Morton Gneiss can be found in buildings and cemeteries across the nation. No two pieces of the rock are the same and one needs only a modest imagination upon which to base a description. For me, descriptions of rock always seem to center on something edib ...
... Quarried in the Minnesota River valley, the Morton Gneiss can be found in buildings and cemeteries across the nation. No two pieces of the rock are the same and one needs only a modest imagination upon which to base a description. For me, descriptions of rock always seem to center on something edib ...
Southern and Central Appalachians
... rocks (Cat Square Terrane), and a truly exotic periGondwanan (Pan-African) Carolina–Avalon Superterrane of Neoproterozoic to Ordovician arc volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks, including the Smith River allochthon (Figure 3). The subsurface Suwannee Terrane lies south of an east- and west-trending sut ...
... rocks (Cat Square Terrane), and a truly exotic periGondwanan (Pan-African) Carolina–Avalon Superterrane of Neoproterozoic to Ordovician arc volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks, including the Smith River allochthon (Figure 3). The subsurface Suwannee Terrane lies south of an east- and west-trending sut ...
The Role of Plate Tectonics in Earth Sciences
... Subduction of Continental Crust High grade metamorphic rocks ...
... Subduction of Continental Crust High grade metamorphic rocks ...
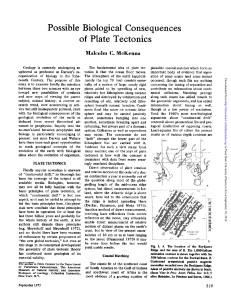
Possible Biological Consequences of Plate Tectonics
... Alpine/Himalayan chain, and several other important past and present mountain chains throughout the world. India smashed, albeit in very slow motion, into southern Asia during the Cenozoic; Australia seems to be colliding with southeast Asia at present. Many ancient collisions seems to be indicated ...
... Alpine/Himalayan chain, and several other important past and present mountain chains throughout the world. India smashed, albeit in very slow motion, into southern Asia during the Cenozoic; Australia seems to be colliding with southeast Asia at present. Many ancient collisions seems to be indicated ...
Power Point view
... continents, no doubt, grew more rapidly along their margins a process called continental accretion as plates collided with island arcs and other plates • Also, ultramafic extrusive igneous rocks were more common due to the higher temperatures ...
... continents, no doubt, grew more rapidly along their margins a process called continental accretion as plates collided with island arcs and other plates • Also, ultramafic extrusive igneous rocks were more common due to the higher temperatures ...
The Late Oligocene-Early Miocene Petrified Forest in Evros and its
... and volcanic rocks (banakites, trachytes, andesites, dacites, rhyolites accompanied by volcano-sedimentary formations (composed of marls, sandstones, clays and intercalations of volcanic rocks as lavas, tuffs, pyroclastics) discordantly covering the basement rocks of the Rhodope massif and Circum Rh ...
... and volcanic rocks (banakites, trachytes, andesites, dacites, rhyolites accompanied by volcano-sedimentary formations (composed of marls, sandstones, clays and intercalations of volcanic rocks as lavas, tuffs, pyroclastics) discordantly covering the basement rocks of the Rhodope massif and Circum Rh ...
Linking collisional and accretionary orogens during Rodinia
... history of Rodinian crustal blocks suggests that internal rifting and breakup of the supercontinent were linked to the initiation of subduction and development of accretionary orogens around its periphery. Thus, breakup was a top-down instigated process. The locus of convergence was initially around ...
... history of Rodinian crustal blocks suggests that internal rifting and breakup of the supercontinent were linked to the initiation of subduction and development of accretionary orogens around its periphery. Thus, breakup was a top-down instigated process. The locus of convergence was initially around ...
Iowa`s Bedrock
... • Early Ordovician – Again on the edge of a shallow sea depositing carbonate, sandy carbonate, and quartz sandstones (Prairie du Chien Group) before another series of weathering and erosion! • Mid-Ordovician – Major sea transgression changed a sandy shallow sea to carbonate shelf. Ash layers appear ...
... • Early Ordovician – Again on the edge of a shallow sea depositing carbonate, sandy carbonate, and quartz sandstones (Prairie du Chien Group) before another series of weathering and erosion! • Mid-Ordovician – Major sea transgression changed a sandy shallow sea to carbonate shelf. Ash layers appear ...
SAI109 Dealing 4 Dynamic Response Earths Surface
... Which layers of the earth are composed primarily of rocky material? ...
... Which layers of the earth are composed primarily of rocky material? ...
ES Chapter 17
... Continental Drift Ancient Climatic Evidence – Various sedimentary rocks offer evidence of vast climatic changes on some continents. – Coal deposits in Antarctica suggested that it must have been closer to the equator. – Glacial deposits found in Africa, India, Australia, and South America suggested ...
... Continental Drift Ancient Climatic Evidence – Various sedimentary rocks offer evidence of vast climatic changes on some continents. – Coal deposits in Antarctica suggested that it must have been closer to the equator. – Glacial deposits found in Africa, India, Australia, and South America suggested ...
Isotope Geochemistry of the Continents
... recognized three Precambrian provinces in the southwestern US based on depleted mantle model ages. Actual rocks are often much younger. ...
... recognized three Precambrian provinces in the southwestern US based on depleted mantle model ages. Actual rocks are often much younger. ...
Seafloor Spreading
... Continental Drift Ancient Climatic Evidence – Various sedimentary rocks offer evidence of vast climatic changes on some continents. – Coal deposits in Antarctica suggested that it must have been closer to the equator. – Glacial deposits found in Africa, India, Australia, and South America suggested ...
... Continental Drift Ancient Climatic Evidence – Various sedimentary rocks offer evidence of vast climatic changes on some continents. – Coal deposits in Antarctica suggested that it must have been closer to the equator. – Glacial deposits found in Africa, India, Australia, and South America suggested ...
Chapter 04
... There are two types of continental Margins (a) passive or trailing margins: margin of continent that moves away from spreading center – Atlantic-style margins (also Artic Ocean, Antarctica and Indian Ocean). Very little volcanic or earthquake activity is associated with passive margins. (b) active o ...
... There are two types of continental Margins (a) passive or trailing margins: margin of continent that moves away from spreading center – Atlantic-style margins (also Artic Ocean, Antarctica and Indian Ocean). Very little volcanic or earthquake activity is associated with passive margins. (b) active o ...
introduction to plate tectonics
... The distribution of Late Paleozoic glaciation strongly supports the idea of Pangaea. ...
... The distribution of Late Paleozoic glaciation strongly supports the idea of Pangaea. ...
Alfred Wegener and continental drift
... Figure 10 : The Gondwana supercontinent of the Mesozoic Era. During the Triassic Period (part of the Mesozoic Era), Pangea (figure 2) splits in two parts, starting from the rift between current Africa and current North America. Two different supercontinents arise: Gondwana and Laurasia. Laurasia is ...
... Figure 10 : The Gondwana supercontinent of the Mesozoic Era. During the Triassic Period (part of the Mesozoic Era), Pangea (figure 2) splits in two parts, starting from the rift between current Africa and current North America. Two different supercontinents arise: Gondwana and Laurasia. Laurasia is ...
studying earths surface R2
... The oldest continental rocks are billions of years old, so the continents have had a lot of time for things to happen to them. Constructive forces cause physical features on Earth’s surface known as landforms to grow. Crustal deformation – when crust compresses, pulls apart, or slides past other cru ...
... The oldest continental rocks are billions of years old, so the continents have had a lot of time for things to happen to them. Constructive forces cause physical features on Earth’s surface known as landforms to grow. Crustal deformation – when crust compresses, pulls apart, or slides past other cru ...
Sea-Floor Spreading - Zion Central Middle School
... carrying continents with it. New ocean floor forms along cracks in the ocean crust as molten material erupts from the mantle spreading out and pushing older rocks to the sides of the ...
... carrying continents with it. New ocean floor forms along cracks in the ocean crust as molten material erupts from the mantle spreading out and pushing older rocks to the sides of the ...
Document
... - REE so named because we could not measure them until high-precision mass spec techniques developed ...
... - REE so named because we could not measure them until high-precision mass spec techniques developed ...
Overview Plate Tectonics
... a. ____________________ fit of the continents b. Similar ________________ have been found on different continents. c. Remains of warm-weather plants in _______________ areas and glacial deposits in __________________areas suggest that continents have moved. d. Similar _____________ structures are fo ...
... a. ____________________ fit of the continents b. Similar ________________ have been found on different continents. c. Remains of warm-weather plants in _______________ areas and glacial deposits in __________________areas suggest that continents have moved. d. Similar _____________ structures are fo ...
Earth Science EOC - Wayne Early/Middle College High School
... because of convection currents (shown above). Convection is the major mechanism of energy transfer in the oceans, atmosphere, and Earth’s ...
... because of convection currents (shown above). Convection is the major mechanism of energy transfer in the oceans, atmosphere, and Earth’s ...
3 - Sea Floor Spreading
... – Why is there so little sediment deposited on the ocean floor? If the oceans have existed for at least 4 billion years, as most geologists believed, shouldn’t there be more? – Why are fossils found on the seafloor no more than 180 million years old? Marine fossils in sedimentary rocks on land -- so ...
... – Why is there so little sediment deposited on the ocean floor? If the oceans have existed for at least 4 billion years, as most geologists believed, shouldn’t there be more? – Why are fossils found on the seafloor no more than 180 million years old? Marine fossils in sedimentary rocks on land -- so ...
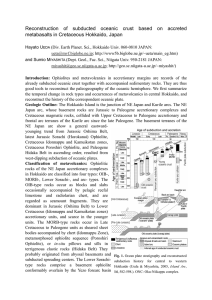
Reconstruction of subducted oceanic crust based on accreted
... limit of the oceanic crust, and the correspondent trench-fill turbidite confines the timing of its accretion, for a single accretionary unit. Based on such concept of ocean plate stratigraphy, we can reconstruct the age distribution within the subducted oceanic plate(s) as follows. The subducted par ...
... limit of the oceanic crust, and the correspondent trench-fill turbidite confines the timing of its accretion, for a single accretionary unit. Based on such concept of ocean plate stratigraphy, we can reconstruct the age distribution within the subducted oceanic plate(s) as follows. The subducted par ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.