Study Portfolio
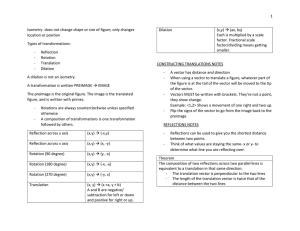
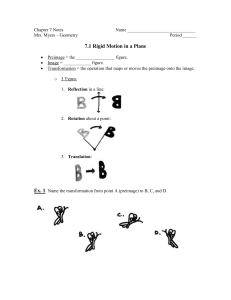
... At the conclusion of each unit, you will create a one page study sheet. You must write the title of the unit and its number. All future study sheets will need to have the same sections! Section #1: Vocabulary (words and/or diagrams) Angle of elevation (include a diagram) Angle of depression (inc ...
... At the conclusion of each unit, you will create a one page study sheet. You must write the title of the unit and its number. All future study sheets will need to have the same sections! Section #1: Vocabulary (words and/or diagrams) Angle of elevation (include a diagram) Angle of depression (inc ...
... molecules, respectively, and M0 is a singleton which denotes the simultaneous collision configuration. We have no need to discuss mechanics on M0 . A quantum Hamiltonian system is defined on L2 (M ), and stratified into those on L2 (Ṁ ) and L2 (M1 ), which are reduced to quantum systems on vector b ...
Electromagnetism: The simplest gauge theory.
... of electric charge. PROBLEM: Show that the Lagrangian density for source-free electromagnetism can be written in terms of the electric and magnetic fields (in any given inertial frame) by L = 12 (E 2 − B 2 ). This is one of the 2 relativistic invariants that can be made algebraically ~ and B. ...
... of electric charge. PROBLEM: Show that the Lagrangian density for source-free electromagnetism can be written in terms of the electric and magnetic fields (in any given inertial frame) by L = 12 (E 2 − B 2 ). This is one of the 2 relativistic invariants that can be made algebraically ~ and B. ...
Noether's theorem

Noether's (first) theorem states that every differentiable symmetry of the action of a physical system has a corresponding conservation law. The theorem was proven by German mathematician Emmy Noether in 1915 and published in 1918. The action of a physical system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function (which may or may not be an integral over space of a Lagrangian density function), from which the system's behavior can be determined by the principle of least action.Noether's theorem has become a fundamental tool of modern theoretical physics and the calculus of variations. A generalization of the seminal formulations on constants of motion in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics (developed in 1788 and 1833, respectively), it does not apply to systems that cannot be modeled with a Lagrangian alone (e.g. systems with a Rayleigh dissipation function). In particular, dissipative systems with continuous symmetries need not have a corresponding conservation law.