Third Grade Science
... • Describe our solar system as a collection of nine planets, moons, and numerous other objects (such as asteroids and comets) with the sun at its center • State that the force of gravity keeps the planets in orbit around the sun • Name the planets in our solar system in order starting with the pl ...
... • Describe our solar system as a collection of nine planets, moons, and numerous other objects (such as asteroids and comets) with the sun at its center • State that the force of gravity keeps the planets in orbit around the sun • Name the planets in our solar system in order starting with the pl ...
Aug 2015 supplement - Hermanus Astronomy
... Astronomers trained ALMA on galaxies that were known to be seen only about 800 million years after the Big Bang. They were not looking for the light from stars, but instead for the faint glow of ionized carbon coming from the clouds of gas from which the stars were forming. They wanted to study the ...
... Astronomers trained ALMA on galaxies that were known to be seen only about 800 million years after the Big Bang. They were not looking for the light from stars, but instead for the faint glow of ionized carbon coming from the clouds of gas from which the stars were forming. They wanted to study the ...
solar system-where are we? - Iowa State University Extension and
... Balls or drawings labeled “Sun, Moon, Venus, Mercury, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto What you do: Give each child a planet or sun or moon. (This works great if you only have 11 children! If you have fewer children you can place the extra planets on the floor-more children-j ...
... Balls or drawings labeled “Sun, Moon, Venus, Mercury, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto What you do: Give each child a planet or sun or moon. (This works great if you only have 11 children! If you have fewer children you can place the extra planets on the floor-more children-j ...
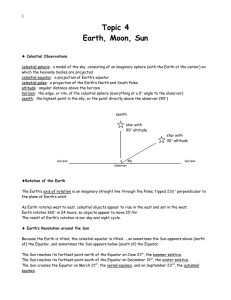
Topic 4: Earth-Moon-Sun
... Because its period of rotation equals its period of revolution, there is only one side of the Moon always seen from Earth. Moon phases are the changing appearances of the Moon as seen from Earth, caused by the Moon’s revolution around the Earth. The period between one cycle of phases = 29½ days, whi ...
... Because its period of rotation equals its period of revolution, there is only one side of the Moon always seen from Earth. Moon phases are the changing appearances of the Moon as seen from Earth, caused by the Moon’s revolution around the Earth. The period between one cycle of phases = 29½ days, whi ...
wk02noQ
... 3. The Sun orbits in the Milky Way The sun (and nearby stars) orbit the center of the Milky Way once per 230,000,000 years. How do we know? (motion of other stars in the Milky Way wrt the Sun; careful study of stellar positions over time) ...
... 3. The Sun orbits in the Milky Way The sun (and nearby stars) orbit the center of the Milky Way once per 230,000,000 years. How do we know? (motion of other stars in the Milky Way wrt the Sun; careful study of stellar positions over time) ...
Big Bang
... • Before a time classified as a Planck time, all of the four fundamental forces are presumed to have been unified into one force. • All matter, energy, space and time are presumed to have exploded outward from the original ...
... • Before a time classified as a Planck time, all of the four fundamental forces are presumed to have been unified into one force. • All matter, energy, space and time are presumed to have exploded outward from the original ...
Seasons:
... Since we are on Earth, we do not perceive the Earth moving. Instead, it appears the sun moves. It appears to travel up and down along the celestial sphere on the ecliptic. During summer, we get more direct sunlight, so the sun appears to be higher in the sky. During winder, we get less direct sunlig ...
... Since we are on Earth, we do not perceive the Earth moving. Instead, it appears the sun moves. It appears to travel up and down along the celestial sphere on the ecliptic. During summer, we get more direct sunlight, so the sun appears to be higher in the sky. During winder, we get less direct sunlig ...
Stars and Galaxies
... 54. Nebula comes from __________________ that was once in stars. 55. Stars eject lots of ________________ during their lifetime. 56. The matter in stars is __________________ many times. 57. Our sun has iron and carbon according to its _____________________; it is too young to have produced it, so i ...
... 54. Nebula comes from __________________ that was once in stars. 55. Stars eject lots of ________________ during their lifetime. 56. The matter in stars is __________________ many times. 57. Our sun has iron and carbon according to its _____________________; it is too young to have produced it, so i ...
P. LeClair - The University of Alabama
... 2. The following class, you will turn in the one problem the instructor requests. 3. Only the chosen problem for the day is graded. 4. Please follow the homework template provided. 5. You may collaborate, but everyone must turn in their own work. Problems for 9 June (due 10 June) 1. On a frictionles ...
... 2. The following class, you will turn in the one problem the instructor requests. 3. Only the chosen problem for the day is graded. 4. Please follow the homework template provided. 5. You may collaborate, but everyone must turn in their own work. Problems for 9 June (due 10 June) 1. On a frictionles ...
File - Mr. Wadnizak
... Gravity works on all objects that have mass. They are attracted to each other according to their masses and the distance between them. It is hard to feel this force unless the object is the size of a planet. ...
... Gravity works on all objects that have mass. They are attracted to each other according to their masses and the distance between them. It is hard to feel this force unless the object is the size of a planet. ...
April 2015 - Astronomical Society of Northern New England
... April 12. Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space on this day in 1961. April 16. Wilbur Wright was born on this day in 1867. It was only 66 years after the Wright Brother’s made their first very tentative powered flight in 1903 that we traveled all the way to the moon. April 18. New moon is tod ...
... April 12. Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space on this day in 1961. April 16. Wilbur Wright was born on this day in 1867. It was only 66 years after the Wright Brother’s made their first very tentative powered flight in 1903 that we traveled all the way to the moon. April 18. New moon is tod ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe
... in the local Solar neighborhood… • typical relative speeds of more than 70,000 km/hr • but stars are so far away that we cannot easily notice ...
... in the local Solar neighborhood… • typical relative speeds of more than 70,000 km/hr • but stars are so far away that we cannot easily notice ...
The Solar System
... •Comet-like composition (ices, rock) •Comet-like orbit (eccentric, highly inclined to ecliptic plane). •Charon is half Pluto’s diameter Fall, 2005 ...
... •Comet-like composition (ices, rock) •Comet-like orbit (eccentric, highly inclined to ecliptic plane). •Charon is half Pluto’s diameter Fall, 2005 ...
Module P1 - The Earth in the universe
... [Possible alternative approach is looking at the historical development of the understanding of the solar system.] ...
... [Possible alternative approach is looking at the historical development of the understanding of the solar system.] ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 12. Define circumpolar star and find the condition for any star to be circumpolar. 13. Define sidereal time ‘t’ and prove that sidereal time is equal to the R.A. ± Hour angle of a star. 14. Find roughly the distance of a star whose parallax is 0.5” given that parallax of the sun is 9” and the earth’ ...
... 12. Define circumpolar star and find the condition for any star to be circumpolar. 13. Define sidereal time ‘t’ and prove that sidereal time is equal to the R.A. ± Hour angle of a star. 14. Find roughly the distance of a star whose parallax is 0.5” given that parallax of the sun is 9” and the earth’ ...
On the hunt for a mystery planet
... and dust that swirled around the newborn Sun 4.6 billion years ago. But Sedna and other objects beyond the main Kuiper belt probably weren’t born where they are today, because there simply wasn’t enough gas and dust available at those great distances to create sizeable worlds. One idea is that they ...
... and dust that swirled around the newborn Sun 4.6 billion years ago. But Sedna and other objects beyond the main Kuiper belt probably weren’t born where they are today, because there simply wasn’t enough gas and dust available at those great distances to create sizeable worlds. One idea is that they ...
SECTION28.1 Formation of the Solar System
... confirmed by other astronomers. • From 1576–1601, before the telescope was used in astronomy, Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer, made accurate observations to within a half arc minute of the planets’ ...
... confirmed by other astronomers. • From 1576–1601, before the telescope was used in astronomy, Tycho Brahe, a Danish astronomer, made accurate observations to within a half arc minute of the planets’ ...
The Pennsylvanian Period in Alabama: Looking Up Astronomy and
... one must observe it with telescopes sensitive to longer wavelengths of light. The Galactic center is important because all objects in the disk of the Milky Way rotate around that point. If the Milky Way could be seen from the outside, it might resemble the galaxy shown in Fig. 8.2, bottom., known as ...
... one must observe it with telescopes sensitive to longer wavelengths of light. The Galactic center is important because all objects in the disk of the Milky Way rotate around that point. If the Milky Way could be seen from the outside, it might resemble the galaxy shown in Fig. 8.2, bottom., known as ...
Chapter 8: The Pennsylvanian Period in Alabama: Looking Up
... past. Both also involve processes that occur over time-spans much longer than a human lifetime. Walking the rock piles of the Minkin Paleozoic Footprint site, and seeing fossils of animals or plants that lived hundreds of millions of years ago, is like looking at a galaxy hundreds of millions of lig ...
... past. Both also involve processes that occur over time-spans much longer than a human lifetime. Walking the rock piles of the Minkin Paleozoic Footprint site, and seeing fossils of animals or plants that lived hundreds of millions of years ago, is like looking at a galaxy hundreds of millions of lig ...
Death by Black Hole Study Guide-Answers - crespiphysics
... 3. What evidence did Galileo cite for a Sun centered universe? Venus has phases; Jupiter has 4 large moons that orbit it 4. Describe how Harlow Shapely used the distribution of globular clusters to determine we were not at the center of the Milky Way (or universe). He observed they were not evenly d ...
... 3. What evidence did Galileo cite for a Sun centered universe? Venus has phases; Jupiter has 4 large moons that orbit it 4. Describe how Harlow Shapely used the distribution of globular clusters to determine we were not at the center of the Milky Way (or universe). He observed they were not evenly d ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.