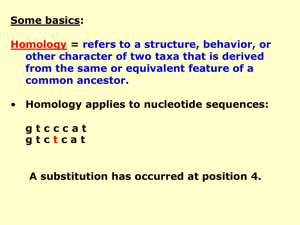
Diapositiva 1 - Universidad Autonoma de Madrid
... alternative character states ( e.g. A, G, C and T) • In addition, these states are chemically identical so that homology and homoplasy are equally similar and cannot be distinguished through detailed study of structure or ...
... alternative character states ( e.g. A, G, C and T) • In addition, these states are chemically identical so that homology and homoplasy are equally similar and cannot be distinguished through detailed study of structure or ...
DNA Unit Practice Questions and In
... 11. RNA, messenger RNA 12. codons, genetic code Study the following six steps in the synthesis of proteins. Determine the order in which the steps take place. Write the number of each step in order. 13. The codon following the start codon then receives the tRNA molecule with the complementary antico ...
... 11. RNA, messenger RNA 12. codons, genetic code Study the following six steps in the synthesis of proteins. Determine the order in which the steps take place. Write the number of each step in order. 13. The codon following the start codon then receives the tRNA molecule with the complementary antico ...
PDBe Motif
... Search Results for 1a0t –based on 3D motif configuration(195:IHWI,196:HWID) • Predominant secondary structure element – beta sheets ...
... Search Results for 1a0t –based on 3D motif configuration(195:IHWI,196:HWID) • Predominant secondary structure element – beta sheets ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... engage a gene at one time • Multiple ribosomes can engage a single mRNA at one time Transcription DNA ...
... engage a gene at one time • Multiple ribosomes can engage a single mRNA at one time Transcription DNA ...
GENE EXPRESSION: CONTROL IN BACTERIA AND PHAGES
... expected to have one phe-phe-phe sequence. c. This discrepancy could be related to the levels of charged (aminoacylated) tRNAs in the cell. Amino acids, such as tryptophan, that normally have low cellular levels of charged tRNAs are likely to have few codons in the leader mRNA. If instead they had m ...
... expected to have one phe-phe-phe sequence. c. This discrepancy could be related to the levels of charged (aminoacylated) tRNAs in the cell. Amino acids, such as tryptophan, that normally have low cellular levels of charged tRNAs are likely to have few codons in the leader mRNA. If instead they had m ...
11.3 Section Summary 6.3 – pages 296
... • A mutation may produce a new trait or it may result in a protein that does not work correctly. • Sometimes, the mutation results in a protein that is nonfunctional, and the embryo may not survive. ...
... • A mutation may produce a new trait or it may result in a protein that does not work correctly. • Sometimes, the mutation results in a protein that is nonfunctional, and the embryo may not survive. ...
第三章 核酸的结构和功能
... A biopolymer composed of nucleotides linked in a linear sequential order through 3’,5’ phosphodiester bonds ...
... A biopolymer composed of nucleotides linked in a linear sequential order through 3’,5’ phosphodiester bonds ...
Carbon Compounds - Model High School
... Derived from fats eaten in _______ in the body from other energy sources like ...
... Derived from fats eaten in _______ in the body from other energy sources like ...
No Slide Title
... BLOSUM Matrix (2) The BLOSUM matrices (BLOcks SUbstitution Matrix) are based on the BLOCKS database. The BLOCKS database utilizes the concept of blocks (ungapped amino acid pattern), which act as signatures of a family of proteins. Substitution frequencies for all pairs of amino acids were then cal ...
... BLOSUM Matrix (2) The BLOSUM matrices (BLOcks SUbstitution Matrix) are based on the BLOCKS database. The BLOCKS database utilizes the concept of blocks (ungapped amino acid pattern), which act as signatures of a family of proteins. Substitution frequencies for all pairs of amino acids were then cal ...
DNA Replication - :: FAPERTA UGM
... Biological processes, such as transcription, and in case of proteins, also translation, that yield a gene product. A gene is expressed when its biological product is present and active. Gene expression is regulated at multiple levels. ...
... Biological processes, such as transcription, and in case of proteins, also translation, that yield a gene product. A gene is expressed when its biological product is present and active. Gene expression is regulated at multiple levels. ...
synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing
... vitro and in vivo, suggesting that PGHS plays an important role in regulating or promoting cell proliferation in some normal and neoplastically transformed cells (12-15). RSV-inducible prostaglandin synthase encoded by the CEF-147 cDNA showed several important features that distinguished it from the ...
... vitro and in vivo, suggesting that PGHS plays an important role in regulating or promoting cell proliferation in some normal and neoplastically transformed cells (12-15). RSV-inducible prostaglandin synthase encoded by the CEF-147 cDNA showed several important features that distinguished it from the ...
HEMOGLOBIN_M-_SASKATOON-1
... Hemoglobin M-Saskatoon Hemoglobin M-Saskatoon is a beta peptide mutation and is one of seven known variants of hemoglobin in which the patient exhibits cyanosis (blue skin color) due to the presence of high levels of methemoglobin (metHb) in the red blood cells. For this reason the hemoglobin varian ...
... Hemoglobin M-Saskatoon Hemoglobin M-Saskatoon is a beta peptide mutation and is one of seven known variants of hemoglobin in which the patient exhibits cyanosis (blue skin color) due to the presence of high levels of methemoglobin (metHb) in the red blood cells. For this reason the hemoglobin varian ...
Minireview Shifty Ciliates: Frequent Programmed
... consist of a poorly recognized termination codon immediately preceded by a sequence that can allow a tRNA to slip ⫹1 on the mRNA while still maintaining at least two base pairs. For example, in the prfB gene of Escherichia coli, a ⫹1 frameshift occurs at the sequence CUUUGA-C, shown in codons of the ...
... consist of a poorly recognized termination codon immediately preceded by a sequence that can allow a tRNA to slip ⫹1 on the mRNA while still maintaining at least two base pairs. For example, in the prfB gene of Escherichia coli, a ⫹1 frameshift occurs at the sequence CUUUGA-C, shown in codons of the ...
Degenerate PCR - Yale School of Medicine
... Using inosine in the primers requires that the DNA polymerase used in the PCR reaction be capable of synthesizing DNA over an inosine-containing template. Taq polymerase is capable of doing this, but some others (e.g. Vent) appear not to be able to. 3) using multiple separate oligo pools at a single ...
... Using inosine in the primers requires that the DNA polymerase used in the PCR reaction be capable of synthesizing DNA over an inosine-containing template. Taq polymerase is capable of doing this, but some others (e.g. Vent) appear not to be able to. 3) using multiple separate oligo pools at a single ...
Milestone4
... In this task, you will generate a random DNA sequence and then repeatedly (1000 times) mutate one of the nucleotides in the sequence. During the 1000 times that you mutate a nucleotide in the sequence, you may at times mutate a nucleotide that has been mutated previously and you may at times mutate ...
... In this task, you will generate a random DNA sequence and then repeatedly (1000 times) mutate one of the nucleotides in the sequence. During the 1000 times that you mutate a nucleotide in the sequence, you may at times mutate a nucleotide that has been mutated previously and you may at times mutate ...
Clicker questions used in the activity, distribution of student answers
... What will the RNA polymerase do when it reaches the nucleotides encoding the premature stop codon? It will: * A. stop when it reaches the first nucleotide encoding the premature stop codon. (9%) B. stop when it reaches the last nucleotide encoding the premature stop codon. (24%) C. not be affected b ...
... What will the RNA polymerase do when it reaches the nucleotides encoding the premature stop codon? It will: * A. stop when it reaches the first nucleotide encoding the premature stop codon. (9%) B. stop when it reaches the last nucleotide encoding the premature stop codon. (24%) C. not be affected b ...
Mutation
... Neutral mutations: • Most mutations do not have a negative or a positive effect • Many mutations are repaired before protein synthesis occurs • Cells containing DNA that cannot be repaired are usually prevented from dividing • Silent point mutations are also neutral mutations because the amino a ...
... Neutral mutations: • Most mutations do not have a negative or a positive effect • Many mutations are repaired before protein synthesis occurs • Cells containing DNA that cannot be repaired are usually prevented from dividing • Silent point mutations are also neutral mutations because the amino a ...
Section 8: Genetic Mutations, Ribosome Structure
... Nucleic acids are always synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction. 2. Which of the following mutations would be MOST likely to have a harmful effect on an organism? A. A base-pair substitution in the middle of the coding sequence. B. A deletion of three nucleotides in the middle of the coding sequence. ...
... Nucleic acids are always synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction. 2. Which of the following mutations would be MOST likely to have a harmful effect on an organism? A. A base-pair substitution in the middle of the coding sequence. B. A deletion of three nucleotides in the middle of the coding sequence. ...
video slide - Independent School District 196
... 1 A small ribosomal subunit binds to a molecule of mRNA. In a prokaryotic cell, the mRNA binding site on this subunit recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence on the mRNA just upstream of the start codon. An initiator tRNA, with the anticodon UAC, base-pairs with the start codon, AUG. This tRNA car ...
... 1 A small ribosomal subunit binds to a molecule of mRNA. In a prokaryotic cell, the mRNA binding site on this subunit recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence on the mRNA just upstream of the start codon. An initiator tRNA, with the anticodon UAC, base-pairs with the start codon, AUG. This tRNA car ...
Chemical organization of cells. Macromolecules
... Recombination - the process of exchanges of fragments between different DNA molecules, resulting in a different genetic combination. Hybridization - The process of forming a double stranded nucleic acid from joining two complementary strands of DNA (or RNA). DNA Functions DNA is the main genetic mol ...
... Recombination - the process of exchanges of fragments between different DNA molecules, resulting in a different genetic combination. Hybridization - The process of forming a double stranded nucleic acid from joining two complementary strands of DNA (or RNA). DNA Functions DNA is the main genetic mol ...
Chapter 6 From DNA to Protein: How Cell Read the Genome
... The genetic code is translated by means of two adaptors that act one after another ...
... The genetic code is translated by means of two adaptors that act one after another ...
Mutations, Karyotyping, Pedigrees
... Look at your codon chart or codon wheel. What would happen if the following Point Mutation Occurred: CCACCC GGAGGU UCUUCA Amino acid meaning was not altered Silent mutation ...
... Look at your codon chart or codon wheel. What would happen if the following Point Mutation Occurred: CCACCC GGAGGU UCUUCA Amino acid meaning was not altered Silent mutation ...
Biological Molecules: Water and Carbohydrates
... It contains six carbon atoms so it is a hexose sugar. Its general formula is C6H12O6. Glucose is the major energy source for most cells. It is highly soluble and is the main form in which carbohydrates are transported around the body of animals. The structure of glucose can be represented in differe ...
... It contains six carbon atoms so it is a hexose sugar. Its general formula is C6H12O6. Glucose is the major energy source for most cells. It is highly soluble and is the main form in which carbohydrates are transported around the body of animals. The structure of glucose can be represented in differe ...
DNA Transcription and Translation Project
... This assignment is due on the day of the Transcription/Translation test. No late work will be accepted. All organisms use proteins to grow and function. These proteins are made up of thousands of amino acids which were created through the processes of DNA transcription and translation. The purpose o ...
... This assignment is due on the day of the Transcription/Translation test. No late work will be accepted. All organisms use proteins to grow and function. These proteins are made up of thousands of amino acids which were created through the processes of DNA transcription and translation. The purpose o ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.