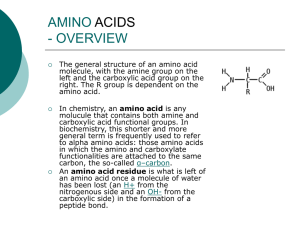
Q1. Lysozyme is an enzyme consisting of a single polypeptide chain
... Explain why the percentages of bases from the middle part of the chromosome and the end part are different. ...
... Explain why the percentages of bases from the middle part of the chromosome and the end part are different. ...
Genetic Mutations Notes
... are no diseases caused by silent mutations, because the protein made is same one called for in the original codon. Silent mutations have NO effect on the organism—no change occurs. EQ: Define a frameshift mutation, and describe its effects. Frameshift Mutation – The addition or deletion of a nucleot ...
... are no diseases caused by silent mutations, because the protein made is same one called for in the original codon. Silent mutations have NO effect on the organism—no change occurs. EQ: Define a frameshift mutation, and describe its effects. Frameshift Mutation – The addition or deletion of a nucleot ...
v semester zoology micro- macro- mega
... in any change in aminoacid synthesis and hence composition of proteins is not changed. They are usually changes in the last base pair of the codon. For example in mRNA strand GCA codes for alanine and if adenine is replaced by guanine, the resulting GCG will still code for the same aminoacid alanine ...
... in any change in aminoacid synthesis and hence composition of proteins is not changed. They are usually changes in the last base pair of the codon. For example in mRNA strand GCA codes for alanine and if adenine is replaced by guanine, the resulting GCG will still code for the same aminoacid alanine ...
C485 Exam I - Chemistry Courses: About
... group with an amino group in nucleotide biosynthesis. (Hint, this is somewhat similar to the two strategies used to install side chain amides in amino acids.) You must illustrate your answer with a relevant structure for each mechanism. ...
... group with an amino group in nucleotide biosynthesis. (Hint, this is somewhat similar to the two strategies used to install side chain amides in amino acids.) You must illustrate your answer with a relevant structure for each mechanism. ...
Taxonomy of Life • Three domains: Eukaryotes, Bacteria (Eubacteria
... membrane, which is a lipid bilayer. Beyond the cell membrane may be a cell wall (present in most bacteria and plant cells but not animal cells). The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and small molecules, and can actively transport such molecules into and out of the interior of the cell. ...
... membrane, which is a lipid bilayer. Beyond the cell membrane may be a cell wall (present in most bacteria and plant cells but not animal cells). The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and small molecules, and can actively transport such molecules into and out of the interior of the cell. ...
DNA
... hydrogen bonds appear. These pairs are called complementary bases (T-A and C-G). Between adenine (A) and thymine (T) two hydrogen bonds The G-C interaction is appear, and between guanine (G) and cytosine – stronger (by about 30%) than A-T three: ...
... hydrogen bonds appear. These pairs are called complementary bases (T-A and C-G). Between adenine (A) and thymine (T) two hydrogen bonds The G-C interaction is appear, and between guanine (G) and cytosine – stronger (by about 30%) than A-T three: ...
Principles of sorting and assembly of peroxisomal alcohol
... the cytosol to its target organelle is generally present within the primary amino acid sequence of the protein. This information (for instance a short sequence of a few amino acids) is recognized by a receptor that brings the protein to the correct target organelle. Sorting of proteins to organelles ...
... the cytosol to its target organelle is generally present within the primary amino acid sequence of the protein. This information (for instance a short sequence of a few amino acids) is recognized by a receptor that brings the protein to the correct target organelle. Sorting of proteins to organelles ...
amino acids - UniMAP Portal
... genetic code and are called proteinogenic or standard amino acids. Combinations of these amino acids produce every single essential protein for the homeostasis of the human body. At least two others are also coded by DNA in a nonstandard manner as follows: Selenocysteine is incorporated into some pr ...
... genetic code and are called proteinogenic or standard amino acids. Combinations of these amino acids produce every single essential protein for the homeostasis of the human body. At least two others are also coded by DNA in a nonstandard manner as follows: Selenocysteine is incorporated into some pr ...
Lecture 10 - Prediction, Engineering, Design of Protein Structures
... • Codons (3 RNA bases in sequence) determine each amino acid that will build the protein expressed • Many amino acids are encoded by more than 1 codon (change in 3rd base). Change of single base may not be significant. ...
... • Codons (3 RNA bases in sequence) determine each amino acid that will build the protein expressed • Many amino acids are encoded by more than 1 codon (change in 3rd base). Change of single base may not be significant. ...
a rapid uplc™ - ms/ms method for determining specific
... polypropylene microcentrifuge tube followed by the addition of 50µL 35% sulfosalicylic acid. The mixture was vortex mixed and centrifuged at 13,000g for 5 min. After centrifugation 100µL of supernatant was transferred to a 0.5mL microcentrifuge tube to which 100µL of Li220 diluting buffer was added. ...
... polypropylene microcentrifuge tube followed by the addition of 50µL 35% sulfosalicylic acid. The mixture was vortex mixed and centrifuged at 13,000g for 5 min. After centrifugation 100µL of supernatant was transferred to a 0.5mL microcentrifuge tube to which 100µL of Li220 diluting buffer was added. ...
Mutations
... that affect an individual may go on to affect a whole species or even an entire ecosystem. Many mutations are created by errors in DNA replication. The cellular machinery that replicated DNA inserts an incorrect base once in every 10 million bases. These small changes can accumulate over time. ...
... that affect an individual may go on to affect a whole species or even an entire ecosystem. Many mutations are created by errors in DNA replication. The cellular machinery that replicated DNA inserts an incorrect base once in every 10 million bases. These small changes can accumulate over time. ...
Chapter 3: Biochemistry
... Most lipids contain fatty acids, unbranched carbon molecules that have a hydrophilic end (head) and a hydrophobic end (tail) ...
... Most lipids contain fatty acids, unbranched carbon molecules that have a hydrophilic end (head) and a hydrophobic end (tail) ...
Protein Folding Activity
... b. Next, fold your proteins so the acidic and basic (charged) sidechains are on the outside surface of the protein and pair one negative sidechain with one positive sidechain so that they come within one inch, thereby neutralizing each other. c. Continue to fold your protein making sure that your hy ...
... b. Next, fold your proteins so the acidic and basic (charged) sidechains are on the outside surface of the protein and pair one negative sidechain with one positive sidechain so that they come within one inch, thereby neutralizing each other. c. Continue to fold your protein making sure that your hy ...
7.3 Translation (HL ONLY)
... Many proteins are enzymes, which catalyze and regulate chemical reactions. Proteins are each specifically designed to build or operate a component of a living cell. ...
... Many proteins are enzymes, which catalyze and regulate chemical reactions. Proteins are each specifically designed to build or operate a component of a living cell. ...
2 Review of Stoichiometry and Genetics
... b) The solubility of oxygen in water is only 7.6 mg/L at 20 oC. What volume of aqueous solution is needed for fish to metabolize 3.0 moles of ...
... b) The solubility of oxygen in water is only 7.6 mg/L at 20 oC. What volume of aqueous solution is needed for fish to metabolize 3.0 moles of ...
Bchm2000_P1 - U of L Class Index
... (22c) At pH 12, this peptide will have a net charge of -2. pH 12 is higher than all pKas of side chains (His, Tyr) and main chain carboxylate and amino groups. Thus, all groups will be deprotonated. The Cterminal carboxylate group and Tyr will have a negative charge and the other groups will be unch ...
... (22c) At pH 12, this peptide will have a net charge of -2. pH 12 is higher than all pKas of side chains (His, Tyr) and main chain carboxylate and amino groups. Thus, all groups will be deprotonated. The Cterminal carboxylate group and Tyr will have a negative charge and the other groups will be unch ...
Gene Mutations
... A gene mutation can help prevent cornornary artery disease like the picture on the lright. ...
... A gene mutation can help prevent cornornary artery disease like the picture on the lright. ...
clicker review
... It replicates the leading strand in fragments It makes pre-mRNA's that need to be edited It is only found in prokaryotes but not eukaryotes ...
... It replicates the leading strand in fragments It makes pre-mRNA's that need to be edited It is only found in prokaryotes but not eukaryotes ...
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Nature`s Che
... The hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic (water-hating) and dissolves well in grease and oil. How to explain the cleaning action of soap. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions which form a scum with soap. Detergents were developed to combat hard-water conditions. Detergents clean in th ...
... The hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic (water-hating) and dissolves well in grease and oil. How to explain the cleaning action of soap. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions which form a scum with soap. Detergents were developed to combat hard-water conditions. Detergents clean in th ...
HIV GENOTYPE ASSAY
... Cycle Sequencing has 4 steps: PCR purification- removes unincorporated dNTPs & primers DNA quantitation- gel electrophoresis Cycle sequencing- 7 primers (4 forward & 3 reverse) to sequence entire region Protease (codon 1-99) and two-thirds RT region (1335). Big Dye Terminator chemistry is used ...
... Cycle Sequencing has 4 steps: PCR purification- removes unincorporated dNTPs & primers DNA quantitation- gel electrophoresis Cycle sequencing- 7 primers (4 forward & 3 reverse) to sequence entire region Protease (codon 1-99) and two-thirds RT region (1335). Big Dye Terminator chemistry is used ...
Aminoaciduria
... Early diagnosis of PKU is important because the disease is treatable by dietary means. Newborn with PKU frequently has normal blood levels of phenylalanine (PA) at birth As the mother clears increased blood PA in her fetus through placenta. So, test performed at birth may show false –ve results. PA ...
... Early diagnosis of PKU is important because the disease is treatable by dietary means. Newborn with PKU frequently has normal blood levels of phenylalanine (PA) at birth As the mother clears increased blood PA in her fetus through placenta. So, test performed at birth may show false –ve results. PA ...
7.5 Proteins – summary of mark schemes
... Outline the difference between fibrous and globular proteins, with reference to two examples of each protein type. Mark Scheme Fibrous vs globular A. repetitive amino-acid sequences B. long and narrow / long strands C. support / structural functions D. (mostly) insoluble in water vs. ...
... Outline the difference between fibrous and globular proteins, with reference to two examples of each protein type. Mark Scheme Fibrous vs globular A. repetitive amino-acid sequences B. long and narrow / long strands C. support / structural functions D. (mostly) insoluble in water vs. ...
Amino acid metabolism
... proteins are constantly turning over and must therefore be constantly replaced by protein synthesis. This requires a steady supply of all 20 amino acids. ...
... proteins are constantly turning over and must therefore be constantly replaced by protein synthesis. This requires a steady supply of all 20 amino acids. ...
Biochemistry-Amino Acids and Proteins(PPT-LS)
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Proteins are natural polymers of successive amino acids There are 20 different amino acids that make up human proteins ...
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Proteins are natural polymers of successive amino acids There are 20 different amino acids that make up human proteins ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.