Chapter 21
... What are three functions of DNA? Review DNA and RNA structure. What are the 3 types of RNA and what are their functions? Compare and contrast the structure and function of DNA and RNA. How does DNA replicate? Describe transcription and translation in detail. Describe the genetic code. Review protein ...
... What are three functions of DNA? Review DNA and RNA structure. What are the 3 types of RNA and what are their functions? Compare and contrast the structure and function of DNA and RNA. How does DNA replicate? Describe transcription and translation in detail. Describe the genetic code. Review protein ...
Enzyme Vs. Extremozyme -32
... Sea. Thus the metabolism and the nature of enzymes from these organisms, collectively called extremophiles, are likely to help us understand and manipulate protein stability. Thus there is not only a need to search for enzymes from extremophiles but also to understand the basis of the tolerance of n ...
... Sea. Thus the metabolism and the nature of enzymes from these organisms, collectively called extremophiles, are likely to help us understand and manipulate protein stability. Thus there is not only a need to search for enzymes from extremophiles but also to understand the basis of the tolerance of n ...
Vectors
... Genetic engineering plays a very important role, not only in scientific research, but also in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. ...
... Genetic engineering plays a very important role, not only in scientific research, but also in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. ...
11.1 Types of Lipids 11.2 Fatty Acids
... 11.2 Fatty Acids The fundamental building blocks of many lipids are long-chain carboxylic acids called fatty acids. Fatty acids always contain an even number of carbon atoms and typically range between 10 and 20. This is a direct result of the biosynthetic pathways used to produce fatty acids. The f ...
... 11.2 Fatty Acids The fundamental building blocks of many lipids are long-chain carboxylic acids called fatty acids. Fatty acids always contain an even number of carbon atoms and typically range between 10 and 20. This is a direct result of the biosynthetic pathways used to produce fatty acids. The f ...
Section 12-1
... Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains called polypeptides. Each polypeptide contains a combination of any or all of the 20 different amino acids. The genetic code shows the amino acid to which each of the 64 possible codons corresponds. There is one codon, AUG, that can either sp ...
... Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains called polypeptides. Each polypeptide contains a combination of any or all of the 20 different amino acids. The genetic code shows the amino acid to which each of the 64 possible codons corresponds. There is one codon, AUG, that can either sp ...
Single Amino Acids as Additives Modulating CaCO3 Mineralization
... forms, emerges in the first stage of pre-nucleation, is amorphous calcium carbonate (ACC). Addadi and coworkers found that an amorphous phase, actually composed of several independent phases, was involved in the formation of certain biomineralized structures (15) (16). Gilbert et al. reports the the ...
... forms, emerges in the first stage of pre-nucleation, is amorphous calcium carbonate (ACC). Addadi and coworkers found that an amorphous phase, actually composed of several independent phases, was involved in the formation of certain biomineralized structures (15) (16). Gilbert et al. reports the the ...
Megan Silas - University of Illinois at Chicago
... CAIR will disappear as it is converted into NCAIR by PurE Measure change in absorbance due to disappearance of CAIR Compare rate of reaction catalyzed by WT PurE versus H70N and truncated PurE Meyer, E., N.J. Leonard, B. Bhat, J. Stubbe, and J.M. Smith. "Purification and characterization of the purE ...
... CAIR will disappear as it is converted into NCAIR by PurE Measure change in absorbance due to disappearance of CAIR Compare rate of reaction catalyzed by WT PurE versus H70N and truncated PurE Meyer, E., N.J. Leonard, B. Bhat, J. Stubbe, and J.M. Smith. "Purification and characterization of the purE ...
2.3.3 Protein and amino acid metabolism
... The catabolism of individual amino acids is tightly controlled, particularly the essential amino acids. This control is accomplished in a number of ways. An important role may be ascribed to glucagon, which is secreted at a higher rate upon ingestion of a high-protein meal. Glucagon activates phenyl ...
... The catabolism of individual amino acids is tightly controlled, particularly the essential amino acids. This control is accomplished in a number of ways. An important role may be ascribed to glucagon, which is secreted at a higher rate upon ingestion of a high-protein meal. Glucagon activates phenyl ...
Sorting the Fatty Acid Chaff from the Toxin Wheat, or is it All
... gene in A. carterae no other PKS modules were found within 12 kb of genomic DNA. This gene was also interspersed with numerous introns. And lastly, when Monroe and Van Dolah (2008) characterized the PKS cDNAs from K. brevis they only found transcripts that contained one catalytic module rather than ...
... gene in A. carterae no other PKS modules were found within 12 kb of genomic DNA. This gene was also interspersed with numerous introns. And lastly, when Monroe and Van Dolah (2008) characterized the PKS cDNAs from K. brevis they only found transcripts that contained one catalytic module rather than ...
LacI_Biochem.ppt
... Binding of regulators to DNA is often at inverted repeats Binding sites have inverted repeats Regulator proteins bind as back-to-back dimer. This puts each binding domain in the right orientation with respect to the inverted repeat ...
... Binding of regulators to DNA is often at inverted repeats Binding sites have inverted repeats Regulator proteins bind as back-to-back dimer. This puts each binding domain in the right orientation with respect to the inverted repeat ...
Document
... – RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA contains deoxyribose (a type of ribose that lacks one oxygen atom) – in RNA the nucleotide uracil substitutes for thymine, which is present in DNA Machine Learning & Bioinformatics ...
... – RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA contains deoxyribose (a type of ribose that lacks one oxygen atom) – in RNA the nucleotide uracil substitutes for thymine, which is present in DNA Machine Learning & Bioinformatics ...
The Necessities of Life
... keep the internal conditions of the cell stable. Phospholipids (FAHS foh LIP idz) are the molecules that form much of the cell membrane. The head of a phospholipid molecule is attracted to water. The tail is not. Cells are mostly water. When phospholipids are in water, the tails come together, and t ...
... keep the internal conditions of the cell stable. Phospholipids (FAHS foh LIP idz) are the molecules that form much of the cell membrane. The head of a phospholipid molecule is attracted to water. The tail is not. Cells are mostly water. When phospholipids are in water, the tails come together, and t ...
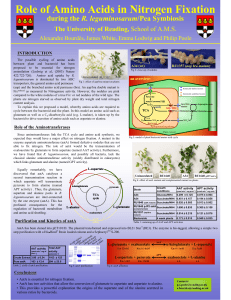
Role of Amino Acids in Nitrogen Fixation
... Role of Amino Acids in Nitrogen Fixation during the R. leguminosarum/Pea Symbiosis The University of Reading, School of A.M.S. Alexandre Bourdès, James White, Emma Lodwig and Philip Poole ...
... Role of Amino Acids in Nitrogen Fixation during the R. leguminosarum/Pea Symbiosis The University of Reading, School of A.M.S. Alexandre Bourdès, James White, Emma Lodwig and Philip Poole ...
ecify proteins via transcription and translation
... Transcription is the synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA. Both nucleic acids use the same language, and the information is simply transcribed, or copied, from one molecule to the other. Just as a DNA strand provides a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand during DNA replic ...
... Transcription is the synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA. Both nucleic acids use the same language, and the information is simply transcribed, or copied, from one molecule to the other. Just as a DNA strand provides a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand during DNA replic ...
Final Examination
... hydrophobic interactions can be disrupted at higher temperatures hydrophobic interactions can involve only a part of a molecule, rather than the whole molecule 10. Nucleolin is a eukaryotic protein containing 710 amino acids that is abundantly expressed in nearly all human cells. About half the ...
... hydrophobic interactions can be disrupted at higher temperatures hydrophobic interactions can involve only a part of a molecule, rather than the whole molecule 10. Nucleolin is a eukaryotic protein containing 710 amino acids that is abundantly expressed in nearly all human cells. About half the ...
Valea LifeScience09 R
... via its amino acid sequence, however, leads to the delicate problem of how to present this sequence to obtain patent protection that actually corresponds to the invention’s contribution to the art (in line with the teachings of T409/91 and T435/91). For instance, the amino acid sequences of many nat ...
... via its amino acid sequence, however, leads to the delicate problem of how to present this sequence to obtain patent protection that actually corresponds to the invention’s contribution to the art (in line with the teachings of T409/91 and T435/91). For instance, the amino acid sequences of many nat ...
Relative expression of wild-type and activated Ki
... PCR products are of identical length. Initially we were concerned that the relationship between RNA transcript and amplified cDNA might be significantly distorted by the extent of heteroduplex formation, since this could influence the kinetics of denaturation and reannealing. This may have been mini ...
... PCR products are of identical length. Initially we were concerned that the relationship between RNA transcript and amplified cDNA might be significantly distorted by the extent of heteroduplex formation, since this could influence the kinetics of denaturation and reannealing. This may have been mini ...
The Human Genome Project - Catholic Health Association
... ethics of scientific design, legal and ethical dimensions of research involving human subjects, standards of care for the use of genetic tests (i.e., who should receive tests and the results df tests to discover distinct gene-linked diseases), failreimbursement policies for testing and rest-related ...
... ethics of scientific design, legal and ethical dimensions of research involving human subjects, standards of care for the use of genetic tests (i.e., who should receive tests and the results df tests to discover distinct gene-linked diseases), failreimbursement policies for testing and rest-related ...
Slide 1
... protein sequence alignment Scoring matrices are created based on biological evidence. Alignments can be thought of as two sequences that differ due to mutations. Some of these mutations have little effect on the protein’s function, therefore some penalties, δ(vi , wj), will be less harsh than ...
... protein sequence alignment Scoring matrices are created based on biological evidence. Alignments can be thought of as two sequences that differ due to mutations. Some of these mutations have little effect on the protein’s function, therefore some penalties, δ(vi , wj), will be less harsh than ...
... a) Hydrogen bonds are much weaker in proteins than in water b) Hydrogen bonds are much stronger in proteins than in water c) Hydrogen bonds are slightly weaker in proteins than in water. d) Hydrogen bonds are slightly stronger in proteins than in water. 6. Antigens bind to which portions of an antib ...
Genetic engineering
... The rabbit in the photograph has no pigment in its skin, fur or eyes. This is due to an inherited condition known as albinism. Such animals are unable to produce melanin, a protein pigment that gives colour to the skin, eyes, fur or hair. This condition makes an animal more likely to be preyed upon. ...
... The rabbit in the photograph has no pigment in its skin, fur or eyes. This is due to an inherited condition known as albinism. Such animals are unable to produce melanin, a protein pigment that gives colour to the skin, eyes, fur or hair. This condition makes an animal more likely to be preyed upon. ...
Syllabus 2012/2013 for Faculty of Medicine (English Division)
... 5. The formation, structure and properties of the peptide bond. Some important peptides in the human organism (glutathione, peptide hormones, peptide antibiotics). The insulin synthesis. 6.The classification of proteins according to their structure, properties and functions. 7.The characteristics of ...
... 5. The formation, structure and properties of the peptide bond. Some important peptides in the human organism (glutathione, peptide hormones, peptide antibiotics). The insulin synthesis. 6.The classification of proteins according to their structure, properties and functions. 7.The characteristics of ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.