CHE-09 Biochemistry
... has a Keq of 0.0001 at pH 7. What is the G for this reaction? Conversion of glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate to 1, 3 – bisphosphoglycerate is an example of substrate level phosphorylation. Explain how? How is the proton motive force determined during oxidative phosphorylation? What would happen if th ...
... has a Keq of 0.0001 at pH 7. What is the G for this reaction? Conversion of glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate to 1, 3 – bisphosphoglycerate is an example of substrate level phosphorylation. Explain how? How is the proton motive force determined during oxidative phosphorylation? What would happen if th ...
$doc.title
... GENETICS DAY May 7, 2010 8th Annual Fred Sherman Lectures Class of ‘62 Auditorium URMC ...
... GENETICS DAY May 7, 2010 8th Annual Fred Sherman Lectures Class of ‘62 Auditorium URMC ...
Mutation - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... proteins are often relatively unimportant to function. However, often nonsense mutations result in completely non-functional proteins. 4. Sense mutations are the opposite of nonsense mutations. Here, a stop codon is converted into an amino acid codon. Since DNA outside of protein-coding regions cont ...
... proteins are often relatively unimportant to function. However, often nonsense mutations result in completely non-functional proteins. 4. Sense mutations are the opposite of nonsense mutations. Here, a stop codon is converted into an amino acid codon. Since DNA outside of protein-coding regions cont ...
Ch18_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C) carbohydrates. D) nucleic acids. E) All of the above are biomolecules. 2) Which functional group is least important in biochemistry? A) amine B) ester C) hydroxyl ...
... 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C) carbohydrates. D) nucleic acids. E) All of the above are biomolecules. 2) Which functional group is least important in biochemistry? A) amine B) ester C) hydroxyl ...
Translation tRNA is a link between the mRNA and the polypeptide
... two subunits, each an aggregate of ribosomal RNA and many proteins. (b) A ribosome has an mRNAbinding site and three tRNA-binding sites, known as the P, A, and E sites. (c) A tRNA fits into a binding site when its anticodon base-pairs with an mRNA codon. The P site holds the tRNA attached to the gro ...
... two subunits, each an aggregate of ribosomal RNA and many proteins. (b) A ribosome has an mRNAbinding site and three tRNA-binding sites, known as the P, A, and E sites. (c) A tRNA fits into a binding site when its anticodon base-pairs with an mRNA codon. The P site holds the tRNA attached to the gro ...
Quiz 2 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... 7. When a membrane is said to be “selectively permeable,” this means that _______. a. half of the membrane is permeable and the other half is not. b. only large molecules can pass through. c. the cell regulates what passes in and out. d. the membrane is permeable part of the time. 8. The process whe ...
... 7. When a membrane is said to be “selectively permeable,” this means that _______. a. half of the membrane is permeable and the other half is not. b. only large molecules can pass through. c. the cell regulates what passes in and out. d. the membrane is permeable part of the time. 8. The process whe ...
Complementation
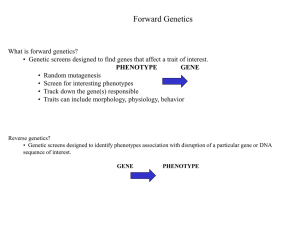
... What is forward genetics? • Genetic screens designed to find genes that affect a trait of interest. ...
... What is forward genetics? • Genetic screens designed to find genes that affect a trait of interest. ...
Macromolecule Review - Mr. Dudley`s Website
... Cyanide is a poison that inhibits the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase. This enzyme is important for creating energy in cells. Without cytochrom c oxidase working properly, an organism will die. Cytochrome c oxidase is made up of what macromolecule? ...
... Cyanide is a poison that inhibits the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase. This enzyme is important for creating energy in cells. Without cytochrom c oxidase working properly, an organism will die. Cytochrome c oxidase is made up of what macromolecule? ...
Ch. 12 Notes
... Substitution (missense) – one base is exchanged for another EX: C is replaced with G (now codes for the wrong amino acid) Substitution (nonsense) – changes the codon for an amino acid to a stop codon causing translation to end early resulting in a protein that cannot function normally. ...
... Substitution (missense) – one base is exchanged for another EX: C is replaced with G (now codes for the wrong amino acid) Substitution (nonsense) – changes the codon for an amino acid to a stop codon causing translation to end early resulting in a protein that cannot function normally. ...
metabolism of amino acids
... • Due to the defective branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex• Lead to accumulation of leucine in blood- and excreted to urine – smell like maple syrup • Untreated lead to abnormal development of the brain, mental retardation, and death in early ...
... • Due to the defective branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex• Lead to accumulation of leucine in blood- and excreted to urine – smell like maple syrup • Untreated lead to abnormal development of the brain, mental retardation, and death in early ...
File
... Genetic determinism: If our behavior is partly influenced by our genes, to what extent do we have free will, i.e. can be held responsible for our actions? 1. Read the summaries of the following studies. Explain which ethical issues into genetic influences of behavior that each of the studies contain ...
... Genetic determinism: If our behavior is partly influenced by our genes, to what extent do we have free will, i.e. can be held responsible for our actions? 1. Read the summaries of the following studies. Explain which ethical issues into genetic influences of behavior that each of the studies contain ...
Powerpoint Slides
... The regain of function for the triple mutant told Brenner and Crick that it was a triplet code, uninterrupted. ...
... The regain of function for the triple mutant told Brenner and Crick that it was a triplet code, uninterrupted. ...
PROTEINS
... This resonance restricts the number of conformations in proteins -- main chain rotations are restricted to f and y. ...
... This resonance restricts the number of conformations in proteins -- main chain rotations are restricted to f and y. ...
LS1a Fall 09
... a. Using the full names of the amino acids, write the sequences of both peptides. Peptide 1: NH2-Glutamic Acid-Lysine-Cysteine-COOH Peptide 2: NH2-Tyrosine-Cysteine-Proline-COOH b. Draw the structure of the connected peptides at physiological pH. The NH 2-Y-C-P-COOH Backbone and one of its side chai ...
... a. Using the full names of the amino acids, write the sequences of both peptides. Peptide 1: NH2-Glutamic Acid-Lysine-Cysteine-COOH Peptide 2: NH2-Tyrosine-Cysteine-Proline-COOH b. Draw the structure of the connected peptides at physiological pH. The NH 2-Y-C-P-COOH Backbone and one of its side chai ...
Biodegradable Polymers – From Delivery of Drugs to Tissue
... Institute of Drug Research, School of Pharmacy- Faculty of Medicine, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel ...
... Institute of Drug Research, School of Pharmacy- Faculty of Medicine, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel ...
The Origin of Life - Earth Life, “Weird Life” and Astrobiology
... defined by describing properties because there is more to their meanings than the features we identify (e.g. water is defined as H2O and not by characteristics such as “cooling”, “tasteless”, “odorless” etc) Defining life from properties of life has problems because there are “non-living” analogues. ...
... defined by describing properties because there is more to their meanings than the features we identify (e.g. water is defined as H2O and not by characteristics such as “cooling”, “tasteless”, “odorless” etc) Defining life from properties of life has problems because there are “non-living” analogues. ...
PPT
... and UAG stop codons. The RF-2 ORF contains an in-frame UGA stop codon and a modest Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence 5 nucleotides upstream of the frameshift site (5´-AGGGGGU-3´). When the RF-2 level is low, the ribosome pauses when a UGA codon is located in the A site. tRNAleu in the P site then sli ...
... and UAG stop codons. The RF-2 ORF contains an in-frame UGA stop codon and a modest Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence 5 nucleotides upstream of the frameshift site (5´-AGGGGGU-3´). When the RF-2 level is low, the ribosome pauses when a UGA codon is located in the A site. tRNAleu in the P site then sli ...
Part 4
... form a larger complex, it is referred to as a quaternary structure. • Many proteins are biologically active as tertiary structures, but some proteins require two or more tertiary structures to be biologically active. • Quaternary structures are held together by bonding between the side chain, R, gro ...
... form a larger complex, it is referred to as a quaternary structure. • Many proteins are biologically active as tertiary structures, but some proteins require two or more tertiary structures to be biologically active. • Quaternary structures are held together by bonding between the side chain, R, gro ...
Grand challenges in bioinformatics.
... from its amino acid sequence. It is widely believed that the amino acid sequence contains all the necessary information to make up the correct three-dimensional structure, since the protein folding is apparently thermodynamically determined; namely, given a proper environment, a protein would fold u ...
... from its amino acid sequence. It is widely believed that the amino acid sequence contains all the necessary information to make up the correct three-dimensional structure, since the protein folding is apparently thermodynamically determined; namely, given a proper environment, a protein would fold u ...
protein synthesis lab
... To define different types of mutations. To understand the three types of point mutations; silent, missense, and nonsense. To understand how an addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a frameshift mutation. To understand the four types of chromosomal mutations; deletion, duplication, inversion, t ...
... To define different types of mutations. To understand the three types of point mutations; silent, missense, and nonsense. To understand how an addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a frameshift mutation. To understand the four types of chromosomal mutations; deletion, duplication, inversion, t ...
Complementary DNA
... Abstract. Recombinant bacterial plasmids that contain DNA complementary to human preproinsulin messenger RNA have been constructed. One clone contains the entire preproinsulin coding region, as well as the 3' untranslated region of the messenger RNA and eight nucleotides of the 5' untranslated regio ...
... Abstract. Recombinant bacterial plasmids that contain DNA complementary to human preproinsulin messenger RNA have been constructed. One clone contains the entire preproinsulin coding region, as well as the 3' untranslated region of the messenger RNA and eight nucleotides of the 5' untranslated regio ...
Modeling Protein Synthesis
... may cause only minor effects to the phenotype of an organism. But sometimes mutations can cause great changes to the gene and therefore greatly alter the protein that is made from that gene. This will likely have great effects on the organism, since the protein will not be able to perform its normal ...
... may cause only minor effects to the phenotype of an organism. But sometimes mutations can cause great changes to the gene and therefore greatly alter the protein that is made from that gene. This will likely have great effects on the organism, since the protein will not be able to perform its normal ...
Protein Synthesis Lab
... in the four bases of DNA: C (cytosine), G (guanine), A (adenine), and T (thymine). The DNA directs the functions of the cell on a daily basis and will also be used to pass on the genetic information to the next generation. Because of its critical role in all the functions of the cell, DNA is kept pr ...
... in the four bases of DNA: C (cytosine), G (guanine), A (adenine), and T (thymine). The DNA directs the functions of the cell on a daily basis and will also be used to pass on the genetic information to the next generation. Because of its critical role in all the functions of the cell, DNA is kept pr ...
Back-translation for discovering distant protein homologies
... proteins. This approach relies on the idea that synonymous mutations cause mismatches in the DNA alignments that can be avoided when all the sequences with the same translation are explored, instead of just the known coding DNA sequences. This allows the algorithm to search for an alignment by deali ...
... proteins. This approach relies on the idea that synonymous mutations cause mismatches in the DNA alignments that can be avoided when all the sequences with the same translation are explored, instead of just the known coding DNA sequences. This allows the algorithm to search for an alignment by deali ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.