Solar System PDF - International Science Center
... second -- faster than any other planet. One Mercury solar day equals 175.97 Earth days. Mercury's elliptical orbit takes the small planet as close as 47 million km (29 million miles) and as far as 70 million km (43 million miles) from the sun. Temperatures on Mercury's surface can reach 800 degrees ...
... second -- faster than any other planet. One Mercury solar day equals 175.97 Earth days. Mercury's elliptical orbit takes the small planet as close as 47 million km (29 million miles) and as far as 70 million km (43 million miles) from the sun. Temperatures on Mercury's surface can reach 800 degrees ...
Space Bits: Outer Space Objects
... “Big Bang” caused a rapid expansion of this dense matter. This expansion turned the hot, dense universe into the spread out, cool place that we are now familiar with. The Big Bang was not actually an explosion, as the name seems to suggest. Instead, the Big Bang was simply a very rapid expansion of ...
... “Big Bang” caused a rapid expansion of this dense matter. This expansion turned the hot, dense universe into the spread out, cool place that we are now familiar with. The Big Bang was not actually an explosion, as the name seems to suggest. Instead, the Big Bang was simply a very rapid expansion of ...
The Search for Extrasolar Earth-like Planets
... be oriented to show transits is the ratio of the stellar radius to planet semi-major axis. For Earth and the sun this is 0.5%, meaning that 200 stars with Earthlike planets would have to be monitored to detect one transiting system. Furthermore, one would want to see two or three transits to measure ...
... be oriented to show transits is the ratio of the stellar radius to planet semi-major axis. For Earth and the sun this is 0.5%, meaning that 200 stars with Earthlike planets would have to be monitored to detect one transiting system. Furthermore, one would want to see two or three transits to measure ...
PPT - Yale University
... Gravitational interactions in these larger systems play a major role in the formation of compact objects by transporting angular momentum. The formation of objects like stars and black holes is then a much more complex, dynamic, and chaotic process than in standard models. Gravitational intera ...
... Gravitational interactions in these larger systems play a major role in the formation of compact objects by transporting angular momentum. The formation of objects like stars and black holes is then a much more complex, dynamic, and chaotic process than in standard models. Gravitational intera ...
Solutions
... the energy levels to the ground state. High energy is required to ionize the hydrogen and this energy is supplied by the newly formed OB Association stars that emit most of their energy as high-energy short-wavelength hardUV photons. The photons from the OB Association stars “power up” the HII regio ...
... the energy levels to the ground state. High energy is required to ionize the hydrogen and this energy is supplied by the newly formed OB Association stars that emit most of their energy as high-energy short-wavelength hardUV photons. The photons from the OB Association stars “power up” the HII regio ...
Planets in orbit around planetesimal belts? ββββββββ
... tend to scatter stellar radiation in forward directions and to stay near the orbit of their parent bodies (e.g., Kresák,1976; Bohren and Huffman, 1983). Polarimetric observations of the β Pic debris disk have revealed an effect of strong forward scattering that decreases the degree of linear polari ...
... tend to scatter stellar radiation in forward directions and to stay near the orbit of their parent bodies (e.g., Kresák,1976; Bohren and Huffman, 1983). Polarimetric observations of the β Pic debris disk have revealed an effect of strong forward scattering that decreases the degree of linear polari ...
Comets- Visitors from the Frozen Edge of the Solar System
... just water ice, but also contains the ices of frozen ammonia, carbon dioxide, methane and carbon monoxide. The ices are blackened as they contain small particles of dust (silicate and carbonate minerals) embedded within them, and the whole nucleus is of a low density, suggesting it to be a partiall ...
... just water ice, but also contains the ices of frozen ammonia, carbon dioxide, methane and carbon monoxide. The ices are blackened as they contain small particles of dust (silicate and carbonate minerals) embedded within them, and the whole nucleus is of a low density, suggesting it to be a partiall ...
Week 2
... week later at midnight this same star … A. will be somewhat southwest. B. will again be due south. C. will be somewhat southeast. D. won’t be visible (below the horizon). ...
... week later at midnight this same star … A. will be somewhat southwest. B. will again be due south. C. will be somewhat southeast. D. won’t be visible (below the horizon). ...
Document
... • At least 15% of the stellar mass in the solar neighborhood is in the form of WDs. They are very common, though hard to see. ...
... • At least 15% of the stellar mass in the solar neighborhood is in the form of WDs. They are very common, though hard to see. ...
Information extracted from Britannica 97
... The detection of methane ice on the planet's surface made scientists confident that Pluto had an atmosphere before one was actually discovered. The atmosphere was finally detected in 1988 when Pluto passed in front of a star as observed from the Earth. The light of the star was dimmed before disappe ...
... The detection of methane ice on the planet's surface made scientists confident that Pluto had an atmosphere before one was actually discovered. The atmosphere was finally detected in 1988 when Pluto passed in front of a star as observed from the Earth. The light of the star was dimmed before disappe ...
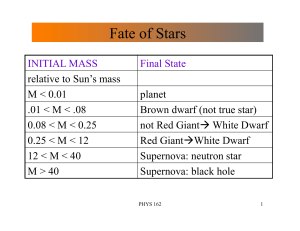
Fate of Stars
... Stars with larger sizes are brighter then a smaller star with the same surface temperature ...
... Stars with larger sizes are brighter then a smaller star with the same surface temperature ...
1. Chapter 10
... The Moon is a place that people have visited and lived on for a few days at a time. We have learned through experiments and observations that the stars are like our Sun, giving off light and heat, but are very far away. Thousands of years ago, what must people have thought when they looked up at the ...
... The Moon is a place that people have visited and lived on for a few days at a time. We have learned through experiments and observations that the stars are like our Sun, giving off light and heat, but are very far away. Thousands of years ago, what must people have thought when they looked up at the ...
Discovering Science through Inquiry: The Solar System
... Background Information for the Teacher Earth is the most unique planet in the solar system for at least two very important reasons. First, it is the only known planet in the universe that supports life. Secondly, it is also the only known planet that has an abundance of water, which is essential for ...
... Background Information for the Teacher Earth is the most unique planet in the solar system for at least two very important reasons. First, it is the only known planet in the universe that supports life. Secondly, it is also the only known planet that has an abundance of water, which is essential for ...
Insights into Bode`s Law
... The matters might have stood there if not for the fact that this object was located at the heliocentric distance as predicted by Bode’s Law. Titus and Bode believed that Piazzi had found and then lost the planet. Thus both Titus and Bode make used of the discovery made by Piazzi and embarked on a jo ...
... The matters might have stood there if not for the fact that this object was located at the heliocentric distance as predicted by Bode’s Law. Titus and Bode believed that Piazzi had found and then lost the planet. Thus both Titus and Bode make used of the discovery made by Piazzi and embarked on a jo ...
pompton lakes high school - Pompton Lakes School District
... Unit 1 – Our Place in the Universe Standard: 5.1 Science Practices: All students will understand that science is both a body of knowledge and an evidence-based, model-building enterprise that continually extends, refines, and revises knowledge. The four Science Practices strands encompass the knowle ...
... Unit 1 – Our Place in the Universe Standard: 5.1 Science Practices: All students will understand that science is both a body of knowledge and an evidence-based, model-building enterprise that continually extends, refines, and revises knowledge. The four Science Practices strands encompass the knowle ...
What makes a planet habitable?
... 20EUV (4.13 Gyr ago): subsolar obstacle distance 12.7REarth N+ion pick up loss rate ~2 ×1030 s-1 Total loss of nitrogen would result in an equivalent amount of ≤ 20 bar during ~ 50 Myr Simulations indicate that the atmosphere should have been protected more efficiently most likely due to higher carb ...
... 20EUV (4.13 Gyr ago): subsolar obstacle distance 12.7REarth N+ion pick up loss rate ~2 ×1030 s-1 Total loss of nitrogen would result in an equivalent amount of ≤ 20 bar during ~ 50 Myr Simulations indicate that the atmosphere should have been protected more efficiently most likely due to higher carb ...
Mystery Detectives_SpaceACedited
... must breathe from air tanks because *F. there is too much oxygen on the surface of the moon.* *G. the moon has little or no atmosphere.* *H. the moon’s atmosphere is thicker than that on the Earth.* *J. the moon’s atmosphere has more carbon dioxide than the Earth’s.* ...
... must breathe from air tanks because *F. there is too much oxygen on the surface of the moon.* *G. the moon has little or no atmosphere.* *H. the moon’s atmosphere is thicker than that on the Earth.* *J. the moon’s atmosphere has more carbon dioxide than the Earth’s.* ...
Smallest Kuiper Belt Object Ever Detected
... The Kuiper belt, a region of small, icy bodies thought to be left over from the formation of the solar system, extends from the orbit of Neptune to more than 5 trillion miles from the Sun. It contains numerous bodies called Kuiper belt objects (KBOs), the most famous being Pluto and its moons. Due t ...
... The Kuiper belt, a region of small, icy bodies thought to be left over from the formation of the solar system, extends from the orbit of Neptune to more than 5 trillion miles from the Sun. It contains numerous bodies called Kuiper belt objects (KBOs), the most famous being Pluto and its moons. Due t ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.