FATS - Typepad
... NUCLEIC ACIDS THEY ARE MADE OF CARBON, HYDROGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, AND PHOSPHORUS SO WE SAY IT’S ...
... NUCLEIC ACIDS THEY ARE MADE OF CARBON, HYDROGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, AND PHOSPHORUS SO WE SAY IT’S ...
Domain Three (3_genetics)
... D. baby 2. During translation, the tRNA anti-codon GGA codes for what amino acid? A. alanine B. tyrosine C. proline D. glutamic 3. Artificial selection is human intervention allowing only the best organisms to produce offspring. How is this process most useful to humanity? A. It allows the developme ...
... D. baby 2. During translation, the tRNA anti-codon GGA codes for what amino acid? A. alanine B. tyrosine C. proline D. glutamic 3. Artificial selection is human intervention allowing only the best organisms to produce offspring. How is this process most useful to humanity? A. It allows the developme ...
Digestion of Proteins
... The plant starches amylopectin and amylose, which are present in grains, tubers, and vegetables, constitute approximately 50 to 60% of the carbohydrate calories consumed. These starches are polysaccharides, containing 10,000 to 1 million glucosyl units. ...
... The plant starches amylopectin and amylose, which are present in grains, tubers, and vegetables, constitute approximately 50 to 60% of the carbohydrate calories consumed. These starches are polysaccharides, containing 10,000 to 1 million glucosyl units. ...
Transcription - My Teacher Pages
... Once the entire gene has been transcribed, the RNA strand detaches completely from the DNA. Exactly how RNA polymerase recognizes the end of a gene is very complicated but we will discuss as it reaching a Stop signal. ...
... Once the entire gene has been transcribed, the RNA strand detaches completely from the DNA. Exactly how RNA polymerase recognizes the end of a gene is very complicated but we will discuss as it reaching a Stop signal. ...
Respiration - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... the time by your body to prevent any big changes. Homeostasis helps your cells to work as efficiently as possible. The chemical reactions in cells are controlled by enzymes. Enzymes work best in particular conditions, so keeping the conditions at a steady level provides enzymes with the best working ...
... the time by your body to prevent any big changes. Homeostasis helps your cells to work as efficiently as possible. The chemical reactions in cells are controlled by enzymes. Enzymes work best in particular conditions, so keeping the conditions at a steady level provides enzymes with the best working ...
sample pages from Biology - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... the time by your body to prevent any big changes. Homeostasis helps your cells to work as efficiently as possible. The chemical reactions in cells are controlled by enzymes. Enzymes work best in particular conditions, so keeping the conditions at a steady level provides enzymes with the best working ...
... the time by your body to prevent any big changes. Homeostasis helps your cells to work as efficiently as possible. The chemical reactions in cells are controlled by enzymes. Enzymes work best in particular conditions, so keeping the conditions at a steady level provides enzymes with the best working ...
Measurement of Diabetes-Predictive Amino Acids from Dried Blood
... using an Agilent 1100 HPLC System interfaced to an AB SCIEX 3200 QTRAP™ Mass Spectrometer. Separation was achieved using an AB SCIEX AAA C18 Column (4.6 X 150mm) heated to 50 °C for an 18 min. gradient run. Quantitation was performed using Analyst™ software or Cliquid™ software for amino acid analys ...
... using an Agilent 1100 HPLC System interfaced to an AB SCIEX 3200 QTRAP™ Mass Spectrometer. Separation was achieved using an AB SCIEX AAA C18 Column (4.6 X 150mm) heated to 50 °C for an 18 min. gradient run. Quantitation was performed using Analyst™ software or Cliquid™ software for amino acid analys ...
Name: 1) Which statement best describes the relationship between
... The diagrams below represent portions of the genes that code for wing structure in two organisms of the same species. Gene 1 was taken from the cells of a female with normal wings, and gene 2 was taken from the cells of a female with abnormal wings. ...
... The diagrams below represent portions of the genes that code for wing structure in two organisms of the same species. Gene 1 was taken from the cells of a female with normal wings, and gene 2 was taken from the cells of a female with abnormal wings. ...
Amino Acids Metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen.
... -This toxic ammonia is converted into amino group of glutamine that transported to liver or kidneys. - Glutamine: non-toxic transport form of NH4+ and also source of amino group in many biosynthesis reactions. - The amide nitrogen of glutamine is released as ammonia only in liver and kidney’s mitoch ...
... -This toxic ammonia is converted into amino group of glutamine that transported to liver or kidneys. - Glutamine: non-toxic transport form of NH4+ and also source of amino group in many biosynthesis reactions. - The amide nitrogen of glutamine is released as ammonia only in liver and kidney’s mitoch ...
Intragenic Suppression of a Capsid Assembly-Defective
... phage assembly reactions demonstrated in vitro (IsRAEL, ANDERSON and LEVINE1967) and was shown to proceed under a wide variety of solution conditions. The noncovalent interaction between phage capsids a n d t h e tailspike protein is quite remarkable in that no evidence of cooperativity during the a ...
... phage assembly reactions demonstrated in vitro (IsRAEL, ANDERSON and LEVINE1967) and was shown to proceed under a wide variety of solution conditions. The noncovalent interaction between phage capsids a n d t h e tailspike protein is quite remarkable in that no evidence of cooperativity during the a ...
proteoma
... sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised and used for further experimentation. ...
... sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised and used for further experimentation. ...
Reactions of I,I-Diacetoxyiodobenzene with Proteins: Conversion of
... no trace of this N-acylurea. Reaction rate studies with insulin and lysozyme also show that (1) is preferable to (2) for converting amide side-chains to amines (see Fig. 2). Although (2) reacts much faster than (1) with lysozyme at first, (1) introduces considerably more amino groups than (2) after ...
... no trace of this N-acylurea. Reaction rate studies with insulin and lysozyme also show that (1) is preferable to (2) for converting amide side-chains to amines (see Fig. 2). Although (2) reacts much faster than (1) with lysozyme at first, (1) introduces considerably more amino groups than (2) after ...
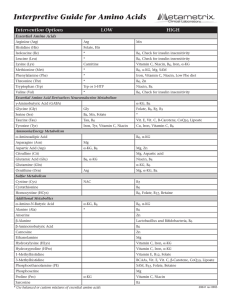
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... quality protein, causing arginine to be poorly absorbed. Because arginine is required for nitric oxide production, deficiencies have wide-ranging effects on cardiovascular and other systems. High - may indicate a functional block in the urea cycle. Manganese activates an arginase enzyme, so supplemen ...
... quality protein, causing arginine to be poorly absorbed. Because arginine is required for nitric oxide production, deficiencies have wide-ranging effects on cardiovascular and other systems. High - may indicate a functional block in the urea cycle. Manganese activates an arginase enzyme, so supplemen ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 4 cellular physiology click here
... -contains enzymes that use this gradient for the synthesis of ATP -also contains pumps to move ATP into the cytosol •matrix - lumen of the mitochondria -breakdown of glucose into water and CO2 ends here and results in the production of ATP ...
... -contains enzymes that use this gradient for the synthesis of ATP -also contains pumps to move ATP into the cytosol •matrix - lumen of the mitochondria -breakdown of glucose into water and CO2 ends here and results in the production of ATP ...
bioCHEMISTRY 480 Molecular Biochemistry-‐
... The subsections of this page are: (1) Introduction & curriculum, biochemical aims , research aims, overall course learning targets, Voet’s web site (2) Lectures Notes, (3) Keys to Spring 2014 tests, (4 ...
... The subsections of this page are: (1) Introduction & curriculum, biochemical aims , research aims, overall course learning targets, Voet’s web site (2) Lectures Notes, (3) Keys to Spring 2014 tests, (4 ...
Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
... Concept 10.4: Genetic variation produced in sexual life cycles contributes to evolution • Mutations (changes in an organism’s DNA) are the original source of genetic diversity • Mutations are what created different versions of genes called alleles • Reshuffling of alleles during sexual reproduction ...
... Concept 10.4: Genetic variation produced in sexual life cycles contributes to evolution • Mutations (changes in an organism’s DNA) are the original source of genetic diversity • Mutations are what created different versions of genes called alleles • Reshuffling of alleles during sexual reproduction ...
Using Yeast to study Eukaryotic Gene Function From Recombinant
... Both editing of apo-B and glutamate receptor by RNA deaminases ...
... Both editing of apo-B and glutamate receptor by RNA deaminases ...
Lecture_2 - Department of Molecular & Cell Biology
... Column Chromatography Molecules can be separated on the basis of: ...
... Column Chromatography Molecules can be separated on the basis of: ...
Presentation Slides II - Vandiver, June 29, 2016
... What is Unique about the models? The models were designed for “acting out“ or simulating the cell’s molecular processes and conveying the key concepts. Key Concepts about DNA 1. DNA is a polymer made from subunits called nucleotides. 2. Nucleotides can pair with one another. One side of the double ...
... What is Unique about the models? The models were designed for “acting out“ or simulating the cell’s molecular processes and conveying the key concepts. Key Concepts about DNA 1. DNA is a polymer made from subunits called nucleotides. 2. Nucleotides can pair with one another. One side of the double ...
Full-Text PDF
... together and where their separate abilities not only reinforced each other’s survival, but allowed life to more quickly climb the ladder of complexity. Essential for our approach is the following: Starting with small molecules (easily) derived from prebiotic chemistry, we will try to reconstruct a p ...
... together and where their separate abilities not only reinforced each other’s survival, but allowed life to more quickly climb the ladder of complexity. Essential for our approach is the following: Starting with small molecules (easily) derived from prebiotic chemistry, we will try to reconstruct a p ...
Biological Sequences: DNA, RNA, Protein
... • apparently passive, but very important role of proteins • provide strngth and protection to cells and tissues • monomeric units of structural proteins typically polymerize to generate long fibers (as in hair) or protective sheets of fibrous arrays • collagen is an important fibrous protein found i ...
... • apparently passive, but very important role of proteins • provide strngth and protection to cells and tissues • monomeric units of structural proteins typically polymerize to generate long fibers (as in hair) or protective sheets of fibrous arrays • collagen is an important fibrous protein found i ...
Mutation
... coding DNA will be advantageous • Deleterious alleles are selected against • The balance between the formation of deleterious alleles and their removal via selection is called ...
... coding DNA will be advantageous • Deleterious alleles are selected against • The balance between the formation of deleterious alleles and their removal via selection is called ...
DNA and Genetics
... Translocation Mutation: A type of gene mutation wherein the deletion (as well as addition) of (a number of) nucleotide(s) causes a shift in the reading frame of the codons in the mRNA, thus, may eventually lead to the alteration in the amino acid sequence at protein translation.. Mutations involving ...
... Translocation Mutation: A type of gene mutation wherein the deletion (as well as addition) of (a number of) nucleotide(s) causes a shift in the reading frame of the codons in the mRNA, thus, may eventually lead to the alteration in the amino acid sequence at protein translation.. Mutations involving ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.