Planets - learnfactsquick.com
... mass: 3.30e23 kg In Roman mythology Mercury is the god of commerce, travel and thievery, the Roman counterpart of the Greek god Hermes, the messenger of the Gods. The planet probably received this name because it moves so quickly across the sky. Mercury has been known since at least the time of the ...
... mass: 3.30e23 kg In Roman mythology Mercury is the god of commerce, travel and thievery, the Roman counterpart of the Greek god Hermes, the messenger of the Gods. The planet probably received this name because it moves so quickly across the sky. Mercury has been known since at least the time of the ...
Formation of the Solar System Section 28.1
... Newton determined that each planet orbits a point between it and the Sun called the center of mass. Just as the balance point on a seesaw is closer to the heavier box, the center of mass between two orbiting bodies is closer to the more massive body. ...
... Newton determined that each planet orbits a point between it and the Sun called the center of mass. Just as the balance point on a seesaw is closer to the heavier box, the center of mass between two orbiting bodies is closer to the more massive body. ...
Review Astronomy - Cowley`s Earth Systems
... energy into space. Later, Edwin Hubble discovered that the speed of a galaxy moving away from Earth was proportional to its distance. This relation was predicted by Lemaitre’s theory. Then, in 1964, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discovered the cosmic background radiation, which was also predicted b ...
... energy into space. Later, Edwin Hubble discovered that the speed of a galaxy moving away from Earth was proportional to its distance. This relation was predicted by Lemaitre’s theory. Then, in 1964, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discovered the cosmic background radiation, which was also predicted b ...
Sky Science
... The Earth has only one NATURAL SATELITE which is called the moon. We only see the moon because the sun illuminates it and makes it shine brightly in the sky. Without the reflected light, the moon is a black chunk of rock orbiting our planet. The moon takes approximately 28 days to complete a counter ...
... The Earth has only one NATURAL SATELITE which is called the moon. We only see the moon because the sun illuminates it and makes it shine brightly in the sky. Without the reflected light, the moon is a black chunk of rock orbiting our planet. The moon takes approximately 28 days to complete a counter ...
Eratosthenes - Allendale School
... Earth in very reliable circles, the planets appeared to wander about the sky. Note: The planets past Saturn were unknown at this time in history.) This is because Earth in its orbit sometimes passes up the slower moving, farther planets, which also have a longer path to travel. Venus and Mercury, cl ...
... Earth in very reliable circles, the planets appeared to wander about the sky. Note: The planets past Saturn were unknown at this time in history.) This is because Earth in its orbit sometimes passes up the slower moving, farther planets, which also have a longer path to travel. Venus and Mercury, cl ...
word
... the Sun. Thereby the apparent brightness depends on their size as well as on the surface reflectivity. Latter is known to vary between 4% for most comets to over 50% for Pluto, which makes any accurate size determination from the optical light alone impossible. The Bonn group therefore used the IRAM ...
... the Sun. Thereby the apparent brightness depends on their size as well as on the surface reflectivity. Latter is known to vary between 4% for most comets to over 50% for Pluto, which makes any accurate size determination from the optical light alone impossible. The Bonn group therefore used the IRAM ...
Astronomy NJASK REview Packet
... Astronomy NJASK Review Multiple Choice (1-25): Circle the best answer for each question below. ...
... Astronomy NJASK Review Multiple Choice (1-25): Circle the best answer for each question below. ...
Pretest
... than low beams do. Also, the closer an oncoming car is to you, the greater the apparent brightness of its headlights (on low or high). 21. Low-mass stars have longer lifetimes than do high-mass stars because low-mass stars use up their fuel much more slowly. 22. Because of high temperatures in the i ...
... than low beams do. Also, the closer an oncoming car is to you, the greater the apparent brightness of its headlights (on low or high). 21. Low-mass stars have longer lifetimes than do high-mass stars because low-mass stars use up their fuel much more slowly. 22. Because of high temperatures in the i ...
Pre SS1 Models of the Solar System - Bolinas
... the apparent brightness of stars along the zodiac; in summer, for instance, when the Earth is on the side of its orbit closer to the star Spica, its proximity would make Spica look brighter than it does in winter, when the Earth is on the far side of its orbit. As no such phenomenon is observed, the ...
... the apparent brightness of stars along the zodiac; in summer, for instance, when the Earth is on the side of its orbit closer to the star Spica, its proximity would make Spica look brighter than it does in winter, when the Earth is on the far side of its orbit. As no such phenomenon is observed, the ...
Ay123 Fall 2011 STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION Problem Set 3
... to argue that the Rosseland mean opacity is largely determined by κν when the frequency ν is a few times kT /h. (iv) Thus show that the Rosseland mean opacity for free-free absorption obeys Kramers law where κ ∝ ρT −3.5 . ...
... to argue that the Rosseland mean opacity is largely determined by κν when the frequency ν is a few times kT /h. (iv) Thus show that the Rosseland mean opacity for free-free absorption obeys Kramers law where κ ∝ ρT −3.5 . ...
10 relativity, black holes_
... and the object you want to escape! For a black hole, the escape velocity (inside the event horizon) is greater than the speed of light! ...
... and the object you want to escape! For a black hole, the escape velocity (inside the event horizon) is greater than the speed of light! ...
Lecture 1 Coordinate Systems - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... Einstein’s theory: space-time is warped … light will be deflected ...
... Einstein’s theory: space-time is warped … light will be deflected ...
Probing the Edge of the Solar System: Formation of
... from the center One of 200 billion stars in our Galaxy ...
... from the center One of 200 billion stars in our Galaxy ...
mayreview3
... • Describe the inferred internal structure. • What is at the core? Site evidence for inference. ...
... • Describe the inferred internal structure. • What is at the core? Site evidence for inference. ...
PDF 630 kB - Prague Relativistic Astrophysics
... of the comet’s original crust. Long-period comets have just recently returned from cold storage in the Oort cloud and are still covered by a crust that resulted from 4.5 billion years of exposure to cosmic rays. When the comet returns to the inner solar system, that crust is crumbled and creates pec ...
... of the comet’s original crust. Long-period comets have just recently returned from cold storage in the Oort cloud and are still covered by a crust that resulted from 4.5 billion years of exposure to cosmic rays. When the comet returns to the inner solar system, that crust is crumbled and creates pec ...
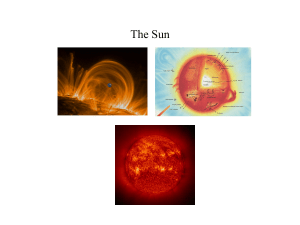
The Sun
... By observing sunspots, scientists have learned that the sun rotates. Sunspots appear to move across the face of the sun. This is because the sun rotates on its axis. But it rotates faster at its equator than it does at the poles. This is called differential rotation. It rotates once every 27 days at ...
... By observing sunspots, scientists have learned that the sun rotates. Sunspots appear to move across the face of the sun. This is because the sun rotates on its axis. But it rotates faster at its equator than it does at the poles. This is called differential rotation. It rotates once every 27 days at ...
Can We Make A Star?
... • Fist we need to get a hold of a lot of helium and hydrogen • Then we need to get the mass of gas to move so that the gasses will react with each other • Then we just sit way back and wait until the gasses explode into a fireball ...
... • Fist we need to get a hold of a lot of helium and hydrogen • Then we need to get the mass of gas to move so that the gasses will react with each other • Then we just sit way back and wait until the gasses explode into a fireball ...
The Solar System
... the solar system planets in our solar system pictures - our solar system includes the sun and the planetary system revolving around it a planetary system is a group of non stellar objects planets dwar, the solar system astronomy for kids kidsastronomy com - our solar neighborhood is an exciting plac ...
... the solar system planets in our solar system pictures - our solar system includes the sun and the planetary system revolving around it a planetary system is a group of non stellar objects planets dwar, the solar system astronomy for kids kidsastronomy com - our solar neighborhood is an exciting plac ...
Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
... R* rate of star formation Pp probability of having planets Pe probability that ecozone lasts long enough N e number of planets in ecozone PL probability that life will arise PI probability that intelligence will arise ...
... R* rate of star formation Pp probability of having planets Pe probability that ecozone lasts long enough N e number of planets in ecozone PL probability that life will arise PI probability that intelligence will arise ...
ppt - University of Waterloo
... •Although astronomy has been practiced for thousands of years, it consisted mostly of observing and cataloguing the motions of stars. •The use of spectroscopy to determine the properties of stars (c.a. 1814) allowed astronomers to investigate the the stars scientifically. ...
... •Although astronomy has been practiced for thousands of years, it consisted mostly of observing and cataloguing the motions of stars. •The use of spectroscopy to determine the properties of stars (c.a. 1814) allowed astronomers to investigate the the stars scientifically. ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.