
Les 1-DNA Structure-review
... Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
... Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
pAmCyan1-N1 Vector Information
... AmCyan1 start codon—has been converted to a Kozak consensus translation initiation site (3) to further increase the translation efficiency in eukaryotic cells. Two amino acid substitutions (Asn-34 to Ser; Lys-68 to Met) have been made to enhance the emission characteristics of AmCyan1 (excitation ma ...
... AmCyan1 start codon—has been converted to a Kozak consensus translation initiation site (3) to further increase the translation efficiency in eukaryotic cells. Two amino acid substitutions (Asn-34 to Ser; Lys-68 to Met) have been made to enhance the emission characteristics of AmCyan1 (excitation ma ...
DNA - PBworks
... A gene is a section of DNA that codes for a protein. Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
... A gene is a section of DNA that codes for a protein. Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
Protein Synthesis
... responsible for shuttling the amino acid glycine contains a binding site for glycine on one end. On the other end it contains an anticodon that complements the glycine codon (GGA is a codon for glycine, and so the tRNAs anticodon would read CCU). Equipped with its particular cargo and matching antic ...
... responsible for shuttling the amino acid glycine contains a binding site for glycine on one end. On the other end it contains an anticodon that complements the glycine codon (GGA is a codon for glycine, and so the tRNAs anticodon would read CCU). Equipped with its particular cargo and matching antic ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Lakewood City Schools
... Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
... Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
Lecture_12
... Branched pathways are regulated by one of several different methods. 1. Feedback inhibition and activation: If two pathways have an initial common step, one pathway is inhibited by its own product and stimulated by the product of the other pathway. Threonine deaminase illustrates this type of regu ...
... Branched pathways are regulated by one of several different methods. 1. Feedback inhibition and activation: If two pathways have an initial common step, one pathway is inhibited by its own product and stimulated by the product of the other pathway. Threonine deaminase illustrates this type of regu ...
Homework 1
... 5) _____ Which of Campbell’s themes for our textbook was emphasized in describing the insulin protein in the video handout? A) Emergent properties B) Organisms interact with environment C) Structure relates to function D) The cell E) Feedback mechanisms ...
... 5) _____ Which of Campbell’s themes for our textbook was emphasized in describing the insulin protein in the video handout? A) Emergent properties B) Organisms interact with environment C) Structure relates to function D) The cell E) Feedback mechanisms ...
Correct response
... a. The genetic sequence is found on the pyrimidine bases, so there must be a pyrimidine in each step of the DNA ladder b. The number of hydrogen bonds between the bases must “match” in order for the helix to be double stranded. c. The phosphate bonds required to hold each single strand together must ...
... a. The genetic sequence is found on the pyrimidine bases, so there must be a pyrimidine in each step of the DNA ladder b. The number of hydrogen bonds between the bases must “match” in order for the helix to be double stranded. c. The phosphate bonds required to hold each single strand together must ...
Genetic Research Lesson 4
... Science was something that I was always excited about. I have one foot in anthropology as an anthropological geneticist; therefore I’m not strictly limited to a laboratory, but can go into the field for my work reconstructing the history of human populations and their origins based on population gen ...
... Science was something that I was always excited about. I have one foot in anthropology as an anthropological geneticist; therefore I’m not strictly limited to a laboratory, but can go into the field for my work reconstructing the history of human populations and their origins based on population gen ...
Ch10_GeneExpression
... • All cells in the human body have the same DNA and the same set of genes, yet different cells look different and do different jobs. • Cells have systems to regulate which genes are “turned on” (transcribed) and which are not. ...
... • All cells in the human body have the same DNA and the same set of genes, yet different cells look different and do different jobs. • Cells have systems to regulate which genes are “turned on” (transcribed) and which are not. ...
Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... iii) What is the strongest type of bond that maintains the quaternary structure of LMGT? Covalent, disulfide bond ...
... iii) What is the strongest type of bond that maintains the quaternary structure of LMGT? Covalent, disulfide bond ...
Mutations
... gene, just as there are many different ways to introduce typos into a sentence. In the following examples of some types of mutations, we use the sentence to represent the sample gene: ...
... gene, just as there are many different ways to introduce typos into a sentence. In the following examples of some types of mutations, we use the sentence to represent the sample gene: ...
Sequencing genomes
... A new species of frog has been introduced into an area where it has too few natural predators. In an attempt to restore the ecological balance, a team of scientists is considering introducing a species of bird which feeds on this frog. Experimental data suggests that the population of frogs and bird ...
... A new species of frog has been introduced into an area where it has too few natural predators. In an attempt to restore the ecological balance, a team of scientists is considering introducing a species of bird which feeds on this frog. Experimental data suggests that the population of frogs and bird ...
11.3 Section Objectives – page 296
... • The greater the exposure to a mutagen such as UV light, the more likely is the chance that a mistake will not be corrected. ...
... • The greater the exposure to a mutagen such as UV light, the more likely is the chance that a mistake will not be corrected. ...
A speculation on the origin of protein synthesis
... errors. On the other hand an occasional incorrect amino acid will not necessarily be unacceptable. It seems likely that one such requirement is that, at any moment, the particular tRNA molecule to which the growing polypeptide chain is attached is bound to the messenger RNA by sufficiently strong bo ...
... errors. On the other hand an occasional incorrect amino acid will not necessarily be unacceptable. It seems likely that one such requirement is that, at any moment, the particular tRNA molecule to which the growing polypeptide chain is attached is bound to the messenger RNA by sufficiently strong bo ...
101 -- 2006
... __ 33. After introns are removed, the ___ are joined together to form functional mRNA. a) axons b) neutrons c) exons d) mesons e) ori sites __ 34. rRNA has an anticodon loop at one end of the molecule and an amino acid acceptor stem at the other end. a) true b) false __ 35. Which of the following is ...
... __ 33. After introns are removed, the ___ are joined together to form functional mRNA. a) axons b) neutrons c) exons d) mesons e) ori sites __ 34. rRNA has an anticodon loop at one end of the molecule and an amino acid acceptor stem at the other end. a) true b) false __ 35. Which of the following is ...
www.njctl.org Biology Large Biological Molecules Multiple Choice
... a. The genetic sequence is found on the pyrimidine bases, so there must be a pyrimidine in each step of the DNA ladder b. The number of hydrogen bonds between the bases must “match” in order for the helix to be double stranded. c. The phosphate bonds required to hold each single strand together must ...
... a. The genetic sequence is found on the pyrimidine bases, so there must be a pyrimidine in each step of the DNA ladder b. The number of hydrogen bonds between the bases must “match” in order for the helix to be double stranded. c. The phosphate bonds required to hold each single strand together must ...
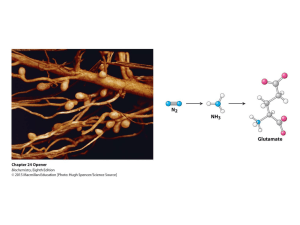
Nine essential amino acids
... amino acids are required by the body every day to use as building blocks for new proteins. Some of these amino acids can be formed within the body, assuming there are adequate substrate molecules, such as nitrogen. These amino acids are called dispensable, or non-essential, amino acids – they are re ...
... amino acids are required by the body every day to use as building blocks for new proteins. Some of these amino acids can be formed within the body, assuming there are adequate substrate molecules, such as nitrogen. These amino acids are called dispensable, or non-essential, amino acids – they are re ...
3.2 and 3.3
... 1) Properties of Amino Acids a) Determined by the “R group” b) there are 20 different Amino Acids c) Amino acids may be: ...
... 1) Properties of Amino Acids a) Determined by the “R group” b) there are 20 different Amino Acids c) Amino acids may be: ...
Class 1
... Types of Homology Orthology: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects speciation Paralogy: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects gene duplication ...
... Types of Homology Orthology: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects speciation Paralogy: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects gene duplication ...
Homology
... Types of Homology Orthology: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects speciation Paralogy: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects gene duplication ...
... Types of Homology Orthology: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects speciation Paralogy: bifurcation in molecular tree reflects gene duplication ...
Nucleic Acids
... proteins in the stomach during digestion. It works at a pH of 2! Trypsin is an enzyme that helps break down proteins as well. It works in the intestines with a pH of 8. Many snake venoms are enzymes that work when directly injected into blood or tissue (pH = 7.4). If swallowed, they are denatured by ...
... proteins in the stomach during digestion. It works at a pH of 2! Trypsin is an enzyme that helps break down proteins as well. It works in the intestines with a pH of 8. Many snake venoms are enzymes that work when directly injected into blood or tissue (pH = 7.4). If swallowed, they are denatured by ...
Peptide bond Polypeptide
... in each chain is glycine. The small size of glycine allows the three strands to lie close together and form a tight coil. The strands are held together by hydrogen bonds. R groups of individual collagen molecules form bonds with other collagen molecules These cross-links form fibrils. Many microfibr ...
... in each chain is glycine. The small size of glycine allows the three strands to lie close together and form a tight coil. The strands are held together by hydrogen bonds. R groups of individual collagen molecules form bonds with other collagen molecules These cross-links form fibrils. Many microfibr ...
Amino acids [qualitative tests]
... 1.Ninhydrin (triketohydrindene hydrate) degrades amino acids into aldehydes (on pH range 4-8), ammonia and CO2 though a series of reactions. 2.Ninhydrin then condenses with ammonia and hydrindantin to produce an intensely blue or purple pigment, sometimes called ruhemann's purple ...
... 1.Ninhydrin (triketohydrindene hydrate) degrades amino acids into aldehydes (on pH range 4-8), ammonia and CO2 though a series of reactions. 2.Ninhydrin then condenses with ammonia and hydrindantin to produce an intensely blue or purple pigment, sometimes called ruhemann's purple ...
Handout 14, 15 - U of L Class Index
... •The initiator tRNA Met is brought to the small subunit of the ribosome by a second initiation factor, IF-2, along with the molecule of GTP, the latter acts as energy source. •Only tRNA Met is only able to decode initiation codon. •NB: During elongation the internal AUG codons are recognized by diff ...
... •The initiator tRNA Met is brought to the small subunit of the ribosome by a second initiation factor, IF-2, along with the molecule of GTP, the latter acts as energy source. •Only tRNA Met is only able to decode initiation codon. •NB: During elongation the internal AUG codons are recognized by diff ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.




















![Amino acids [qualitative tests]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008282328_1-c8bb4ef27caebe478c13494a7af59cc2-300x300.png)
