Chapter 2
... • Inferior planets never too far from Sun • Superior planets not tied to Sun; exhibit retrograde motion ...
... • Inferior planets never too far from Sun • Superior planets not tied to Sun; exhibit retrograde motion ...
empower-maine-grade7-reading-practice-test
... 16 At the time of the ruling, the IAU noted that the new definition does not apply to anything outside the solar system, leaving it unclear how the organization defines the planetary objects found orbiting other stars. ...
... 16 At the time of the ruling, the IAU noted that the new definition does not apply to anything outside the solar system, leaving it unclear how the organization defines the planetary objects found orbiting other stars. ...
PLANETS
... transit across its surface from the perspective of Earth (1.7% dimming). Subsequent spectroscopic studies with the Hubble Space Telescope have even indicated that the exoplanet's atmosphere must have sodium vapor in it. The planet of HD 209458, unofficially named Osiris, is so close to its star that ...
... transit across its surface from the perspective of Earth (1.7% dimming). Subsequent spectroscopic studies with the Hubble Space Telescope have even indicated that the exoplanet's atmosphere must have sodium vapor in it. The planet of HD 209458, unofficially named Osiris, is so close to its star that ...
Why Pluto is No Longer a Planet
... Over the last few decades, powerful new ground and space-based observatories have completely changed previous understanding of the outer Solar System. Instead of being the only planet in its region, like the rest of the Solar System, Pluto and its moons are now known to be just a large example of a ...
... Over the last few decades, powerful new ground and space-based observatories have completely changed previous understanding of the outer Solar System. Instead of being the only planet in its region, like the rest of the Solar System, Pluto and its moons are now known to be just a large example of a ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... dark nebula rapidly become main sequence O and B stars • They emit strong ultraviolet radiation that ionizes hydrogen in the surrounding cloud, thus creating the reddish emission nebulae called H II regions • Ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from the O and B stars at the core of an H II regio ...
... dark nebula rapidly become main sequence O and B stars • They emit strong ultraviolet radiation that ionizes hydrogen in the surrounding cloud, thus creating the reddish emission nebulae called H II regions • Ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from the O and B stars at the core of an H II regio ...
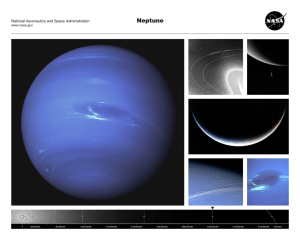
Neptune - TeacherLINK
... cause the observed changes to Uranus’ orbit. After being ignored by French astronomers, Le Verrier sent his predictions to Johann Gottfried Galle at the Berlin Observatory, who found Neptune on his first night of searching in 1846. Seventeen days later, its larg est moon, Triton, was also discovered. ...
... cause the observed changes to Uranus’ orbit. After being ignored by French astronomers, Le Verrier sent his predictions to Johann Gottfried Galle at the Berlin Observatory, who found Neptune on his first night of searching in 1846. Seventeen days later, its larg est moon, Triton, was also discovered. ...
Cairo Governorate Helwan Education Zone El
... 2. There are two kinds of mirrors which are ...............and ............... 3. The earth rotates around the ............... while the sun rotates around the center of ............... B) What are the reasons lead to: 1. Difference in year from planet to another. 2. Difference in day length from pl ...
... 2. There are two kinds of mirrors which are ...............and ............... 3. The earth rotates around the ............... while the sun rotates around the center of ............... B) What are the reasons lead to: 1. Difference in year from planet to another. 2. Difference in day length from pl ...
The New Astronomy and Cosmology of the Scientific Revolution
... as the stationary center of the universe around which the planets and sun revolved. In the Copernican system, on the other hand, the Earth was merely “another planet,” that is, a “wandering star.” Because his philosophy and theology held that God created only perfect order and harmony, Copernicus en ...
... as the stationary center of the universe around which the planets and sun revolved. In the Copernican system, on the other hand, the Earth was merely “another planet,” that is, a “wandering star.” Because his philosophy and theology held that God created only perfect order and harmony, Copernicus en ...
Pluto and the Galactic Center
... Pluto is (on average) about forty times more distant from the Sun than the Earth is from the Sun. However, its elliptical orbit around the Sun is very eccentric. It is so strongly eccentric that at its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) it is just under 30 astronomical units away, and when it ...
... Pluto is (on average) about forty times more distant from the Sun than the Earth is from the Sun. However, its elliptical orbit around the Sun is very eccentric. It is so strongly eccentric that at its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) it is just under 30 astronomical units away, and when it ...
American Scientist
... a distance a third the size of Mercury’s orbit. Perhaps the most puzzling case study comes from the Kepler-36 system. Two planets are found at roughly the same distance from the star: one with a density less than that of water, whereas the other is as dense as iron. Theorists are just coming to grip ...
... a distance a third the size of Mercury’s orbit. Perhaps the most puzzling case study comes from the Kepler-36 system. Two planets are found at roughly the same distance from the star: one with a density less than that of water, whereas the other is as dense as iron. Theorists are just coming to grip ...
Lecture 16
... A later scheme, called the B-V Index, classed stars according to a logarithmic ratio of the peak amount of radiation in the blue and violet colors. The current scheme is to class stars according to color in a way which is more or less logarithmically proportional to temperature. In this scheme stars ...
... A later scheme, called the B-V Index, classed stars according to a logarithmic ratio of the peak amount of radiation in the blue and violet colors. The current scheme is to class stars according to color in a way which is more or less logarithmically proportional to temperature. In this scheme stars ...
EARTH REVOVLES ROUND THE SUN IN A SPIRAL PATH
... The rotated spiral paths of satellites planets and a star are twisted one another to form a rope path. Due to this rope theory, a satellite revolves round its planet, a planet revolves round its star and a star revolves round its galaxy. That is why, they live together. The celestial body which is c ...
... The rotated spiral paths of satellites planets and a star are twisted one another to form a rope path. Due to this rope theory, a satellite revolves round its planet, a planet revolves round its star and a star revolves round its galaxy. That is why, they live together. The celestial body which is c ...
Space Jeopardy
... Stars for 4 Question:Planets that are close to the sun…. a)move through the asteroid belt b)orbit faster than the outer planets c)orbit slower than the outer planets d)move closer and closer to the sun ...
... Stars for 4 Question:Planets that are close to the sun…. a)move through the asteroid belt b)orbit faster than the outer planets c)orbit slower than the outer planets d)move closer and closer to the sun ...
The Sun - Driving Force for Climate
... Prague, stated that to be a planet an object must meet three criteria: ...
... Prague, stated that to be a planet an object must meet three criteria: ...
Mission 1: What`s In Our Sky
... orbiting around the Earth, we see different parts of the Moon at different times. This makes the Moon seem to disappear slowly and then reappear. There are eight phases of the Moon, and the Moon cycles through all eight phases every 29 1/2 days. This is almost once a month. Phase 1 - New Moon Phase ...
... orbiting around the Earth, we see different parts of the Moon at different times. This makes the Moon seem to disappear slowly and then reappear. There are eight phases of the Moon, and the Moon cycles through all eight phases every 29 1/2 days. This is almost once a month. Phase 1 - New Moon Phase ...
Sun Powerpoint
... OUR STAR – TIMES! • The core rotates at the same rate but the outer parts of the Sun do not! • 34 Earth days to rotate at Poles • 25 Earth days to rotate at Equator • There is no period of revolution… http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/EducationResource/Universe/framed_e/lecture/ch11/imgs/rotat ...
... OUR STAR – TIMES! • The core rotates at the same rate but the outer parts of the Sun do not! • 34 Earth days to rotate at Poles • 25 Earth days to rotate at Equator • There is no period of revolution… http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/EducationResource/Universe/framed_e/lecture/ch11/imgs/rotat ...
Habitability and Life Parameters in our Solar System
... galactic habitable zone to decide which regions are most likely to form solar system. Solar systems decide within star’s planetary habitable zones to provide stable environment for the life in which the life emerged from planet to planet according to the theory of energy distribution on a planet for ...
... galactic habitable zone to decide which regions are most likely to form solar system. Solar systems decide within star’s planetary habitable zones to provide stable environment for the life in which the life emerged from planet to planet according to the theory of energy distribution on a planet for ...
Student Literacy
... Most stars belong to a galaxy, a group of millions of stars held together by gravity. Our solar system lies on the outer edge of a huge galaxy called the Milky Way Galaxy, a group of about 200 billion stars formed in a disk-shaped spiral. Our solar system is a tiny dot compared to the Milky Way Gala ...
... Most stars belong to a galaxy, a group of millions of stars held together by gravity. Our solar system lies on the outer edge of a huge galaxy called the Milky Way Galaxy, a group of about 200 billion stars formed in a disk-shaped spiral. Our solar system is a tiny dot compared to the Milky Way Gala ...
Lecture notes 11
... Assuming that a star forms from a gas cloud that is homogeneous in its heavy metal distribution (a safe assumption), then all Stars should start off using the pp chain or CNO cycle to convert H to He. During nucleosynthesis, surface of the star is not completely static, The observational characteris ...
... Assuming that a star forms from a gas cloud that is homogeneous in its heavy metal distribution (a safe assumption), then all Stars should start off using the pp chain or CNO cycle to convert H to He. During nucleosynthesis, surface of the star is not completely static, The observational characteris ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.