Final Exam - Practice questions for Unit V
... the smaller its radius when on the main sequence. ...
... the smaller its radius when on the main sequence. ...
Sir Isaac Newton
... regions outside the Earth was perfect and eternally unchanging. All objects in the heavens were supposed to be perfect circles, except for stars, which were featureless points of light. ...
... regions outside the Earth was perfect and eternally unchanging. All objects in the heavens were supposed to be perfect circles, except for stars, which were featureless points of light. ...
PSCI 1414 General Astronomy
... Because Mercury and Venus are always observed fairly near the Sun in the sky, their orbits must be smaller than the Earth’s. Planets in such orbits are called inferior planets. The other visible planets (Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) are sometimes seen on the side of the celestial sphere opposite the S ...
... Because Mercury and Venus are always observed fairly near the Sun in the sky, their orbits must be smaller than the Earth’s. Planets in such orbits are called inferior planets. The other visible planets (Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) are sometimes seen on the side of the celestial sphere opposite the S ...
Article on Pluto (for 1st science news)
... region (there are thought to be hundreds of thousands), the astronomical community in the early 1850s demoted Ceres and the others and coined the new term "asteroid." Xena was discovered on January 8, 2005, at Palomar Observatory with the NASA-funded 48-inch Samuel Oschin Telescope. Xena is about 2, ...
... region (there are thought to be hundreds of thousands), the astronomical community in the early 1850s demoted Ceres and the others and coined the new term "asteroid." Xena was discovered on January 8, 2005, at Palomar Observatory with the NASA-funded 48-inch Samuel Oschin Telescope. Xena is about 2, ...
Exoplanet Discovery
... planets (astroseismology) and atmospheric composition – what will we find? ...
... planets (astroseismology) and atmospheric composition – what will we find? ...
PHYS178 2008 week 11 part-1
... (b) A protostar with a surrounding disk of material forms at the centre, accumulating additional material from the molecular cloud through gravitational attraction. (c) A stellar wind breaks out, confined by the disk to flow along the stellar poles. (d) Eventually this wind sweeps away the cloud and ...
... (b) A protostar with a surrounding disk of material forms at the centre, accumulating additional material from the molecular cloud through gravitational attraction. (c) A stellar wind breaks out, confined by the disk to flow along the stellar poles. (d) Eventually this wind sweeps away the cloud and ...
Phys133 SAMPLE questions for MidTerm#1
... 2) What is an astronomical unit? A) the average speed of the earth around the Sun B) any basic unit used in astronomy C) the length of time it takes the earth to revolve around the Sun D) the average distance from the earth to the Sun E) the diameter of the earth's orbit around the Sun ...
... 2) What is an astronomical unit? A) the average speed of the earth around the Sun B) any basic unit used in astronomy C) the length of time it takes the earth to revolve around the Sun D) the average distance from the earth to the Sun E) the diameter of the earth's orbit around the Sun ...
Exoplanet Discoveries and the Fermi Paradox
... continuously habitable zones may be zero width, because the location changes by more than its width as the star heats up. Even if there is a CHZ, it is so close to the star that planets would have tidally locked rotations. This situation is sketched in Figure 5, from Impey19. The tidal lock radius i ...
... continuously habitable zones may be zero width, because the location changes by more than its width as the star heats up. Even if there is a CHZ, it is so close to the star that planets would have tidally locked rotations. This situation is sketched in Figure 5, from Impey19. The tidal lock radius i ...
in the Solar System!
... ROCKY PLANETS (Mercury - Venus - Earth - Mars - Pluto) The rocky planets are mostly made up of rock and metal. These planets are very heavy and move slowly. They also do not have rings and very few moons. ...
... ROCKY PLANETS (Mercury - Venus - Earth - Mars - Pluto) The rocky planets are mostly made up of rock and metal. These planets are very heavy and move slowly. They also do not have rings and very few moons. ...
apparent retrograde motion - Indiana University Astronomy
... Star, made the very short bright circle near the NCP. About 12,000 years ago, the bright star Vega was the North Star, and in about 14,000 years, as the Earth's spin axis slowly continues to precess, Vega will become the North ...
... Star, made the very short bright circle near the NCP. About 12,000 years ago, the bright star Vega was the North Star, and in about 14,000 years, as the Earth's spin axis slowly continues to precess, Vega will become the North ...
Space - SSHS Science 9
... • A lump of rock or metal that is trapped by the Earth’s gravity and pulled down through the Earth’s atmosphere. • As it falls it rubs against the molecules of the air causing friction. This friction causes the meteoroid to become hot and vaporize. • This produces a bright streak across the sky. • I ...
... • A lump of rock or metal that is trapped by the Earth’s gravity and pulled down through the Earth’s atmosphere. • As it falls it rubs against the molecules of the air causing friction. This friction causes the meteoroid to become hot and vaporize. • This produces a bright streak across the sky. • I ...
Chapter 10
... around the Sun once a year. (Heliocentric model) The Earth’s motion around the Sun is relatively recent ...
... around the Sun once a year. (Heliocentric model) The Earth’s motion around the Sun is relatively recent ...
The fantastic journey of that ring on your finger: From
... burst) is such that not only are a multitude of elements heavier than iron produced, but the remaining mass collapses into an object so dense and with such strong gravitational effects that not even light can escape it: a black hole, capable of altering the structure of spacetime. But more to the to ...
... burst) is such that not only are a multitude of elements heavier than iron produced, but the remaining mass collapses into an object so dense and with such strong gravitational effects that not even light can escape it: a black hole, capable of altering the structure of spacetime. But more to the to ...
Venus - Uplift Education
... looks now if the former volcano activities are increased by hundreds of thousands of times. Geologically speaking, Venus' surface is relatively young that seems to have completely reconstructed 300 to 500 million years ago. Volcano activities, deformation of the crust have shaped the surface. At lea ...
... looks now if the former volcano activities are increased by hundreds of thousands of times. Geologically speaking, Venus' surface is relatively young that seems to have completely reconstructed 300 to 500 million years ago. Volcano activities, deformation of the crust have shaped the surface. At lea ...
Astronomy 1001/1005 Midterm (200 points) Name:
... Describe the two most important properties of a telescope. Explain what they mean and why they are important. The most important property of a telescope is its collecting area or the size of its objective lens. The only information we get in astronomy comes from light, so the more light we can colle ...
... Describe the two most important properties of a telescope. Explain what they mean and why they are important. The most important property of a telescope is its collecting area or the size of its objective lens. The only information we get in astronomy comes from light, so the more light we can colle ...
Two new transiting extra-solar planets discovered with SuperWASP
... SOPHIE spectrograph at Haute-Provence, France. These two new planets, of the "hot Jupiter" type, join the very "exclusive club" of extrasolar planets showing transits. More than 200 planets are known today to orbit stars other than the Sun. Among these exoplanets, the search for and study of planets ...
... SOPHIE spectrograph at Haute-Provence, France. These two new planets, of the "hot Jupiter" type, join the very "exclusive club" of extrasolar planets showing transits. More than 200 planets are known today to orbit stars other than the Sun. Among these exoplanets, the search for and study of planets ...
Sorting the Solar System - California Academy of Sciences
... way up to the massive star at its center. Yet it is common for us to think of the Solar System as consisting of the Sun and the planets – a misconception reinforced by the typical depiction of the Solar System as planetary orbits circling the Sun. Other common misconceptions are that there is more t ...
... way up to the massive star at its center. Yet it is common for us to think of the Solar System as consisting of the Sun and the planets – a misconception reinforced by the typical depiction of the Solar System as planetary orbits circling the Sun. Other common misconceptions are that there is more t ...
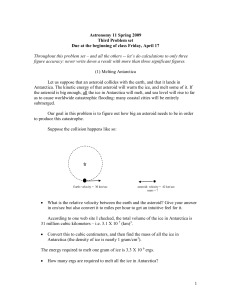
Third problem set
... [Now you can see why finding such planets is so hard: they would be very much fainter than their stars, and they would lie very close to them as seen from here. Any planets that exist would be overwhelmed by the far brighter glare from their stars. NASA’s Terrestrial Planet Finder is a project to cr ...
... [Now you can see why finding such planets is so hard: they would be very much fainter than their stars, and they would lie very close to them as seen from here. Any planets that exist would be overwhelmed by the far brighter glare from their stars. NASA’s Terrestrial Planet Finder is a project to cr ...
CT9
... airless planet of radius R with the escape velocity vesc (meaning the projectile will just barely escape the planet's gravity -- it will assymtotically approach infinite distance and zero speed.) What is the projectile's speed when it is a distance 4R from the planet's center (3R from the surface). ...
... airless planet of radius R with the escape velocity vesc (meaning the projectile will just barely escape the planet's gravity -- it will assymtotically approach infinite distance and zero speed.) What is the projectile's speed when it is a distance 4R from the planet's center (3R from the surface). ...
The Sun and Space Objects
... equator….Spring is March 21st and Fall is September 22nd. (12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of night) 4. The sun is a star that is made up of the 2 gases hydrogen and ________. helium ...
... equator….Spring is March 21st and Fall is September 22nd. (12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of night) 4. The sun is a star that is made up of the 2 gases hydrogen and ________. helium ...
33_drake
... atmosphere. This finally melts ice and converts earth from frozen to very warm. With ice gone, eventually high CO2 in atmosphere recaptured into rocks. ...
... atmosphere. This finally melts ice and converts earth from frozen to very warm. With ice gone, eventually high CO2 in atmosphere recaptured into rocks. ...
Chapter 28.3 Topic questions
... 10. On the H-R diagram what are the stars called that have luminosity greater than red giant stars and their diameters are how much larger than the sun’s? 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The ...
... 10. On the H-R diagram what are the stars called that have luminosity greater than red giant stars and their diameters are how much larger than the sun’s? 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The ...
Today`s Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... orbited, we would feel its motion. In Aristotle’s time, the size of the solar system and distances to stars were assumed to be much, much smaller. Parallax was expected to be seen. ...
... orbited, we would feel its motion. In Aristotle’s time, the size of the solar system and distances to stars were assumed to be much, much smaller. Parallax was expected to be seen. ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.