PPT CH 18
... • All of the carbonyl O and amide H are involved in the H bonds with the chain nearly completely extended • Two possible orientations – Parallel if the N-termini are head-to-head – Antiparallel if the N-terminus of one chain is aligned with the C-terminus of the other ...
... • All of the carbonyl O and amide H are involved in the H bonds with the chain nearly completely extended • Two possible orientations – Parallel if the N-termini are head-to-head – Antiparallel if the N-terminus of one chain is aligned with the C-terminus of the other ...
Organic Compounds Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test!~ 1
... C. None of them are very high in energy content D. They are all acidic when mixed with water E. They don’t dissolve in water 11. Which of the following is NOT the proper pairing of a polymer and its monomer? A. polysaccharide and monosaccharide B. fatty acids and steroid C. nucleic acid and nucleoti ...
... C. None of them are very high in energy content D. They are all acidic when mixed with water E. They don’t dissolve in water 11. Which of the following is NOT the proper pairing of a polymer and its monomer? A. polysaccharide and monosaccharide B. fatty acids and steroid C. nucleic acid and nucleoti ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: TRANSLATION AND
... 42 5 16 amino acids. Neither is sufficient since 20 amino acids occur in most proteins. The actual three-letter genetic code has 43 5 64 permutations or words, which is also sufficient to encode start and stop signals, equivalent to punctuation. The three-base words are called codons and they are cu ...
... 42 5 16 amino acids. Neither is sufficient since 20 amino acids occur in most proteins. The actual three-letter genetic code has 43 5 64 permutations or words, which is also sufficient to encode start and stop signals, equivalent to punctuation. The three-base words are called codons and they are cu ...
Data/hora: 31/03/2017 07:20:58 Provedor de dados: 105 País
... Resumo: Plant Genetic Resources (PGR) continue to play an important role in the development of agriculture. The following aspects receive a special consideration: 1. Definition. The term was coined in 1970. The genepool concept served as an important tool in the further development. Different approa ...
... Resumo: Plant Genetic Resources (PGR) continue to play an important role in the development of agriculture. The following aspects receive a special consideration: 1. Definition. The term was coined in 1970. The genepool concept served as an important tool in the further development. Different approa ...
Bioplex Granules - Amazon Web Services
... proteins and as a structural component of phosphoproteins, phospholipids and nucleic acids. Plants suffering from deficiency amongst other effects are susceptible to growth suppression, less tolerant to low temperatures, use water less efficiently, take longer to root and are less disease resistant. ...
... proteins and as a structural component of phosphoproteins, phospholipids and nucleic acids. Plants suffering from deficiency amongst other effects are susceptible to growth suppression, less tolerant to low temperatures, use water less efficiently, take longer to root and are less disease resistant. ...
dna and protein synthesis webquest
... b. What organic molecule group do enzymes belong? (prior knowledge) ________________ c. What gene specifies the amino acid sequence to produce the enzyme from question 12a? ________________________________________________________________________ d. RNA polymerase is used to unwind and unzip the DNA ...
... b. What organic molecule group do enzymes belong? (prior knowledge) ________________ c. What gene specifies the amino acid sequence to produce the enzyme from question 12a? ________________________________________________________________________ d. RNA polymerase is used to unwind and unzip the DNA ...
Supplementary Information
... Such a violation could be, for instance, that a reaction is used by an elementary flux mode ...
... Such a violation could be, for instance, that a reaction is used by an elementary flux mode ...
Biology- Semester 2 Final Exam Review 2012
... 6. Explain how and why DNA replicates prior to cell division. Include the enzymes DNA polymerase, DNA helicase and DNA ligase. 7. How does spontaneous mutation relate to replication? ...
... 6. Explain how and why DNA replicates prior to cell division. Include the enzymes DNA polymerase, DNA helicase and DNA ligase. 7. How does spontaneous mutation relate to replication? ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... • In certain body tissues, this enzyme catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of valine, isoleucine, and leucine yielding CO2, and acyl-CoA derivatives. • Shares ancestry with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, -KG dehydrogenase complex – another example of gene duplication ...
... • In certain body tissues, this enzyme catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of valine, isoleucine, and leucine yielding CO2, and acyl-CoA derivatives. • Shares ancestry with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, -KG dehydrogenase complex – another example of gene duplication ...
Gilbert - C-MORE
... 1. How to acess the habitat specific gene pool information? Recommendation : Create a comprehensive portal that can store such datasets. 2. High-throughput methods to screen orthologous genes across multipule population genomes a. some methods exist, but they are specific for genome sequences of cul ...
... 1. How to acess the habitat specific gene pool information? Recommendation : Create a comprehensive portal that can store such datasets. 2. High-throughput methods to screen orthologous genes across multipule population genomes a. some methods exist, but they are specific for genome sequences of cul ...
DNA Review (study guide)
... _______, ______, and ______ have specific roles in this process. Structure B/G, known as __________, is important because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the seco ...
... _______, ______, and ______ have specific roles in this process. Structure B/G, known as __________, is important because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the seco ...
PP Notes DNA continued
... 4. Describe translation. The cell uses information from MRNA to produce proteins. 5. What are the main differences between DNA and RNA. DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose; DNA has 2 strands, RNA has one strand; DNA has thymine, RNA has uracil. 6. Using the chart on page 303, identify the amino aci ...
... 4. Describe translation. The cell uses information from MRNA to produce proteins. 5. What are the main differences between DNA and RNA. DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose; DNA has 2 strands, RNA has one strand; DNA has thymine, RNA has uracil. 6. Using the chart on page 303, identify the amino aci ...
College Accounting: A Practical Approach, Cdn
... Mathews, van Holde, Appling, and Anthony-Cahill, Biochemistry 4th edition Chapter 5: Introduction to Proteins: The Primary Level of Protein Structure ...
... Mathews, van Holde, Appling, and Anthony-Cahill, Biochemistry 4th edition Chapter 5: Introduction to Proteins: The Primary Level of Protein Structure ...
Microbial Genetics
... • The newly synthesized DNA contains an old strand and a new strand. • The two new strands are then separated into the two new daughter cells. ...
... • The newly synthesized DNA contains an old strand and a new strand. • The two new strands are then separated into the two new daughter cells. ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... mRNA is the “messenger” or vehicle that carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA polymerase, ...
... mRNA is the “messenger” or vehicle that carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA polymerase, ...
Semester Final Review
... 25. Explain how crossing over can unlink genes. 26. Describe sex determination in humans and explain the types of genes located on both chromosomes. 27. Explain why a recessive sex-linked gene is always expressed in males. 28. Be able to read a table of codons and give the sequence of amino acids fr ...
... 25. Explain how crossing over can unlink genes. 26. Describe sex determination in humans and explain the types of genes located on both chromosomes. 27. Explain why a recessive sex-linked gene is always expressed in males. 28. Be able to read a table of codons and give the sequence of amino acids fr ...
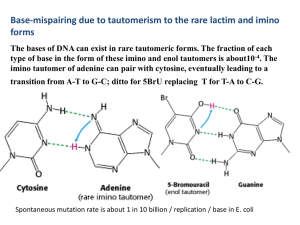
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... the natural hexoses in the same way that RNA relates to ribose, none exhibit discernible Watson-Crick base pairing between adenine and uracil Instead, some purine-purine self-pairing occurs, although much weaker than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent ...
... the natural hexoses in the same way that RNA relates to ribose, none exhibit discernible Watson-Crick base pairing between adenine and uracil Instead, some purine-purine self-pairing occurs, although much weaker than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent ...
1 Proteins: Workshop I Amino Acids
... investigate the structure of amino acids and how they affect the structure of a protein. We will also investigate the affect of structure on the function of a protein. Why learn about proteins? Of the three classes of biomolecules - lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins – proteins have some of the mos ...
... investigate the structure of amino acids and how they affect the structure of a protein. We will also investigate the affect of structure on the function of a protein. Why learn about proteins? Of the three classes of biomolecules - lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins – proteins have some of the mos ...
Beyond Mendel: Molecular genetics, cell division, and sex
... − the remaining 3 codons indicate the beginning or end of a protein − DNA physically controls the production of proteins in a complex process that we will cover only very superficially here − DNA normally is inside the cell nucleus, a specialized sack of material inside the cell − inside the nucleus ...
... − the remaining 3 codons indicate the beginning or end of a protein − DNA physically controls the production of proteins in a complex process that we will cover only very superficially here − DNA normally is inside the cell nucleus, a specialized sack of material inside the cell − inside the nucleus ...
Properties of the Genetic Code under Directional, Asymmetric
... can be coded by many (up to six) different codons – tri-nucleotide sequences. It means that DNA sequences with different nucleotide composition can code for the same protein. Thus, a coding nucleotide sequence under directional mutational pressure could adapt to this pressure by using preferred or mor ...
... can be coded by many (up to six) different codons – tri-nucleotide sequences. It means that DNA sequences with different nucleotide composition can code for the same protein. Thus, a coding nucleotide sequence under directional mutational pressure could adapt to this pressure by using preferred or mor ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.