Galactic Evolution:
... • The H flux from HII regions, which are ionized by young and hot stars, under the assumption that such flux is proportional to the SFR • The integrated UBV colors and spectra of galaxies (one can estimate the relative proportions of young and old stars and derive the ratio between the present time ...
... • The H flux from HII regions, which are ionized by young and hot stars, under the assumption that such flux is proportional to the SFR • The integrated UBV colors and spectra of galaxies (one can estimate the relative proportions of young and old stars and derive the ratio between the present time ...
Darwin – A Mission to Detect, and Search for Life on, Extrasolar
... modern astronomy. The detection of planets with a wide range of masses demonstrates that extra-solar planets of low mass exist. In this paper we describe a mission, called Darwin, whose primary goal is the search for, and characterization of, terrestrial extrasolar planets and the search for life. A ...
... modern astronomy. The detection of planets with a wide range of masses demonstrates that extra-solar planets of low mass exist. In this paper we describe a mission, called Darwin, whose primary goal is the search for, and characterization of, terrestrial extrasolar planets and the search for life. A ...
1. - TeacherWeb
... • Stars are powered by nuclear fusion reactions. – The core of a star is extremely hot, extremely dense, and under extreme pressure. – Nuclear fusion takes place in the core of a star. – Fusion combines the nuclei of hydrogen atoms into helium. – When two particles fuse, energy is released. ...
... • Stars are powered by nuclear fusion reactions. – The core of a star is extremely hot, extremely dense, and under extreme pressure. – Nuclear fusion takes place in the core of a star. – Fusion combines the nuclei of hydrogen atoms into helium. – When two particles fuse, energy is released. ...
Dwarf planet Ceres: `A game changer in the solar system`
... Castillo-Rogez pointed out that not only will Dawn reach Ceres in 2015, the European Space Though it would be more challenging to drill into Agency's Rosetta spacecraft will be escorting the than Europa, which boasts an icy surface layer, the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko around the Sun dwarf planet w ...
... Castillo-Rogez pointed out that not only will Dawn reach Ceres in 2015, the European Space Though it would be more challenging to drill into Agency's Rosetta spacecraft will be escorting the than Europa, which boasts an icy surface layer, the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko around the Sun dwarf planet w ...
across
... energy came from gravity- the Sun was converting gravitational energy to heat. Egrav=GMm/R. So as R get smaller, energy can be released. Lord Kelvin estimated the Sun could last 30 million years based on this. ...
... energy came from gravity- the Sun was converting gravitational energy to heat. Egrav=GMm/R. So as R get smaller, energy can be released. Lord Kelvin estimated the Sun could last 30 million years based on this. ...
star - TeacherWeb
... Why do stars shine? • In the main sequence of a stars life, 96-99% of the star’s composition is hydrogen and helium. • Due to the extreme mass of the Sun, within the core of a star, gravitational forces cause nuclear fusion. • Four hydrogen atoms are fused to produce one helium atom. • The remainin ...
... Why do stars shine? • In the main sequence of a stars life, 96-99% of the star’s composition is hydrogen and helium. • Due to the extreme mass of the Sun, within the core of a star, gravitational forces cause nuclear fusion. • Four hydrogen atoms are fused to produce one helium atom. • The remainin ...
Here
... • If the initial mass of the star is more than about 8 solar masses, the core will be too massive to form a white dwarf, since at that stage the gravity is stronger than the electron degeneracy pressure. The collapse continues. • Protons and electrons are fused to form neutrons and neutrinos. The co ...
... • If the initial mass of the star is more than about 8 solar masses, the core will be too massive to form a white dwarf, since at that stage the gravity is stronger than the electron degeneracy pressure. The collapse continues. • Protons and electrons are fused to form neutrons and neutrinos. The co ...
Solar-like oscillations in intermediate red giants
... To see if the star can sustain pulsations one need to evaluate work ontegral, W, which is defined as an increase of the total energy over ...
... To see if the star can sustain pulsations one need to evaluate work ontegral, W, which is defined as an increase of the total energy over ...
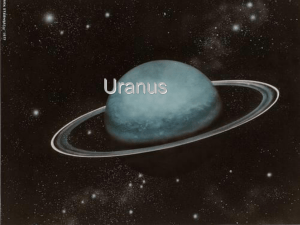
Uranus
... light, giving Uranus its blue-green color. The atmosphere is arranged into clouds running at constant latitudes, similar to the orientation of the more vivid latitudinal bands seen on Jupiter and Saturn. ...
... light, giving Uranus its blue-green color. The atmosphere is arranged into clouds running at constant latitudes, similar to the orientation of the more vivid latitudinal bands seen on Jupiter and Saturn. ...
Slide 1
... • However clumps are rotating suggesting that there are some clumps in the disk in corotation with a planet • Possible 1 or two inner planets in central AU from Radial velocity and proper motion scatter ...
... • However clumps are rotating suggesting that there are some clumps in the disk in corotation with a planet • Possible 1 or two inner planets in central AU from Radial velocity and proper motion scatter ...
CHAPTER XI
... Jupiter is on one side or on the other of the Sun, relatively to the Earth, at the minimum and maximum distance. If the light takes 16 minutes, 34 seconds to traverse the terrestrial orbit, it must take less than that time, or 8 minutes, 17 seconds, to come to us from the Sun, which is situated at ...
... Jupiter is on one side or on the other of the Sun, relatively to the Earth, at the minimum and maximum distance. If the light takes 16 minutes, 34 seconds to traverse the terrestrial orbit, it must take less than that time, or 8 minutes, 17 seconds, to come to us from the Sun, which is situated at ...
jackie822 beanerbutt777 life cycle of a star
... A protostar gets enough mass to ignite fusion. All main sequence stars fuse hydrogen. Stars spend most of their life in the main sequence stage. ...
... A protostar gets enough mass to ignite fusion. All main sequence stars fuse hydrogen. Stars spend most of their life in the main sequence stage. ...
CHP 24
... c. Triton and Nereid are both captured objects from the inner solar system, probably the asteroid belt. d. Triton and Nereid may both have suffered major impacts that radically changed their orbits. e. Triton and Nereid should both have relatively strong magnetic fields. The particles in the rings o ...
... c. Triton and Nereid are both captured objects from the inner solar system, probably the asteroid belt. d. Triton and Nereid may both have suffered major impacts that radically changed their orbits. e. Triton and Nereid should both have relatively strong magnetic fields. The particles in the rings o ...
Chapter 2. Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... Keep a model “Sun” on a table in the center of the lecture area; have your left fist represent Earth, and hold a ball in the other hand to represent the Moon. Then you can show how the Moon orbits your “fist” at an inclination to the ecliptic plane, explaining the meaning of the nodes. You can also ...
... Keep a model “Sun” on a table in the center of the lecture area; have your left fist represent Earth, and hold a ball in the other hand to represent the Moon. Then you can show how the Moon orbits your “fist” at an inclination to the ecliptic plane, explaining the meaning of the nodes. You can also ...
The Planetarium Fleischmann Planetarium
... bright spot was coming from clouds or heat. The Spitzer Space Telescope played a crucial role in answering this question. Like Kepler, Spitzer can fix its gaze at a star system as a planet orbits around the star, gathering clues about the planet's atmosphere. Spitzer's ability to detect infrared lig ...
... bright spot was coming from clouds or heat. The Spitzer Space Telescope played a crucial role in answering this question. Like Kepler, Spitzer can fix its gaze at a star system as a planet orbits around the star, gathering clues about the planet's atmosphere. Spitzer's ability to detect infrared lig ...
ARTICLE A closely packed system of low-mass, low-density planets transiting Kepler-11
... the fraction of transiting planets observed as multiples has implications for the planarity of planetary systems. But few stars have more than one known transiting planet, and none has more than three. Here we report Kepler spacecraft observations of a single Sun-like star, which we call Kepler-11, ...
... the fraction of transiting planets observed as multiples has implications for the planarity of planetary systems. But few stars have more than one known transiting planet, and none has more than three. Here we report Kepler spacecraft observations of a single Sun-like star, which we call Kepler-11, ...
Part I Light, Telescopes, Atoms and Stars
... The Sun The SUN – an average star Like a star- it’s a ball of mainly Hydrogen and Helium gas in a balance between downward gravity and outward pressure It is in the middle of the field in size, temperature, mass and life (compared to other stars – more later!) Spectral Class: G2 ...
... The Sun The SUN – an average star Like a star- it’s a ball of mainly Hydrogen and Helium gas in a balance between downward gravity and outward pressure It is in the middle of the field in size, temperature, mass and life (compared to other stars – more later!) Spectral Class: G2 ...
The Earth, the Sun, and the Constellations of the Zodiac
... constellations is known as the ecliptic, which is the plane defined by Earth’s orbit. The constellations that the ecliptic passes through are the constellations of the zodiac, or simply, “the zodiac.” For thousands of years, people all over the world have paid attention to the Sun’s path through th ...
... constellations is known as the ecliptic, which is the plane defined by Earth’s orbit. The constellations that the ecliptic passes through are the constellations of the zodiac, or simply, “the zodiac.” For thousands of years, people all over the world have paid attention to the Sun’s path through th ...
ph507rev1
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
The Sun and the Stars
... If at the end of -process,core mass exceeds 1.4Msun (Chandrasekhar limit), electron degeneracy pressure can no longer support star and core collapses (1~sec). When T> 6x109K, photodisintegration occurs ...
... If at the end of -process,core mass exceeds 1.4Msun (Chandrasekhar limit), electron degeneracy pressure can no longer support star and core collapses (1~sec). When T> 6x109K, photodisintegration occurs ...
Chap4-Timing
... Fate of planetary systems during the red giant phase. All planets within the final extent of the red giant envelope will be engulfed and migrate inwards. Planets further out will have greater chance of survival, migrating outwards as mass is lost from central star. In mass is loss instantane ...
... Fate of planetary systems during the red giant phase. All planets within the final extent of the red giant envelope will be engulfed and migrate inwards. Planets further out will have greater chance of survival, migrating outwards as mass is lost from central star. In mass is loss instantane ...
The Birth of Stars Guiding Questions • Because stars shine by
... • The most massive protostars to form out of a dark nebula rapidly become main sequence O and B stars • They emit strong ultraviolet radiation that ionizes hydrogen in the surrounding cloud, thus creating the reddish emission nebulae called H II regions • Ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from ...
... • The most massive protostars to form out of a dark nebula rapidly become main sequence O and B stars • They emit strong ultraviolet radiation that ionizes hydrogen in the surrounding cloud, thus creating the reddish emission nebulae called H II regions • Ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from ...
The Birth of Stars
... of the Galaxy Clouds within the interstellar medium are called nebulae Dark nebulae are so dense that they are opaque – They appear as dark blots against a background of distant stars ...
... of the Galaxy Clouds within the interstellar medium are called nebulae Dark nebulae are so dense that they are opaque – They appear as dark blots against a background of distant stars ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.