Balance Between Protein Synthesis and Degradation
... negative balanced is observed when amino acids used for tissue building and energy are not replaced. In eukaryotes nitrogen balance can be affected by several catabolic conditions, such as disease, starvation, trauma, metabolic acidosis, composition of diet, and stage of growth. Regulation of Protei ...
... negative balanced is observed when amino acids used for tissue building and energy are not replaced. In eukaryotes nitrogen balance can be affected by several catabolic conditions, such as disease, starvation, trauma, metabolic acidosis, composition of diet, and stage of growth. Regulation of Protei ...
B left E
... 22. Which of the following is true about post-transcriptional RNA modifications in prokaryotes A. The 5’ end of the transcript is capped and the 3’ end is polyadenylated. B. Introns are spliced out of the transcript to form the mature mRNA. C. They do not occur, since translation and trascription ar ...
... 22. Which of the following is true about post-transcriptional RNA modifications in prokaryotes A. The 5’ end of the transcript is capped and the 3’ end is polyadenylated. B. Introns are spliced out of the transcript to form the mature mRNA. C. They do not occur, since translation and trascription ar ...
Slides of short summary on Molecular Biology
... • P-site: site where the new peptide bond is formed. • E-site: the exit site Two subunits join together on a mRNA molecule near the 5’ end. The ribosome will read the codons until AUG is reached and then the initiator tRNA binds to the P-site of the ribosome. Stop codons have tRNA that recognize a s ...
... • P-site: site where the new peptide bond is formed. • E-site: the exit site Two subunits join together on a mRNA molecule near the 5’ end. The ribosome will read the codons until AUG is reached and then the initiator tRNA binds to the P-site of the ribosome. Stop codons have tRNA that recognize a s ...
From DNA to Protein Structure and Function - Science Take-Out
... shape. It is this specific shape that allows each protein to perform a specific job. The combination of specific proteins that your body makes gives you your traits. ...
... shape. It is this specific shape that allows each protein to perform a specific job. The combination of specific proteins that your body makes gives you your traits. ...
Powerpoint Slides
... • A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. • DNA contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine deoxyribonucleotides, whereas RNA contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil ribonucleotides. • Phosphodiester bonds link nucleo ...
... • A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. • DNA contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine deoxyribonucleotides, whereas RNA contains adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil ribonucleotides. • Phosphodiester bonds link nucleo ...
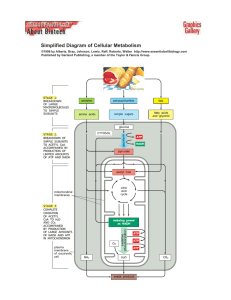
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Browning Reactions
... Important Types of Browning • Enzymatic (polyphenoloxidase). Fresh cut vegetables, non-toxic, no flavor • Caramelization. Sugars at very high temperatures. • Lipid Browning. Polymerization of frying oils • Vitamin C Browning. Similar to Maillard • THE MAILLARD REACTION ...
... Important Types of Browning • Enzymatic (polyphenoloxidase). Fresh cut vegetables, non-toxic, no flavor • Caramelization. Sugars at very high temperatures. • Lipid Browning. Polymerization of frying oils • Vitamin C Browning. Similar to Maillard • THE MAILLARD REACTION ...
Analitical chemistry 1
... 2- Quantitative analysis deals with the determination of how much of a material is present in a sample. The goal is to determine the amount of each component in a sample. Quantitative analysis may be classified based on the size of sample which is available for analysis. When a sample weighing more ...
... 2- Quantitative analysis deals with the determination of how much of a material is present in a sample. The goal is to determine the amount of each component in a sample. Quantitative analysis may be classified based on the size of sample which is available for analysis. When a sample weighing more ...
Biology DNA MCAS questions
... In phenylketonuria (PKU), an enzyme that converts one amino acid into another does not work properly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this genetic condition? A. an error in the transcription of the gene for the enzyme B. a mutation in the DNA sequence that codes for the enzyme C. ...
... In phenylketonuria (PKU), an enzyme that converts one amino acid into another does not work properly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this genetic condition? A. an error in the transcription of the gene for the enzyme B. a mutation in the DNA sequence that codes for the enzyme C. ...
Biological Molecules: Water and Carbohydrates
... Given that there are four bases in DNA, and these code for 20 amino acids, what is the basis for the genetic code? ...
... Given that there are four bases in DNA, and these code for 20 amino acids, what is the basis for the genetic code? ...
Review Ribosome-independent Peptide Synthesis in Nature and
... system. NRPS is also a huge enzyme and less flexible but can be designed to synthesize any peptide. Lal is a simple enzyme but lesser flexible. On the other hand, the high-energy phosphate bonds consumed to form one peptide bond are 4 (2 x ATP → AMP) in NRPS and 1 (ATP → ADP) in Lal. It would be int ...
... system. NRPS is also a huge enzyme and less flexible but can be designed to synthesize any peptide. Lal is a simple enzyme but lesser flexible. On the other hand, the high-energy phosphate bonds consumed to form one peptide bond are 4 (2 x ATP → AMP) in NRPS and 1 (ATP → ADP) in Lal. It would be int ...
Biomolecules … another worksheet
... _______________________ 2. Animal fat, corn oil, cholesterol, chlorophyll, and bee’s wax, olive oil, whale blubber _______________________ 3. Meat, hair, skin, muscle, enzymes _______________________ 4. Information molecules like DNA & RNA, energy transfer molecules like ATP ...
... _______________________ 2. Animal fat, corn oil, cholesterol, chlorophyll, and bee’s wax, olive oil, whale blubber _______________________ 3. Meat, hair, skin, muscle, enzymes _______________________ 4. Information molecules like DNA & RNA, energy transfer molecules like ATP ...
Chromosome Microarray (CMA) Pre-Test Patient
... smaller than can be detected by karyotyping. These missing or extra pieces are known as copy number variants (CNV). CMA can identify differences between a patient’s DNA and control DNA. In this way, duplications (gains) or deletions (losses) will be identified, as well as the genes contained in t ...
... smaller than can be detected by karyotyping. These missing or extra pieces are known as copy number variants (CNV). CMA can identify differences between a patient’s DNA and control DNA. In this way, duplications (gains) or deletions (losses) will be identified, as well as the genes contained in t ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... atomic # of 6 which means it has 6 protons and 6 electrons It has 4 vacancies in the outer energy level ...
... atomic # of 6 which means it has 6 protons and 6 electrons It has 4 vacancies in the outer energy level ...
Exam 1
... A. ____________ The conversion of an alkene into an alcohol is an example of an oxidation reaction. B. ____________The first pKa of NaH2PO4 is about 7. C. ____________ DNA double helices with high G-C content have higher melting points than those with lower G-C content. D. ____________ In blue/white ...
... A. ____________ The conversion of an alkene into an alcohol is an example of an oxidation reaction. B. ____________The first pKa of NaH2PO4 is about 7. C. ____________ DNA double helices with high G-C content have higher melting points than those with lower G-C content. D. ____________ In blue/white ...
ppt - University of Illinois Urbana
... – Matching a sequence to the profile HMMs – Score a sequence S by p(S|HMM)/p(S|Random) • Return top k best matching profile HMMs for a given sequence • Given an HMM, find additional sequences in the family ...
... – Matching a sequence to the profile HMMs – Score a sequence S by p(S|HMM)/p(S|Random) • Return top k best matching profile HMMs for a given sequence • Given an HMM, find additional sequences in the family ...
9.4 DNA-Binding Proteins
... • R-O complex DNA deviates from normal shape • DNA bends to accommodate base /aa contacts • Central part of helix is wound extra tightly • Outer parts are wound more loosely than normal • DNA sequence of operator facilitates bending ...
... • R-O complex DNA deviates from normal shape • DNA bends to accommodate base /aa contacts • Central part of helix is wound extra tightly • Outer parts are wound more loosely than normal • DNA sequence of operator facilitates bending ...
Study Guide B
... start of a gene and begins to unwind the DNA. Using one strand of the DNA as a template, RNA polymerase strings together a complementary strand of RNA. The RNA strand detaches from the DNA as it is transcribed, and the DNA zips back together. mRNA: intermediate message that is translated to form a p ...
... start of a gene and begins to unwind the DNA. Using one strand of the DNA as a template, RNA polymerase strings together a complementary strand of RNA. The RNA strand detaches from the DNA as it is transcribed, and the DNA zips back together. mRNA: intermediate message that is translated to form a p ...
A dietary supplement is intended to provide nutrients that may
... Some nutritionists claim that osteoporosis may occur from excessive protein intake because protein can put pressure on the kidneys and lead to bone loss due to calcium leaching.[1] However, some have suggested that higher calcium excretion may be due to a corresponding increase in proteininduced cal ...
... Some nutritionists claim that osteoporosis may occur from excessive protein intake because protein can put pressure on the kidneys and lead to bone loss due to calcium leaching.[1] However, some have suggested that higher calcium excretion may be due to a corresponding increase in proteininduced cal ...
FRAGMENT LENGTH ANALYSIS SCREENING FOR CEBPa
... family that is essential for myeloid differentiation. CEBPa gene consists of two N-terminal transactivating domains (TAD1 and TAD2) and a C-terminal basic and leucine zipper region (bZIP). Inactivating CEBPa mutations have been reported predominantly in normal karyotype acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) ...
... family that is essential for myeloid differentiation. CEBPa gene consists of two N-terminal transactivating domains (TAD1 and TAD2) and a C-terminal basic and leucine zipper region (bZIP). Inactivating CEBPa mutations have been reported predominantly in normal karyotype acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) ...
Computational Protein Design as a Cost Function Network
... (CPD) methods therefore try to intelligently guide this process by producing a collection of proteins, intended to be rich in functional proteins and whose size is small enough to be experimentally evaluated. The challenge of choosing a sequence of amino acids to perform a given task is formulated a ...
... (CPD) methods therefore try to intelligently guide this process by producing a collection of proteins, intended to be rich in functional proteins and whose size is small enough to be experimentally evaluated. The challenge of choosing a sequence of amino acids to perform a given task is formulated a ...
Preconceptional or Prenatal Genetic Testing of a Parent
... One or both parents or prospective parent(s) have a first degree relative who has an affected child with either an autosomal recessive disorder, an x-linked disorder, or an inherited disorder with variable penetrance Other (please specify): ____________ Genetic testing is to determine carrier status ...
... One or both parents or prospective parent(s) have a first degree relative who has an affected child with either an autosomal recessive disorder, an x-linked disorder, or an inherited disorder with variable penetrance Other (please specify): ____________ Genetic testing is to determine carrier status ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.