From: Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 408
... the three kingdoms of life, as well as to elaborate first identifiers of IDP function. The first predictor of ID regions was reported in 1997 (54). This two-layer feedforward neural network, which achieved a surprising accuracy of about 70% clearly marked the beginning of a new epoch by showing that ...
... the three kingdoms of life, as well as to elaborate first identifiers of IDP function. The first predictor of ID regions was reported in 1997 (54). This two-layer feedforward neural network, which achieved a surprising accuracy of about 70% clearly marked the beginning of a new epoch by showing that ...
Carbonyl Chemistry - Fundamentals
... 3 Fundamental Carbonyl Group Mechanism Steps: (Thinkbook Lecture Supplement pg 26) 1. Accept Nucleophile at Carbonyl Carbon a. the highly EN oxygen accepts an electron pair b. all carbonyl addition and substitution mechanisms contain this step ...
... 3 Fundamental Carbonyl Group Mechanism Steps: (Thinkbook Lecture Supplement pg 26) 1. Accept Nucleophile at Carbonyl Carbon a. the highly EN oxygen accepts an electron pair b. all carbonyl addition and substitution mechanisms contain this step ...
Likelihood Based Clustering (LiBaC) for Codon Models, a method
... of natural selection via a parameter for the nonsynonymous/synonymous rate ratio (ω = dN /dS). Different codon models are available to account for diversity of the evolutionary patterns among sites. Codon models which specify data partitions as fixed effects allow the most evolutionary diversity amo ...
... of natural selection via a parameter for the nonsynonymous/synonymous rate ratio (ω = dN /dS). Different codon models are available to account for diversity of the evolutionary patterns among sites. Codon models which specify data partitions as fixed effects allow the most evolutionary diversity amo ...
Function of ribosomes and glutamyl-tRNA isoacceptors
... not clear at thise time whether the molecular modifications responsible for the observed effects result in a decrease in the activity of control ribosomes (in which case the modification would presumably be reversed during the regeneration process) or whether 'normal' ribosomes are modified during r ...
... not clear at thise time whether the molecular modifications responsible for the observed effects result in a decrease in the activity of control ribosomes (in which case the modification would presumably be reversed during the regeneration process) or whether 'normal' ribosomes are modified during r ...
Shared mutations: Common descent or common mechanism?
... consequence is that the shared mutations in the 1G5 genes are due to a biological or physical mechanism. In other words, the mutations in the 1G5 gene are non-random mutations that would produce an alignment of mutations in separated species that do not reproduce together. The alignment is not due t ...
... consequence is that the shared mutations in the 1G5 genes are due to a biological or physical mechanism. In other words, the mutations in the 1G5 gene are non-random mutations that would produce an alignment of mutations in separated species that do not reproduce together. The alignment is not due t ...
Amino Acid Requirements and Post-absorptive Metabolism in Cattle
... The last route assessed by Swanson (1977) was MFP, for which it is not easy to have a clear description. For example, the definition of MFP has changed with time, from “a residue of body secretions and tissue incident to movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract” (Swanson, 1977) to the de ...
... The last route assessed by Swanson (1977) was MFP, for which it is not easy to have a clear description. For example, the definition of MFP has changed with time, from “a residue of body secretions and tissue incident to movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract” (Swanson, 1977) to the de ...
Protocol
... means RNA that is not degraded and is free from DNA contamination. The Stratagene kit uses a spin column packed with a silica-based matrix that specifically binds RNA in the presence of the chaotropic salt guanidine thiocyanate. "Chaotropic" means chaos-forming, a term which in biochemistry, usually ...
... means RNA that is not degraded and is free from DNA contamination. The Stratagene kit uses a spin column packed with a silica-based matrix that specifically binds RNA in the presence of the chaotropic salt guanidine thiocyanate. "Chaotropic" means chaos-forming, a term which in biochemistry, usually ...
Early frameshift alleles of zebrafish tbx5a that fail to
... mRNA expression of versican a (vcana) in homozygous tbx5aΔ5 mutants was expanded in tbx5a-mutant hearts (Fig. 1V,W). All these phenotypes are well-documented for both tbx5a morphants in which tbx5a mRNA is downregulated via morpholino injection7,9,10,18 and in embryos homozygous for the classic tbx5 ...
... mRNA expression of versican a (vcana) in homozygous tbx5aΔ5 mutants was expanded in tbx5a-mutant hearts (Fig. 1V,W). All these phenotypes are well-documented for both tbx5a morphants in which tbx5a mRNA is downregulated via morpholino injection7,9,10,18 and in embryos homozygous for the classic tbx5 ...
Conserved Tryptophan Residues within Putative Transmembrane
... (Hagenbuch and Meier, 2003), which are well-conserved among human, rat, and mouse OATPs/Oatps. However, the underlying importance of this highly conserved domain within OATPs remains unclear. In a computer-generated model of OATP1B3, an OATP family member that has high homology compared with OATP1B1 ...
... (Hagenbuch and Meier, 2003), which are well-conserved among human, rat, and mouse OATPs/Oatps. However, the underlying importance of this highly conserved domain within OATPs remains unclear. In a computer-generated model of OATP1B3, an OATP family member that has high homology compared with OATP1B1 ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... Historically, Biochemistry is intimately related to Organic Chemistry, which deals with the chemical properties of compounds that make part of living matter, and to Physiology, which deals with the functions of living organisms. The terms “physiological chemistry” and “biochemistry” as equivalent co ...
... Historically, Biochemistry is intimately related to Organic Chemistry, which deals with the chemical properties of compounds that make part of living matter, and to Physiology, which deals with the functions of living organisms. The terms “physiological chemistry” and “biochemistry” as equivalent co ...
Fish Protein Hydrolysate Production by Acid and Enzymatic Hydrolysis
... In order to end the reaction, the mixture was heated at 90°C for 15 minutes. For acid hydrolysis, HCl with concentrations of 2, 4 and 6 M were used to hydrolyze the raw material. The temperature was set at 80, 100 and 120°C using an autoclave. The reactions were terminated by adjusting pH value to 5 ...
... In order to end the reaction, the mixture was heated at 90°C for 15 minutes. For acid hydrolysis, HCl with concentrations of 2, 4 and 6 M were used to hydrolyze the raw material. The temperature was set at 80, 100 and 120°C using an autoclave. The reactions were terminated by adjusting pH value to 5 ...
Diet
... adults over the age of 18 years adolescense with poor dietary adherence patients with untreated/late diagnosed PKU NOT recommended for children and pregnanty woman with PKU 25-30% of daily protein from LNAAs 70-75% of daily protein from natural low-Phe products (vs 20% w/o LNAA) Phe levels up to 1.5 ...
... adults over the age of 18 years adolescense with poor dietary adherence patients with untreated/late diagnosed PKU NOT recommended for children and pregnanty woman with PKU 25-30% of daily protein from LNAAs 70-75% of daily protein from natural low-Phe products (vs 20% w/o LNAA) Phe levels up to 1.5 ...
Isolation, Properties and a Possible Function of a Water
... The rapeseed and radish proteins were postulated to function as an inhibitor of proteases since their amino acid sequences contain the signature motif of the Kiinitz family of protease inhibitors (Reviron et al. 1992, Lopez et al. 1994). This possibility could not be examined, however, because the p ...
... The rapeseed and radish proteins were postulated to function as an inhibitor of proteases since their amino acid sequences contain the signature motif of the Kiinitz family of protease inhibitors (Reviron et al. 1992, Lopez et al. 1994). This possibility could not be examined, however, because the p ...
Proteinase K, solution
... Proteinase K (CAS: 39450-01-6) is a non-specific serine protease having a very high specific activity (cleaves the carboxylic ends of aromatic, hydrophobic and aliphatic amino acids). It has been used for isolation of mRNA, high molecular weight DNA and to inactivate other enzymatic activities. Prot ...
... Proteinase K (CAS: 39450-01-6) is a non-specific serine protease having a very high specific activity (cleaves the carboxylic ends of aromatic, hydrophobic and aliphatic amino acids). It has been used for isolation of mRNA, high molecular weight DNA and to inactivate other enzymatic activities. Prot ...
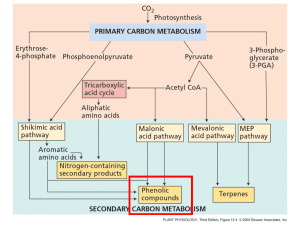
Bio426Lecture28Apr10
... What’s a phenolic compound? A secondary product that contains a phenol group - a hydroxyl functional group on an aromatic ring. ...
... What’s a phenolic compound? A secondary product that contains a phenol group - a hydroxyl functional group on an aromatic ring. ...
Molecular Evolution of Nitrate Reductase Genes
... All eukaryotic NRs have three highly conserved functional domains binding FAD, heme, and molybdenum cofactor (MoCo) (Kleinhofs et al. 1989). The three functional domains are separated by two short hinge regions (Kubo et al. 1988). They are encoded in a linear order with the MoCo region at the N-term ...
... All eukaryotic NRs have three highly conserved functional domains binding FAD, heme, and molybdenum cofactor (MoCo) (Kleinhofs et al. 1989). The three functional domains are separated by two short hinge regions (Kubo et al. 1988). They are encoded in a linear order with the MoCo region at the N-term ...
RFX6v5 - Open Research Exeter
... compound heterozygote, the remaining seven homozygous), six affect splicing and/or the reading frame in exons 2-8; the remaining three are mis-sense mutations clustering within or close to the DNA-binding domain (Figure 2). The cases in the present report are compound heterozygotes for premature tru ...
... compound heterozygote, the remaining seven homozygous), six affect splicing and/or the reading frame in exons 2-8; the remaining three are mis-sense mutations clustering within or close to the DNA-binding domain (Figure 2). The cases in the present report are compound heterozygotes for premature tru ...
Blamires SJ, Wu CL, Tso IM (2012)
... protein intake regimes: high, low or no protein intake. While the relative genetic inputs into the silks of these species are unknown, species of the former two genera have been reported to exhibit high proline (,9–12%), hence most likely MaSp2 predominant, MA silks [20,21,41,42]. Species from the l ...
... protein intake regimes: high, low or no protein intake. While the relative genetic inputs into the silks of these species are unknown, species of the former two genera have been reported to exhibit high proline (,9–12%), hence most likely MaSp2 predominant, MA silks [20,21,41,42]. Species from the l ...
Characterization and Cloning of the Chlorophyll
... a PPD-specific antisense primer containing the initiation and termination codons, respectively, were then designed. Finally, the 792-bp cDNA fragment from the initiation codon, ATG, to the termination codon, TGA, was cloned by a combination of PCRs with the template synthesized from radish RNA (Fig. ...
... a PPD-specific antisense primer containing the initiation and termination codons, respectively, were then designed. Finally, the 792-bp cDNA fragment from the initiation codon, ATG, to the termination codon, TGA, was cloned by a combination of PCRs with the template synthesized from radish RNA (Fig. ...
STRONG AND WEAK HYDROGEN BONDS IN Sm/LSm
... with members in all living kingdoms. Arcaeabacteria harbour between one or two Sm/LSm proteins. The Escherichia coli Hfq protein and its ortologues represent a family in several bacterial lineages. Genomes of eukaryotes contain a minimum of 24 Sm/LSm genes. Phylogenetic distribution suggests that th ...
... with members in all living kingdoms. Arcaeabacteria harbour between one or two Sm/LSm proteins. The Escherichia coli Hfq protein and its ortologues represent a family in several bacterial lineages. Genomes of eukaryotes contain a minimum of 24 Sm/LSm genes. Phylogenetic distribution suggests that th ...
ANSWER - Issaquah Connect
... Populations have variation for traits that allows some to be advantageous depending on the environment and those traits enable the organism to survive, reproduce, and pass on that beneficial trait to the next generation. Over time those traits become more common. If there is no variation it is possi ...
... Populations have variation for traits that allows some to be advantageous depending on the environment and those traits enable the organism to survive, reproduce, and pass on that beneficial trait to the next generation. Over time those traits become more common. If there is no variation it is possi ...
Interaction of cycloheximide with 25S ribosomal RNA from yeast
... domain that is, in S.cerevisiae, involved with the interaction of cyclEheximide contains ribosomal protein L41. It is likely, however. that the actual binding site for the drug is located on ribosomal RNA. RNA target sites have now been confirmed for a large number of antibiotics (see, for example, ...
... domain that is, in S.cerevisiae, involved with the interaction of cyclEheximide contains ribosomal protein L41. It is likely, however. that the actual binding site for the drug is located on ribosomal RNA. RNA target sites have now been confirmed for a large number of antibiotics (see, for example, ...
Full text in pdf - International Microbiology
... heavy-metal cofactor and is oxygen sensitive, were distinctly different from that of any other NADP+-dependent GAPDHN (not shown). The 12 deduced partial bacterial GAPDHN sequences determined in this study were compared using the CLUSTAL X (v. 1.8) program with other published amino acid sequences o ...
... heavy-metal cofactor and is oxygen sensitive, were distinctly different from that of any other NADP+-dependent GAPDHN (not shown). The 12 deduced partial bacterial GAPDHN sequences determined in this study were compared using the CLUSTAL X (v. 1.8) program with other published amino acid sequences o ...
CHMI 2227E Biochemistry I
... Yield: (Total activity at Step Y / Total activity in crude extract) x 100; Purification level: Specific activity at Step Y / Specific activity in crude extract; CHMI 2227 - E.R. Gauthier, Ph.D. ...
... Yield: (Total activity at Step Y / Total activity in crude extract) x 100; Purification level: Specific activity at Step Y / Specific activity in crude extract; CHMI 2227 - E.R. Gauthier, Ph.D. ...
Effects of monosulfuron-ester on metabolic processes of nitrogen
... concentration, and by 61, 52, and 55% at the 30 nmol/L concentration. The other amino acids content of A. azotica and A. flos-aquae cells such as glycine, alanine, phenylalanine, serine, threonine, methionine, glutarnine, asparticacid, lysine, and arginine were respectively reduced 8–55% and 67–90% ...
... concentration, and by 61, 52, and 55% at the 30 nmol/L concentration. The other amino acids content of A. azotica and A. flos-aquae cells such as glycine, alanine, phenylalanine, serine, threonine, methionine, glutarnine, asparticacid, lysine, and arginine were respectively reduced 8–55% and 67–90% ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.