Formation of the Solar System
... Radiation pressure: Photons act like particles and push whatever particles and dust they run into. ...
... Radiation pressure: Photons act like particles and push whatever particles and dust they run into. ...
Day-37
... and differentiation. These are called regular moons. They revolve around their planets in the same direction that they rotate. Almost all are tidally locked, meaning one hemisphere always faces the planet the moon is orbiting. ...
... and differentiation. These are called regular moons. They revolve around their planets in the same direction that they rotate. Almost all are tidally locked, meaning one hemisphere always faces the planet the moon is orbiting. ...
Chapter 26
... Gives off energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation 2. The sun’s energy is produced in its central region by the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. 3. Been a stable energy source for billions of years. 4. The sun remains stable because the inward pull of gravity balances outward pus ...
... Gives off energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation 2. The sun’s energy is produced in its central region by the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. 3. Been a stable energy source for billions of years. 4. The sun remains stable because the inward pull of gravity balances outward pus ...
Here
... • But then there were the 5 “planets”: These are star-like objects that move through the constellations. Mercury: the “fastest” planet, always near the Sun. Venus: the brightest planet, always near the Sun. Mars: the red planet, “slower” than Venus. Jupiter: the second brightest planet, “s ...
... • But then there were the 5 “planets”: These are star-like objects that move through the constellations. Mercury: the “fastest” planet, always near the Sun. Venus: the brightest planet, always near the Sun. Mars: the red planet, “slower” than Venus. Jupiter: the second brightest planet, “s ...
I. Layers of the Sun
... 99% of all the matter in our solar system is in the sun. The sun is the center of the solar system. The sun is a main-sequence star. The sun produces energy by fusion. 75% Hydrogen and 25% Helium fuse in the core. Fusing means two atoms combine to form a heavier atom. ...
... 99% of all the matter in our solar system is in the sun. The sun is the center of the solar system. The sun is a main-sequence star. The sun produces energy by fusion. 75% Hydrogen and 25% Helium fuse in the core. Fusing means two atoms combine to form a heavier atom. ...
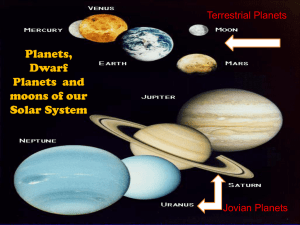
dwarf planets
... • A minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is neither a dominant planet nor originally classified as a comet. • Minor planets can be dwarf planets, asteroids, trojans, centaurs, Kuiper belt objects, and other trans-Neptunian objects.[1] • The first minor planet di ...
... • A minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is neither a dominant planet nor originally classified as a comet. • Minor planets can be dwarf planets, asteroids, trojans, centaurs, Kuiper belt objects, and other trans-Neptunian objects.[1] • The first minor planet di ...
Topic 3 – Waves and the Universe
... Stars with considerably more mass than the Sun are hotter and brighter The fusion reactions in a massive star’s core happen at a faster ratestable main sequence is shorter than in smaller stars Once hydrogen runs out and the core cools, massive stars become red supergiants At the end of the supergi ...
... Stars with considerably more mass than the Sun are hotter and brighter The fusion reactions in a massive star’s core happen at a faster ratestable main sequence is shorter than in smaller stars Once hydrogen runs out and the core cools, massive stars become red supergiants At the end of the supergi ...
Topic 3 notes - WordPress.com
... Stars with considerably more mass than the Sun are hotter and brighter The fusion reactions in a massive star’s core happen at a faster ratestable main sequence is shorter than in smaller stars Once hydrogen runs out and the core cools, massive stars become red supergiants At the end of the supergi ...
... Stars with considerably more mass than the Sun are hotter and brighter The fusion reactions in a massive star’s core happen at a faster ratestable main sequence is shorter than in smaller stars Once hydrogen runs out and the core cools, massive stars become red supergiants At the end of the supergi ...
exam_1spring_02 - University of Maryland Astronomy
... A. The Sun's magnetic field attracted all of the iron in the nebula toward the inner solar system. B. The forming sun's heat prevented other substances such as ices to condense near it. C. The planets that today are far from the Sun were captured. D. The planets that today are near the Sun were capt ...
... A. The Sun's magnetic field attracted all of the iron in the nebula toward the inner solar system. B. The forming sun's heat prevented other substances such as ices to condense near it. C. The planets that today are far from the Sun were captured. D. The planets that today are near the Sun were capt ...
spring_2002_final - University of Maryland Astronomy
... C. using its angular size and distance from Earth. D. using data from spacecraft flybys. E. by measuring the time that it takes for the Red Spot to disappear from view. 49. If you were thrown onto the Martian surface near the equator without a spacesuit, what would be the most likely cause of your d ...
... C. using its angular size and distance from Earth. D. using data from spacecraft flybys. E. by measuring the time that it takes for the Red Spot to disappear from view. 49. If you were thrown onto the Martian surface near the equator without a spacesuit, what would be the most likely cause of your d ...
File
... d. all of the above e. none of the above 18. When the moon is directly between Earth and the sun, it is called a a. crescent moon b. full moon c. gibbous moon d. new moon 19. A moon that is larger than a semi-circle but not a complete circle of light, it is a a. crescent moon b. new moon c. three-q ...
... d. all of the above e. none of the above 18. When the moon is directly between Earth and the sun, it is called a a. crescent moon b. full moon c. gibbous moon d. new moon 19. A moon that is larger than a semi-circle but not a complete circle of light, it is a a. crescent moon b. new moon c. three-q ...
ASTRO OTTER (for secondary students)
... This lesson covers many important topics including the Copernican Heliocentric model of the solar system. Details are given about observations that Galileo made that supported this scientific model of the solar system. This presentation also discusses the Sun's orbit around the center of the Milky W ...
... This lesson covers many important topics including the Copernican Heliocentric model of the solar system. Details are given about observations that Galileo made that supported this scientific model of the solar system. This presentation also discusses the Sun's orbit around the center of the Milky W ...
Life Cycle of a Star Notes
... It will eventually collapse and explode. Its fate is determined by the original mass of the star; it will become a brown dwarf (or black dwarf), neutron star, or black hole. HT Stars glow because of a nuclear fusion reaction whereby hydrogen fuses together to form heavier elements such as helium and ...
... It will eventually collapse and explode. Its fate is determined by the original mass of the star; it will become a brown dwarf (or black dwarf), neutron star, or black hole. HT Stars glow because of a nuclear fusion reaction whereby hydrogen fuses together to form heavier elements such as helium and ...
Announcements Ancient astronomers: Why did they do it? Why did
... Many observations (with the new-fangled invention called the telescope showed that the heavens are far from perfect (e.g., spots on the Sun, jagged mountains and valleys on the Moon) The Milky Way indicated that stars are far more numerous than thought, and probably much more distant than appreciate ...
... Many observations (with the new-fangled invention called the telescope showed that the heavens are far from perfect (e.g., spots on the Sun, jagged mountains and valleys on the Moon) The Milky Way indicated that stars are far more numerous than thought, and probably much more distant than appreciate ...
Lesson 28 - Purdue Math
... Finally Kepler (1571-1630) is credited with discovering that the planets revolve in elliptical orbits about the sun. He wrote 3 laws of planetary motion. The first law states: The orbit of each planet in the solar system is an ellipse with the sun as one focus. (The sun is not at the center or an or ...
... Finally Kepler (1571-1630) is credited with discovering that the planets revolve in elliptical orbits about the sun. He wrote 3 laws of planetary motion. The first law states: The orbit of each planet in the solar system is an ellipse with the sun as one focus. (The sun is not at the center or an or ...
Applications of Light to Astronomy
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
The Universe in a Day - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... Looking to the future, we can expect the Universe of stars to go on for at least another millennium (using the same time compression factor). After that, there are other ages of the Universe (not dominated by stars), which grow colder and more bizarre, and take place on astronomical timescales… ...
... Looking to the future, we can expect the Universe of stars to go on for at least another millennium (using the same time compression factor). After that, there are other ages of the Universe (not dominated by stars), which grow colder and more bizarre, and take place on astronomical timescales… ...
Round 1
... $1600 This tells you how much energy is released in the fusion of hydrogen to helium. (E = ∆mc2 where ∆m is the mass difference between the input H’s and output He’s.) $2000 Stars are in hydrostatic equilibrium, which means that this supports them against gravitational collapse. (thermal pressure du ...
... $1600 This tells you how much energy is released in the fusion of hydrogen to helium. (E = ∆mc2 where ∆m is the mass difference between the input H’s and output He’s.) $2000 Stars are in hydrostatic equilibrium, which means that this supports them against gravitational collapse. (thermal pressure du ...
Motions of the Night Sky - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... North Celestial Pole, earth’s axis of rotation projected out into space. Here’s a surprising observation: for a given star to travel from a set spot in the sky (let’s say on the meridian) to the exact same spot the next night doesn’t take 24 hours, but only 23 hours and 56 minutes. What happened t ...
... North Celestial Pole, earth’s axis of rotation projected out into space. Here’s a surprising observation: for a given star to travel from a set spot in the sky (let’s say on the meridian) to the exact same spot the next night doesn’t take 24 hours, but only 23 hours and 56 minutes. What happened t ...
WORD - UWL faculty websites
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
What is a Planet
... Revolution= 248.6 years Gravity- 1/8 that of Earth Orbit- Pluto has a more elliptical and titled orbit, one of the reasons its lost identification as a planet. This tilted orbit sometimes allows it to be closer to the sun than Neptune, making Neptune the further most planet. Eccentricity: .25 ...
... Revolution= 248.6 years Gravity- 1/8 that of Earth Orbit- Pluto has a more elliptical and titled orbit, one of the reasons its lost identification as a planet. This tilted orbit sometimes allows it to be closer to the sun than Neptune, making Neptune the further most planet. Eccentricity: .25 ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.