Unit 6 - John Adams Academy
... As tRNA moves the amino acids together, long chains are formed (proteins) There are 20 different amino acids The structure and function of the protein depends upon the amino acids present and the order in which they are attached The base pairs (A, U, C, G) are arranged in codons or words of 3 Each c ...
... As tRNA moves the amino acids together, long chains are formed (proteins) There are 20 different amino acids The structure and function of the protein depends upon the amino acids present and the order in which they are attached The base pairs (A, U, C, G) are arranged in codons or words of 3 Each c ...
File
... A build up of waste products can become poisonous, any which remain must be stored in a safe chemical form. Some are changed into insoluble substances like calcium oxalate, oils and alkaloids and kept in living cells. Some oils are used such as citrus oils and pimento, etc. ...
... A build up of waste products can become poisonous, any which remain must be stored in a safe chemical form. Some are changed into insoluble substances like calcium oxalate, oils and alkaloids and kept in living cells. Some oils are used such as citrus oils and pimento, etc. ...
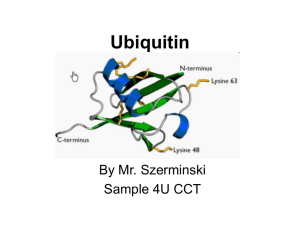
Ubiquitin
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
... Topics to be discussed • General info: - it is a regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotes - one of its functions: it directs protein recycling - can attach to proteins and label them for destruction. - discovery won the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 2004 ...
Chapter 17 Notes
... anticodons with mRNA codons in protein synthesis • The two ribosomal subunits (large and small) are made of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • A ribosome has three binding sites for tRNA – The P site holds the tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide chain – The A site holds the tRNA that carries ...
... anticodons with mRNA codons in protein synthesis • The two ribosomal subunits (large and small) are made of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • A ribosome has three binding sites for tRNA – The P site holds the tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide chain – The A site holds the tRNA that carries ...
Lecture #6
... You will learn to be a retrosynthetic analysis and find the building blocks of these molecules. Outline of this part of module 2 ...
... You will learn to be a retrosynthetic analysis and find the building blocks of these molecules. Outline of this part of module 2 ...
GENE MUTATIONS
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
2. Organic Compounds and the Four Biomolec
... A polypeptide is one linear chain of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides. Proteins also sometimes contain small helper molecules such as heme. After the polypeptides are synthesized by the cell, they spontaneously fold up into a characteristic conformation which allows them t ...
... A polypeptide is one linear chain of amino acids. A protein may contain one or more polypeptides. Proteins also sometimes contain small helper molecules such as heme. After the polypeptides are synthesized by the cell, they spontaneously fold up into a characteristic conformation which allows them t ...
GENE MUTATIONS - mrbemrose / FrontPage
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
... Split this into codons! Thesunwashotbuttheoldmandidnotgethishat. It should look like this... The sun was hot but the old man did not get his hat. What if we added another T at the beginning? T hes unw ash otb utt heo ldm and idn otg eth ish at. ...
Macromolecules Worksheet #2
... group (–COOH), an amine group (–NH2), a hydrogen atom (–H), and a side group that varies depending on the type of amino acid. Twenty common amino acids can combine in various ways to make different protein molecules. The sequence of amino acids in each protein is unique to that protein, so each prot ...
... group (–COOH), an amine group (–NH2), a hydrogen atom (–H), and a side group that varies depending on the type of amino acid. Twenty common amino acids can combine in various ways to make different protein molecules. The sequence of amino acids in each protein is unique to that protein, so each prot ...
Protein Synthesis
... bond between methionine and its tRNA. The tRNA floats away, allowing the ribosome to bind to another tRNA. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, binding new tRNA molecules and amino acids. ...
... bond between methionine and its tRNA. The tRNA floats away, allowing the ribosome to bind to another tRNA. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, binding new tRNA molecules and amino acids. ...
1 Molecular Evolution I: Protein Evolution 1. Protein Evolution We
... than proteins. Thus the vast majority of protein sequences found in current databases, such as GenBank or SwissProt, were not determined by sequencing the amino acids of the proteins, but instead were inferred from DNA sequences using the universal genetic code. Second, protein evolution is typicall ...
... than proteins. Thus the vast majority of protein sequences found in current databases, such as GenBank or SwissProt, were not determined by sequencing the amino acids of the proteins, but instead were inferred from DNA sequences using the universal genetic code. Second, protein evolution is typicall ...
Biological Macromolecules
... organic, meaning they all contain hydrocarbons…Carbon atoms (with attached Hydrogens!) Other elements may include Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur ...
... organic, meaning they all contain hydrocarbons…Carbon atoms (with attached Hydrogens!) Other elements may include Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur ...
DNA Vocabulary Study Option
... the open end to secure and make the flash card that should show the definition on one side and the vocabulary word on the other. ...
... the open end to secure and make the flash card that should show the definition on one side and the vocabulary word on the other. ...
Notes - people.vcu.edu
... Let's summarize the semester up to now: · What determines the form and function of a cell? Protein, mostly through their activity as enzymes. · What is a protein? A protein is a linear array of amino acids, formed through the interactions of the amino acids into a three-dimensional structure. · What ...
... Let's summarize the semester up to now: · What determines the form and function of a cell? Protein, mostly through their activity as enzymes. · What is a protein? A protein is a linear array of amino acids, formed through the interactions of the amino acids into a three-dimensional structure. · What ...
Protein Synthesis
... • The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. The genetic code matches each RNA codon with its amino acid or function. ...
... • The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. The genetic code matches each RNA codon with its amino acid or function. ...
Biochemisty Class notes
... together in a line. Here are two polypeptide chains that are 12 amino acids long. Note however, that they have different primary structures (different sequences of the 20 amino acids). ii. SECONDARY STRUCTURE: since peptide bonds are polar, HBonding routinely occurs between amino acids. Often, this ...
... together in a line. Here are two polypeptide chains that are 12 amino acids long. Note however, that they have different primary structures (different sequences of the 20 amino acids). ii. SECONDARY STRUCTURE: since peptide bonds are polar, HBonding routinely occurs between amino acids. Often, this ...
4.7.08 105 lecture
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase promoter – the genetic information in the DNA that tells where, when, and how much the gene should be expressed. ------------------------------coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the codi ...
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase promoter – the genetic information in the DNA that tells where, when, and how much the gene should be expressed. ------------------------------coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the codi ...
DNA Structure and Function
... 2. A tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid matches up to a complementary triplet on mRNA on the ribosome 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attached to the growing chain of amin ...
... 2. A tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid matches up to a complementary triplet on mRNA on the ribosome 3. The ribosome attaches one amino acid to another as it moves along the mRNA molecule 4. The tRNA molecules are released after the amino acids they carry are attached to the growing chain of amin ...
Molecular Genetics
... The basic building-block of proteins. Each amino acid consists of an acid (carboxyl) and basic (amino) end. It is the joining between acidic and basic ends of adjacent amino acids (condensation) that forms the protein polymer. Where there is not a complete set of chromosomes e.g. 2n – 1, 2n + 1. A g ...
... The basic building-block of proteins. Each amino acid consists of an acid (carboxyl) and basic (amino) end. It is the joining between acidic and basic ends of adjacent amino acids (condensation) that forms the protein polymer. Where there is not a complete set of chromosomes e.g. 2n – 1, 2n + 1. A g ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.