Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... Telescope turns quickly and points XRT and UVOT. Pinpoints position of the source. ...
... Telescope turns quickly and points XRT and UVOT. Pinpoints position of the source. ...
Primordial Planet Formation - University of California San Diego
... Detection of µBD planetary objects from temperature happened because the temperature found was an important one in the physical chemistry of hydrogen, the most common element in the universe and the most probable candidate for the ordinary dark matter. Hydrogen is a gas that condenses to liquid ...
... Detection of µBD planetary objects from temperature happened because the temperature found was an important one in the physical chemistry of hydrogen, the most common element in the universe and the most probable candidate for the ordinary dark matter. Hydrogen is a gas that condenses to liquid ...
Measuring Double Stars with a Micrometer and Digital Image
... The observation and measurement of visual double stars is an important area of study in astronomy and astrophysics. This type of observing is an area of research well suited for amateur participation. The amateur can still carry out important scientific work, and make a valuable contribution to astr ...
... The observation and measurement of visual double stars is an important area of study in astronomy and astrophysics. This type of observing is an area of research well suited for amateur participation. The amateur can still carry out important scientific work, and make a valuable contribution to astr ...
June, 2001 AAS poster - David P. Bennett
... range, the planetary events (such as the one on the right) can be long enough so that a single site can get enough data to characterize the planetary light curve deviation. Our detection criteria does not take this possibility into account. However, there are still some Jupiter-mass planet events (s ...
... range, the planetary events (such as the one on the right) can be long enough so that a single site can get enough data to characterize the planetary light curve deviation. Our detection criteria does not take this possibility into account. However, there are still some Jupiter-mass planet events (s ...
Moonlight project - Observations of Lunar rotation and Ephemeris by
... PZT (Photographic Zenith Tube) or astrolabe is assumed as the telescope for this purpose. Fluctuations in rotation of the Moon consists of the physical librations and the free librations. Since the physical librations are caused by the attraction of the Sun and the Earth, the period is the combinati ...
... PZT (Photographic Zenith Tube) or astrolabe is assumed as the telescope for this purpose. Fluctuations in rotation of the Moon consists of the physical librations and the free librations. Since the physical librations are caused by the attraction of the Sun and the Earth, the period is the combinati ...
Seeing another Earth: Detecting and Characterizing Rocky Planets
... ubiquity compared to gas giant planets. Improved instrumental stability has allowed detection of planets with masses <10 ME, using radial velocity (RV) measurements. These detections have occurred despite the strong selection effect against this due to the lower mass. Planets with minimum masses of ...
... ubiquity compared to gas giant planets. Improved instrumental stability has allowed detection of planets with masses <10 ME, using radial velocity (RV) measurements. These detections have occurred despite the strong selection effect against this due to the lower mass. Planets with minimum masses of ...
Historic mass loss from the RS Ophiuchi system
... Stars with an initial mass between ∼ 1 and ∼ 40 M¯ become hydrogen/heliumshell-burning Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) stars or core-helium-burning red supergiants (RSG). These phases are characterised by cool, molecular atmospheres giving rise to M spectral types (S or C for some chemically peculiar ...
... Stars with an initial mass between ∼ 1 and ∼ 40 M¯ become hydrogen/heliumshell-burning Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) stars or core-helium-burning red supergiants (RSG). These phases are characterised by cool, molecular atmospheres giving rise to M spectral types (S or C for some chemically peculiar ...
SkyProdigy Series Manual
... itself with the night sky and determine where the telescope is currently pointing.The camera automatically captures an image of the sky, which is processed internally to positively identify the stars in the image. Once a positive match is found, SkyProdigy determines the coordinates of the center of ...
... itself with the night sky and determine where the telescope is currently pointing.The camera automatically captures an image of the sky, which is processed internally to positively identify the stars in the image. Once a positive match is found, SkyProdigy determines the coordinates of the center of ...
story of telescope
... the way they did. The Aristotelian universe was thought to be made up of five basic elements: earth, fire, air and water for terrestrial objects, and a pure, ‘fifth essence’ (quintessence) for celestial objects. All these elements had their ‘natural’ places of rest, and things moved to seek their na ...
... the way they did. The Aristotelian universe was thought to be made up of five basic elements: earth, fire, air and water for terrestrial objects, and a pure, ‘fifth essence’ (quintessence) for celestial objects. All these elements had their ‘natural’ places of rest, and things moved to seek their na ...
Chapter 4 Telescope Making Basics
... There are five steps in the making the primary mirror: rough grinding, fine grinding, smoothing, and polishing/figuring. At every stage, the mirror-maker guides the process with specific tests. Rough grinding (sometimes called hogging) consists of systematically working a glass disk (the future mirr ...
... There are five steps in the making the primary mirror: rough grinding, fine grinding, smoothing, and polishing/figuring. At every stage, the mirror-maker guides the process with specific tests. Rough grinding (sometimes called hogging) consists of systematically working a glass disk (the future mirr ...
Chapter 20
... settled down to a steady and reliable existence on the main sequence. (T Tauri stars always have the word “stars” in their name though technically they haven’t reached the main sequence, so they are not yet fully formed stars.) In astronomical teaching, we have the question of whether to first consi ...
... settled down to a steady and reliable existence on the main sequence. (T Tauri stars always have the word “stars” in their name though technically they haven’t reached the main sequence, so they are not yet fully formed stars.) In astronomical teaching, we have the question of whether to first consi ...
Imaging with Hexagonal Segmented Mirror in the Presence of
... The binary star is a two impulse stars separated by a certain distance from the center of an array. The separation is chosen with respect to the ratio “separation/D” (D = 2 R ). This ratio is taken to be 0.1. This will produce a binary star that has a separation to be just within the full extent of ...
... The binary star is a two impulse stars separated by a certain distance from the center of an array. The separation is chosen with respect to the ratio “separation/D” (D = 2 R ). This ratio is taken to be 0.1. This will produce a binary star that has a separation to be just within the full extent of ...
The Milky Way Model - University of Chicago
... closely packed stars, was it part of the Earth’s atmosphere or at great astronomical distances? These days, looking up at the sky from even a small city or suburb, the Milky Way isn’t even visible anymore due to light pollution and has lost its hold on imagination of most people on Earth. Yet at the ...
... closely packed stars, was it part of the Earth’s atmosphere or at great astronomical distances? These days, looking up at the sky from even a small city or suburb, the Milky Way isn’t even visible anymore due to light pollution and has lost its hold on imagination of most people on Earth. Yet at the ...
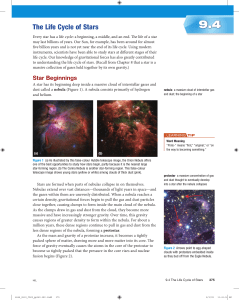
The Life Cycle of Stars
... temperature of 15 million °C (1.5 × 107 °C). At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins. Hydrogen atoms in the core fuse to form helium atoms, producing an enormous amount of energy. This energy rushes outward from the core of the star, counteracting the gravitational forces that caused the protosta ...
... temperature of 15 million °C (1.5 × 107 °C). At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins. Hydrogen atoms in the core fuse to form helium atoms, producing an enormous amount of energy. This energy rushes outward from the core of the star, counteracting the gravitational forces that caused the protosta ...
Nebula
... A planetary nebula is an astronomical object consisting of a glowing shell of gas and plasma formed by certain types of stars at the end of their lives. The name originates from a similarity in appearance to giant planets when viewed through a small optical telescope and is unrelated to planets of t ...
... A planetary nebula is an astronomical object consisting of a glowing shell of gas and plasma formed by certain types of stars at the end of their lives. The name originates from a similarity in appearance to giant planets when viewed through a small optical telescope and is unrelated to planets of t ...
z - STScI
... forming regions/galaxies that appeared 1 billion years after the Big Bang (to z ~ 5.6) – New stars appear to be forming at roughly a constant rate until very recently (1 < z < 5) – SCUBA may have detected a significant component of dust-hidden star formation at cosmological distances ...
... forming regions/galaxies that appeared 1 billion years after the Big Bang (to z ~ 5.6) – New stars appear to be forming at roughly a constant rate until very recently (1 < z < 5) – SCUBA may have detected a significant component of dust-hidden star formation at cosmological distances ...
Space Information Booklet (English)
... Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. It is very hot. It is only 57,900,000 Km away from the sun. Each day lasts 59 earth days and a year lasts 88 earth days. Mercury is a world of extremes. Because it is so close to the Sun, a visitor could easily cook to death. However because Mercury spins so ...
... Mercury is the closest planet to the sun. It is very hot. It is only 57,900,000 Km away from the sun. Each day lasts 59 earth days and a year lasts 88 earth days. Mercury is a world of extremes. Because it is so close to the Sun, a visitor could easily cook to death. However because Mercury spins so ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
... Distance to the Cluster Place the clear plastic over your graph, and using the ruler trace both x and y axes. Label and scale the x axis the same as the graph paper, but number the scale of the y axis of the plastic overlay to range from -8 (at the top) to +17 (at the bottom). Label this new y axis ...
... Distance to the Cluster Place the clear plastic over your graph, and using the ruler trace both x and y axes. Label and scale the x axis the same as the graph paper, but number the scale of the y axis of the plastic overlay to range from -8 (at the top) to +17 (at the bottom). Label this new y axis ...
What You need to know - Peterborough Astronomical Society
... • Learn to find and see things through binoculars, especially the Moon, Jupiter, and bright “deep-sky objects” like the Orion Nebula, Andromeda Galaxy, and the Pleiades. It takes practice to look through an eyepiece, and binoculars are much more forgiving than a telescope • Look through someone else ...
... • Learn to find and see things through binoculars, especially the Moon, Jupiter, and bright “deep-sky objects” like the Orion Nebula, Andromeda Galaxy, and the Pleiades. It takes practice to look through an eyepiece, and binoculars are much more forgiving than a telescope • Look through someone else ...
VNOS/VOSI-ASTR
... 5. What types of activities do astronomers do to learn about the universe? Be specific about how they go about their work. A: Observation of cosmos. Measuring of star movement. Taking pictures. Using instruments to receive electromagnet radiation from space. Discussion with other scientists. B: Ast ...
... 5. What types of activities do astronomers do to learn about the universe? Be specific about how they go about their work. A: Observation of cosmos. Measuring of star movement. Taking pictures. Using instruments to receive electromagnet radiation from space. Discussion with other scientists. B: Ast ...
On the telescopic disks of stars-a review and analysis of stellar
... were partly a product of the telescope, but partly a product of the star itself. When George Airy produced a theoretical explanation for these disks (1835: 283-291), astronomers in the mid-19th century were slow to reconcile this theory, which said that all stellar images were characterized only by ...
... were partly a product of the telescope, but partly a product of the star itself. When George Airy produced a theoretical explanation for these disks (1835: 283-291), astronomers in the mid-19th century were slow to reconcile this theory, which said that all stellar images were characterized only by ...
Chapter14(4-7-11)
... • 14.2 Galactic Recycling (closely related to Ch. 13) • 14.3 The History of the Milky Way • 14.4 The Mysterious Galactic Center ...
... • 14.2 Galactic Recycling (closely related to Ch. 13) • 14.3 The History of the Milky Way • 14.4 The Mysterious Galactic Center ...
2_ISM - UCT Astronomy Department
... - the normalized amount of extinction as a function of wavelength, - derived from looking at pairs of stellar spectra with similar temperatures but different foreground extinctions. - The general extinction curve within each of the Milky Way, LMC, and SMC is fairly well defined - The overall increas ...
... - the normalized amount of extinction as a function of wavelength, - derived from looking at pairs of stellar spectra with similar temperatures but different foreground extinctions. - The general extinction curve within each of the Milky Way, LMC, and SMC is fairly well defined - The overall increas ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.