Perspectives of the Earth, Moon and Sun
... 3. Students know that our solar system consists of one star, eight planets and numerous other smaller objects. (10 mins) The view zooms into our solar system, showing the eight planets, the Sun and the asteroid belt in between the terrestrial planets and the gas giants. Students consider what the Ea ...
... 3. Students know that our solar system consists of one star, eight planets and numerous other smaller objects. (10 mins) The view zooms into our solar system, showing the eight planets, the Sun and the asteroid belt in between the terrestrial planets and the gas giants. Students consider what the Ea ...
Star Jeopardy Review #2
... What is the ejected envelope, often bipolar, of a red giant surrounding a white dwarf ...
... What is the ejected envelope, often bipolar, of a red giant surrounding a white dwarf ...
part 2 - Stardome
... the star can no longer the star This is the point where and d, war out ng iati rad of energy of gravity with the force ire ent the in – the largest explosion explodes in a supernova nts heavier rks the creation of eleme spa on losi exp universe. The supernovae are rs outer layers of these sta than i ...
... the star can no longer the star This is the point where and d, war out ng iati rad of energy of gravity with the force ire ent the in – the largest explosion explodes in a supernova nts heavier rks the creation of eleme spa on losi exp universe. The supernovae are rs outer layers of these sta than i ...
All About Astronomy The Planets
... Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, moons, many dwarf planets (or plutoids), an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, a belt of asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas orbit the sun. The eight planets that ...
... Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, moons, many dwarf planets (or plutoids), an asteroid belt, comets, meteors, and others. The sun is the center of our solar system; the planets, their moons, a belt of asteroids, comets, and other rocks and gas orbit the sun. The eight planets that ...
Astronomy - Dalriada at dalriada.org.uk
... Star clusters are important because they are closely related to each other in space. They probably all formed at about the same time from the same giant molecular cloud, so they should have a similar chemical composition. Because they are relatively closely co-located their relative apparent magnitu ...
... Star clusters are important because they are closely related to each other in space. They probably all formed at about the same time from the same giant molecular cloud, so they should have a similar chemical composition. Because they are relatively closely co-located their relative apparent magnitu ...
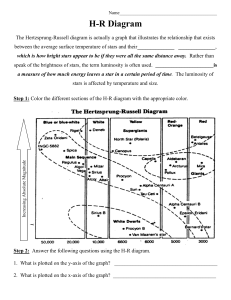
H-R Diagram Student
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
The Origin of Our Solar System
... – Believed force was exerted by contact betwn physical entities and the universe was filled with vortices of “whirling invisible particles.” – Posited that the sun and planets formed when a large vortex contracted and condensed. ...
... – Believed force was exerted by contact betwn physical entities and the universe was filled with vortices of “whirling invisible particles.” – Posited that the sun and planets formed when a large vortex contracted and condensed. ...
Chapter 24 PowerPoint
... approximately 25 times in the last 5 million years. It's been about 740,000 years since the last flip, however, so we're long overdue. There is evidence that we may be heading towards a reversal (the dipole magnetic field is weakening and the higher order terms are increasing), but we can't predict ...
... approximately 25 times in the last 5 million years. It's been about 740,000 years since the last flip, however, so we're long overdue. There is evidence that we may be heading towards a reversal (the dipole magnetic field is weakening and the higher order terms are increasing), but we can't predict ...
Document
... physical reality, have stood the test of time and been shown to have great and general validity ...
... physical reality, have stood the test of time and been shown to have great and general validity ...
Lecture 1 – Astronomy
... The Earth is the largest and the only one with liquid water. Mars is the one most similar to the Earth. Here we find old canyons where water may have flowed. Its polar caps are covered with ice. Several orbiters, landers and robotic rovers have explored Mars in great detail. The ultimate question is ...
... The Earth is the largest and the only one with liquid water. Mars is the one most similar to the Earth. Here we find old canyons where water may have flowed. Its polar caps are covered with ice. Several orbiters, landers and robotic rovers have explored Mars in great detail. The ultimate question is ...
Lecture 2 - The University Centre in Svalbard
... The Earth is the largest and the only one with liquid water. Mars is the one most similar to the Earth. Here we find old canyons where water may have flowed. Its polar caps are covered with ice. Several orbiters, landers and robotic rovers have explored Mars in great detail. The ultimate question is ...
... The Earth is the largest and the only one with liquid water. Mars is the one most similar to the Earth. Here we find old canyons where water may have flowed. Its polar caps are covered with ice. Several orbiters, landers and robotic rovers have explored Mars in great detail. The ultimate question is ...
... 25. As you move across a time zone boundary from East to West you would ? an hour. A.add B.subtract 26. The shape of the orbits of planets around the Sun would best be explained by Newton’s A.First Law of Motion B.Second Law of Motion C.Third Law of Motion D.concept of Centripetal Acceleration E.obs ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF - e
... organic molecules in the Milky Way. The basic idea is that only molecules formed around carbon in combination with water would probably be the basis for life because of the properties and the abundancy of these elements in the universe. For these reasons we will concentrate on water and carbon in di ...
... organic molecules in the Milky Way. The basic idea is that only molecules formed around carbon in combination with water would probably be the basis for life because of the properties and the abundancy of these elements in the universe. For these reasons we will concentrate on water and carbon in di ...
Problem Set No. 5
... A one solar mass star will spend 10 billion years on the main sequence. The universe is only 13-14 billion years old. From the formula T = 1/M 2.5 and the sun’s lifetime, we see that a star of 0.9 solar masses should spend 13 billion years on the main sequence. So no stars of lower mass would have h ...
... A one solar mass star will spend 10 billion years on the main sequence. The universe is only 13-14 billion years old. From the formula T = 1/M 2.5 and the sun’s lifetime, we see that a star of 0.9 solar masses should spend 13 billion years on the main sequence. So no stars of lower mass would have h ...
Intro to Astronomy
... model is called the Big Bang theory. Which states that the universe started from an infinitesimal point that exploded in a huge release of energy and matter 10 to 15 billion years ago. • The study of the origin and changes of the universe is called cosmology. ...
... model is called the Big Bang theory. Which states that the universe started from an infinitesimal point that exploded in a huge release of energy and matter 10 to 15 billion years ago. • The study of the origin and changes of the universe is called cosmology. ...
What would life on other planets be like?
... years ago, you could have access to thousands instant access to of brains worth of information, and accumulate billions of brains’ knowledge. Fast rise of cities, scholarly class, worth of information and technology. ...
... years ago, you could have access to thousands instant access to of brains worth of information, and accumulate billions of brains’ knowledge. Fast rise of cities, scholarly class, worth of information and technology. ...
Astr40 HWIII(new) - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... 17. The closest supernova in 4 centuries is called A. Supernova I. B. Supernova 1987A. C. the Branch Supernova. 18. The Pauli Exclusion principle which says that no two electrons can occupy the same state, means that electrons need a certain amount of space. This is what holds up a White Dwarf again ...
... 17. The closest supernova in 4 centuries is called A. Supernova I. B. Supernova 1987A. C. the Branch Supernova. 18. The Pauli Exclusion principle which says that no two electrons can occupy the same state, means that electrons need a certain amount of space. This is what holds up a White Dwarf again ...
Space – Align the Stars - VUTechieTeacher
... Space – Align the Stars 1. The sun, together with all the planets, asteroids, comets, and meteors that orbit around it, collectively make up our _____________. ...
... Space – Align the Stars 1. The sun, together with all the planets, asteroids, comets, and meteors that orbit around it, collectively make up our _____________. ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... brightness vs spectral type is basically the same as luminosity vs temperature. They found that stars only appear in certain parts of the diagram. ...
... brightness vs spectral type is basically the same as luminosity vs temperature. They found that stars only appear in certain parts of the diagram. ...
Owsley Brown II Portable Planetarium 9
... ● Although active geologic processes, such as plate tectonics and erosion, have destroyed or altered most of the very early rock record on Earth, other objects in the solar system, such as lunar rocks, asteroids, and meteorites, have changed little over billions of years. Studying these objects can ...
... ● Although active geologic processes, such as plate tectonics and erosion, have destroyed or altered most of the very early rock record on Earth, other objects in the solar system, such as lunar rocks, asteroids, and meteorites, have changed little over billions of years. Studying these objects can ...
Midterm 2 - SwRI Boulder
... atmosphere to help hold in heat and it is still possible that slow life living in the cold methane seas could survive. Extra credit: Why have there been so many more missions (and mission attempts) to Mars than to any other planet in the solar system? There are both scientific reasons and engineerin ...
... atmosphere to help hold in heat and it is still possible that slow life living in the cold methane seas could survive. Extra credit: Why have there been so many more missions (and mission attempts) to Mars than to any other planet in the solar system? There are both scientific reasons and engineerin ...
No Slide Title
... • the distance it takes light to travel in one year moving at 186,000 miles per second or about 6 million million miles (6 trillion miles) ...
... • the distance it takes light to travel in one year moving at 186,000 miles per second or about 6 million million miles (6 trillion miles) ...
Star Life Guided Notes
... Small stars last longer (don’t consume fuel as quickly) ____________on HR diagrams. “Burn” ________ for most of their lifetime. ...
... Small stars last longer (don’t consume fuel as quickly) ____________on HR diagrams. “Burn” ________ for most of their lifetime. ...
View/Open - SUNY DSpace
... what’s within it and how it came to be. Depending on a person’s knowledge and or beliefs, how our solar system came to be is debatable. One of the strongest theories on it is called The Solar Nebula Theory; which states our solar system was probably formed out of a spinning ball of gas (Stander). Wh ...
... what’s within it and how it came to be. Depending on a person’s knowledge and or beliefs, how our solar system came to be is debatable. One of the strongest theories on it is called The Solar Nebula Theory; which states our solar system was probably formed out of a spinning ball of gas (Stander). Wh ...
Core Theme 3: The Solar System
... protoplanetary disk from which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed. ...
... protoplanetary disk from which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed. ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.