2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
Text S1.
... “We have used both the water-vapor transfer free energies and the interior-exterior distribution of amino acid side-chains determined by Chothia (1976) in assigning the final hydropathy values (Table 2). Results presented later in this paper indicate clearly that the number in the second place of th ...
... “We have used both the water-vapor transfer free energies and the interior-exterior distribution of amino acid side-chains determined by Chothia (1976) in assigning the final hydropathy values (Table 2). Results presented later in this paper indicate clearly that the number in the second place of th ...
Review on Biochemistry: Protein Chemistry
... Circular dichroism (CD, 圓二色極化光譜儀) can estimate the 2o structure content. Tertiary structure: 3D folding evolutionary relationship Quaternary structure: Subunits arrangement within a protein X-ray crystallography = protein crystal + X-ray diffraction Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) 7. Pr ...
... Circular dichroism (CD, 圓二色極化光譜儀) can estimate the 2o structure content. Tertiary structure: 3D folding evolutionary relationship Quaternary structure: Subunits arrangement within a protein X-ray crystallography = protein crystal + X-ray diffraction Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) 7. Pr ...
What is a Designer Baby?
... promoter polymorphism become depressed more often after stressful events than individuals homozygous for the long allele. ...
... promoter polymorphism become depressed more often after stressful events than individuals homozygous for the long allele. ...
The Proteomic Code: a molecular recognition code for proteins
... transferred into the physico-chemical properties of amino acids. It determines how individual amino acids interact with each other during folding and in specific protein-protein interactions. The Proteomic Code is part of the redundant Genetic Code. Review: The 25-year-old history of this concept is ...
... transferred into the physico-chemical properties of amino acids. It determines how individual amino acids interact with each other during folding and in specific protein-protein interactions. The Proteomic Code is part of the redundant Genetic Code. Review: The 25-year-old history of this concept is ...
Human Genetic Testing Services (Public Availability)Bill*2005
... For the purposes of making genetic testing services available to members of the public in accordance with a statement published under this section, the Minister may (but need not) authorise a person or body to provide some (or all) of the relevant services on behalf of the State. ...
... For the purposes of making genetic testing services available to members of the public in accordance with a statement published under this section, the Minister may (but need not) authorise a person or body to provide some (or all) of the relevant services on behalf of the State. ...
DNA, RNA, and the Flow of Genetic Information
... NA and RNA are long linear polymers, called nucleic acids, that carry information in a form that can be passed from one generation to the next. These macromolecules consist of a large number of linked nucleotides, each composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. Sugars linked by phosphates form a ...
... NA and RNA are long linear polymers, called nucleic acids, that carry information in a form that can be passed from one generation to the next. These macromolecules consist of a large number of linked nucleotides, each composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. Sugars linked by phosphates form a ...
17 - Wiley
... 17.67 The Watson–Crick model of DNA requires that there be a complementary base for each base in a given strand: one G for every C, one C for every G, one A for every T, and one T for every A. This requires that the molar ratios of A to T and G to C be 1.0. Chargoff’s observations indicate that this ...
... 17.67 The Watson–Crick model of DNA requires that there be a complementary base for each base in a given strand: one G for every C, one C for every G, one A for every T, and one T for every A. This requires that the molar ratios of A to T and G to C be 1.0. Chargoff’s observations indicate that this ...
Suppl Y1 Genetics 20.. - UR - College of Science and Technology
... b) What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? ...
... b) What is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? ...
pptx - WVU School of Medicine
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
Hamilton
... Although 23andMe isn't the only company selling DNA tests to the public, it does the best job of making them accessible and affordable. The 600,000 genetic markers that 23andMe identifies and interprets for each customer are "the digital manifestation of you," says Wojcicki (pronounced Wo-jis-key), ...
... Although 23andMe isn't the only company selling DNA tests to the public, it does the best job of making them accessible and affordable. The 600,000 genetic markers that 23andMe identifies and interprets for each customer are "the digital manifestation of you," says Wojcicki (pronounced Wo-jis-key), ...
Carbon Compounds slideshow Carbon Compounds
... nitrogen, and p____________________ Used by living things to store and transmit hereditary information, i.e. characteristics passed on from parents to offspring Most common forms: _____________ and ...
... nitrogen, and p____________________ Used by living things to store and transmit hereditary information, i.e. characteristics passed on from parents to offspring Most common forms: _____________ and ...
CHANGES IN THE GENETIC CODE
... But- if you look at the amino acid chartseveral different codons code for the same amino acids Mutations can occur but wouldn’t be noticed Some mutations are masked by other ...
... But- if you look at the amino acid chartseveral different codons code for the same amino acids Mutations can occur but wouldn’t be noticed Some mutations are masked by other ...
ppt - Carnegie Mellon University
... Amino acid conservation is strongly associated with functional and structural significance, and thus can be used to identify functionally or structurally important features, such as active sites and protein-protein interaction domains. However, identifying positional conservation is only a first ste ...
... Amino acid conservation is strongly associated with functional and structural significance, and thus can be used to identify functionally or structurally important features, such as active sites and protein-protein interaction domains. However, identifying positional conservation is only a first ste ...
Guided Reading Chapter 1: The Science of Heredity Section 1-1
... 5. Circle the letter of characteristic in pea plants that make them good for studying the passing of traits from parent to offspring. a. Peas produce small numbers of offspring. b. Peas readily cross-pollinate in nature. c. Peas have many traits that exist in only two forms. d. Peas do not have stam ...
... 5. Circle the letter of characteristic in pea plants that make them good for studying the passing of traits from parent to offspring. a. Peas produce small numbers of offspring. b. Peas readily cross-pollinate in nature. c. Peas have many traits that exist in only two forms. d. Peas do not have stam ...
classes of mutation
... Although mutations that cause changes in protein sequences can be harmful to an organism, on occasions the effect may be positive in a given environment. In this case, the mutation may enable the mutant organism to withstand particular environmental stresses better than wild-type organisms, or repro ...
... Although mutations that cause changes in protein sequences can be harmful to an organism, on occasions the effect may be positive in a given environment. In this case, the mutation may enable the mutant organism to withstand particular environmental stresses better than wild-type organisms, or repro ...
Polysaccharides Homo- and heteroglycans
... Proteoglycans are components of the ECM, made up of GAGs, core protein, and link proteins in a complex structure •Hyaluronate forms a backbone onto which large core proteins are attached via linker proteins; other GAGs are attached to core proteins via association with protein-linked glycans. The en ...
... Proteoglycans are components of the ECM, made up of GAGs, core protein, and link proteins in a complex structure •Hyaluronate forms a backbone onto which large core proteins are attached via linker proteins; other GAGs are attached to core proteins via association with protein-linked glycans. The en ...
Proteins - Winona State University
... Your body needs to take in new amino acids from your diet, but this must be balanced by the excretion of nitrogen in the form of urea. If your liver can’t form enough urea, the nitrogen produced by the breakdown of amino acids can be toxic to the body. This is called “nitrogen balance”: Your intake ...
... Your body needs to take in new amino acids from your diet, but this must be balanced by the excretion of nitrogen in the form of urea. If your liver can’t form enough urea, the nitrogen produced by the breakdown of amino acids can be toxic to the body. This is called “nitrogen balance”: Your intake ...
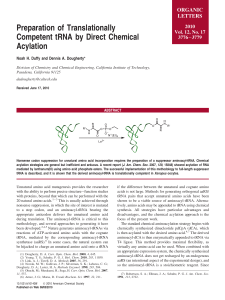
Preparation of Translationally Competent tRNA by Direct Chemical
... with the ability to perform precise structure-function studies with proteins, beyond that which can be performed with the 20 natural amino acids.1-3 This is usually achieved through nonsense suppression, in which the site of interest is mutated to a stop codon, and an aminoacyl-tRNA bearing the appr ...
... with the ability to perform precise structure-function studies with proteins, beyond that which can be performed with the 20 natural amino acids.1-3 This is usually achieved through nonsense suppression, in which the site of interest is mutated to a stop codon, and an aminoacyl-tRNA bearing the appr ...
When completed, this form will contain Protected Health Information
... indicate which clinical features increase the probability that this test will provide a diagnosis. Our patient’s clinical features are highly suspicious of a mitochondrial disorder including ***. The likelihood this test will be positive is unknown. -If this is a request is for a gene panel, then pl ...
... indicate which clinical features increase the probability that this test will provide a diagnosis. Our patient’s clinical features are highly suspicious of a mitochondrial disorder including ***. The likelihood this test will be positive is unknown. -If this is a request is for a gene panel, then pl ...
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is
... B. French cells are able to speak to German cells C. tRNA carries amino acid molecules to the nucleus, where they are added to a growing polypeptide chain D. ribosomes move into the nucleus E. mRNA is synthesized by the bonding of free nucleotides to the bases on the template strand of DNA ...
... B. French cells are able to speak to German cells C. tRNA carries amino acid molecules to the nucleus, where they are added to a growing polypeptide chain D. ribosomes move into the nucleus E. mRNA is synthesized by the bonding of free nucleotides to the bases on the template strand of DNA ...
ChemistryofLifeOLDve..
... Histidine) have electrical properties that can change depending on the pH. Cysteine can form covalent disulfide bonds Proline had a unique structure and causes kinks in the protein chain ...
... Histidine) have electrical properties that can change depending on the pH. Cysteine can form covalent disulfide bonds Proline had a unique structure and causes kinks in the protein chain ...
PowerPoint
... If you think you have an Open Reading Frame (ORF) then align at protein level – (i) Many mutations within DNA are synonymous, leading to overestimation of sequence divergence if compared at the DNA level. – (ii) Evolutionary relationships can be more finely expressed using a 20×20 amino acid exchang ...
... If you think you have an Open Reading Frame (ORF) then align at protein level – (i) Many mutations within DNA are synonymous, leading to overestimation of sequence divergence if compared at the DNA level. – (ii) Evolutionary relationships can be more finely expressed using a 20×20 amino acid exchang ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.