Protein
... other peptidases specifically attack the linkages between the amino acids. These peptidases digest all the remaining dipeptides and tripeptides into individual amino acids for absorption into the bloodstream. Undigested protein Any parts of proteins that are not digested and absorbed in the small i ...
... other peptidases specifically attack the linkages between the amino acids. These peptidases digest all the remaining dipeptides and tripeptides into individual amino acids for absorption into the bloodstream. Undigested protein Any parts of proteins that are not digested and absorbed in the small i ...
Biological Complexity - The University of Auckland
... external changes. Some networks have the ability both to "remember" and to "learn" about what changes have been imposed on them. One feature of biological networks that is especially important in genetic networks is the distribution of control among several different mechanisms. This is known as deg ...
... external changes. Some networks have the ability both to "remember" and to "learn" about what changes have been imposed on them. One feature of biological networks that is especially important in genetic networks is the distribution of control among several different mechanisms. This is known as deg ...
CHAPTER 19 DNA Mutation and Repair
... substitutes arginine for lysine. The amino acids have similar properties, so the protein’s function may not be altered). ii. Silent mutations occur when the mutant codon encodes the same amino acid as the wild-type gene, so that no change occurs in the protein produced (e.g., AAA and AAG both encode ...
... substitutes arginine for lysine. The amino acids have similar properties, so the protein’s function may not be altered). ii. Silent mutations occur when the mutant codon encodes the same amino acid as the wild-type gene, so that no change occurs in the protein produced (e.g., AAA and AAG both encode ...
All Proteins Have a Basic Molecular Formula
... digestive enzymes and muscle proteins that bring about metabolism and locomotion, respectively. Proteins are biopolymers constructed of amino acid monomers. The sequence of amino acids of a specific protein is determined by the sequence of the nucleic acid bases in the gene that encodes the protein. ...
... digestive enzymes and muscle proteins that bring about metabolism and locomotion, respectively. Proteins are biopolymers constructed of amino acid monomers. The sequence of amino acids of a specific protein is determined by the sequence of the nucleic acid bases in the gene that encodes the protein. ...
15 N- 1 H HSQC spectra as
... 0 ppm is defined by the signal from an internal standard such as DSS or TMSP x axis is the chemical shift d, in units of parts per million (ppm) of the B0 field strength chemical shift dispersion is very small (~12 ppm) compared to the B0 field strength (like ripples on an ocean surface). At 500 MHz ...
... 0 ppm is defined by the signal from an internal standard such as DSS or TMSP x axis is the chemical shift d, in units of parts per million (ppm) of the B0 field strength chemical shift dispersion is very small (~12 ppm) compared to the B0 field strength (like ripples on an ocean surface). At 500 MHz ...
Transcription
... chains of nucleotide molecules. During DNA replication DNA is duplicated, producing two double helices. Imbedded in these long strands of DNA are genes that control the production of proteins to the cell. ...
... chains of nucleotide molecules. During DNA replication DNA is duplicated, producing two double helices. Imbedded in these long strands of DNA are genes that control the production of proteins to the cell. ...
... DNA sequence obtained directly from PCR amplified genomic DNA from strain 2342 showed a single T to C transition at position 1411, resulting in a tryptophan to arginine change in amino acid residue 471. This tryptophan residue is conserved among most fungi (Figure 1) and even higher eukaryotes. The ...
RNA Ligands to Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase
... • RNA was added to gp43 in excess of binding sites so that competitive binding occurred. • Amount of RNA retrieved was roughly equal to the amount of gp43 in the reaction ...
... • RNA was added to gp43 in excess of binding sites so that competitive binding occurred. • Amount of RNA retrieved was roughly equal to the amount of gp43 in the reaction ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Lee Lab
... markers in a population more often or less often than would be expected from a random formation of haplotypes from alleles based on their frequencies. • Linkage disequilibrium can be caused by evolutionary factors such as natural selection and genetic drift. • Recombination will break down linkage d ...
... markers in a population more often or less often than would be expected from a random formation of haplotypes from alleles based on their frequencies. • Linkage disequilibrium can be caused by evolutionary factors such as natural selection and genetic drift. • Recombination will break down linkage d ...
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy ...
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy ...
sequence - Université d`Ottawa
... for mammalian nuclear DNA (regions not under functional constraint) ~ 4 x 10 -9 nt sub per site per year ...
... for mammalian nuclear DNA (regions not under functional constraint) ~ 4 x 10 -9 nt sub per site per year ...
Slide 1
... • Alignment answers the question of whether two or more sequences are (evolutionarily) related. • Example: A new gene is found in human. We wish to study its properties. To get a hint, we try to find its corresponding part in mouse. Among the tens of thousands of genes in mouse, which is the one tha ...
... • Alignment answers the question of whether two or more sequences are (evolutionarily) related. • Example: A new gene is found in human. We wish to study its properties. To get a hint, we try to find its corresponding part in mouse. Among the tens of thousands of genes in mouse, which is the one tha ...
BIOCHEMISTRY, CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TEST Time—170 minutes
... d. energy which does not cost anything. e. energy which is available to do work. 13. When diffusion occurs, so that molecules are arranged more randomly in a solution, which of the following would increase? a. Heat b. Gravity c. Entropy d. magnetism e. potential energy ...
... d. energy which does not cost anything. e. energy which is available to do work. 13. When diffusion occurs, so that molecules are arranged more randomly in a solution, which of the following would increase? a. Heat b. Gravity c. Entropy d. magnetism e. potential energy ...
Nucleic Acids Research
... an N-mer is added to the list described above, the positions in K or more sequences of the last N-mers to have differed from it at M or fewer positions are read from the new arrays and listed with it. Moreover, this set of positions is compared with all sets of positions already on the list, and if ...
... an N-mer is added to the list described above, the positions in K or more sequences of the last N-mers to have differed from it at M or fewer positions are read from the new arrays and listed with it. Moreover, this set of positions is compared with all sets of positions already on the list, and if ...
Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
H &
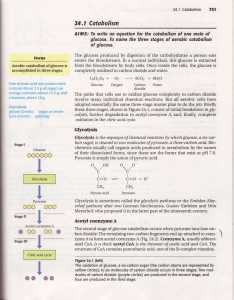
... involve many individual chemical reactions. But all aerobic cells have adopted essentially the same three-stagemaster plan to do the job. Briefly these three stages,sho'*min Figure 24.1, consist of initial breakdor.min glycolysis, further degradation to acetyl coenzymeA, and, flnally complete oxidat ...
... involve many individual chemical reactions. But all aerobic cells have adopted essentially the same three-stagemaster plan to do the job. Briefly these three stages,sho'*min Figure 24.1, consist of initial breakdor.min glycolysis, further degradation to acetyl coenzymeA, and, flnally complete oxidat ...
Slide 1
... Sickle-Cell Disease: A Change in Primary Protein Structure A slight change in primary structure can affect a protein’s structure and ability to function Sickle-cell disease, an inherited blood disorder, results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin ...
... Sickle-Cell Disease: A Change in Primary Protein Structure A slight change in primary structure can affect a protein’s structure and ability to function Sickle-cell disease, an inherited blood disorder, results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin ...
05_lecture_presentation
... • Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds • A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids • Polypeptides range in length from a few to more than a thousand monomers • Each polypeptide has a unique linear sequence of amino acids, with a carboxyl end (C-terminus) and an amino end (N-terminus) ...
... • Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds • A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids • Polypeptides range in length from a few to more than a thousand monomers • Each polypeptide has a unique linear sequence of amino acids, with a carboxyl end (C-terminus) and an amino end (N-terminus) ...
Slide 1
... formation of cystine calculi in the kidneys due to low solubility of cystine in acidic environment. Clinically, cystinuria is divided into two types: • Type I cystinuria – heterozygotes have normal excretion of cystine and dibasic amino acids, which implies that the disease is inherited autosomal-re ...
... formation of cystine calculi in the kidneys due to low solubility of cystine in acidic environment. Clinically, cystinuria is divided into two types: • Type I cystinuria – heterozygotes have normal excretion of cystine and dibasic amino acids, which implies that the disease is inherited autosomal-re ...
Supplemental Methods 1. Amino acid conformation clustering Amino
... reference system P-R-Q as described in the previous section, the amino acid type of the parent residue containing atom P, and the conformational type of the parent amino acid. Interacting atoms outside the sphere with the radius equal to the sum of the van der Waals radii of the interacting atom and ...
... reference system P-R-Q as described in the previous section, the amino acid type of the parent residue containing atom P, and the conformational type of the parent amino acid. Interacting atoms outside the sphere with the radius equal to the sum of the van der Waals radii of the interacting atom and ...
1. The table below refers to some disaccharides, their constituent
... Read through the following passage about protein structure, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. Proteins are composed of long chains of monomers called ..............................................., which are linked together by ............... ...
... Read through the following passage about protein structure, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. Proteins are composed of long chains of monomers called ..............................................., which are linked together by ............... ...
Chap 11 Section 1 - SunsetRidgeMSBiology
... ______________________ 16. A scientist uses a pedigree to study family history. ______________________ 17. A pedigree traces the inheritance of a particular trait through only two generations. ______________________ 18. In a pedigree, one who does not express the trait is represented by a darkened s ...
... ______________________ 16. A scientist uses a pedigree to study family history. ______________________ 17. A pedigree traces the inheritance of a particular trait through only two generations. ______________________ 18. In a pedigree, one who does not express the trait is represented by a darkened s ...
Vitamin В 1
... organic compounds that have different chemical structure and are not synthesized or are synthesized in small amount in the human organism, are not used as building material, but have marked biological effect and are necessary components of diet Hypovitaminosis – decrease of vitamin amount in the org ...
... organic compounds that have different chemical structure and are not synthesized or are synthesized in small amount in the human organism, are not used as building material, but have marked biological effect and are necessary components of diet Hypovitaminosis – decrease of vitamin amount in the org ...
投影片 1 - Center for Ethics of Science and Technology
... Declaration on Bioethical Norms:the subjects of right to genetic privacy include: testee, consanguine relatives and other relevant groups. Accord with Article 14 of The International Declaration on Human Genetic Data:the objects of right to genetic privacy include: the individual privacy that take p ...
... Declaration on Bioethical Norms:the subjects of right to genetic privacy include: testee, consanguine relatives and other relevant groups. Accord with Article 14 of The International Declaration on Human Genetic Data:the objects of right to genetic privacy include: the individual privacy that take p ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.