Chapter 3 Notes
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
We Are Stardust: Synthesis of the Elements Essential for Life Aparna
... energy), revealed that the Sun could shine at its current luminosity levels for only 30 million years. So what has been enabling the Sun to shine for the last few billion years? • The Sun’s source of energy is Thermonuclear Fusion, where heavier chemical elements are made from lighter elements throu ...
... energy), revealed that the Sun could shine at its current luminosity levels for only 30 million years. So what has been enabling the Sun to shine for the last few billion years? • The Sun’s source of energy is Thermonuclear Fusion, where heavier chemical elements are made from lighter elements throu ...
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
Assignment 1 - utoledo.edu
... and has taken to going out into an open field and staring at the stars for hours, while slowly chanting the names of the 92 stable elements. But he gets very easily dizzy from watching the slow turning of the stars in the sky. Where in the sky would you advise him to look to see stars that are not ...
... and has taken to going out into an open field and staring at the stars for hours, while slowly chanting the names of the 92 stable elements. But he gets very easily dizzy from watching the slow turning of the stars in the sky. Where in the sky would you advise him to look to see stars that are not ...
newsletter - Thanet Astronomy Group
... From time to time, and not very often, various groups of planets will, of course, group together or 'align' around one particular direction from the Sun. When this happens if the alignment is in a direction visible from the side of the Earth that faces away from the Sun, the planets can be observed ...
... From time to time, and not very often, various groups of planets will, of course, group together or 'align' around one particular direction from the Sun. When this happens if the alignment is in a direction visible from the side of the Earth that faces away from the Sun, the planets can be observed ...
Semantics - Bases Produced Home
... “It can only be the thought of verdure to come, which prompts us in the autumn to buy these dormant white lumps of vegetable matter covered by a brown papery skin, and lovingly to plant them and care for them. It is a marvel to me that under this cover they are labouring unseen at such a rate within ...
... “It can only be the thought of verdure to come, which prompts us in the autumn to buy these dormant white lumps of vegetable matter covered by a brown papery skin, and lovingly to plant them and care for them. It is a marvel to me that under this cover they are labouring unseen at such a rate within ...
G485 5.5.1 Structure of the Universe
... by direct visual observation. This is because of their relatively small size and the tremendous distances from one star to another. Proxima Centauri, the closest star to the Sun, is 4.5 light-years away, so if it has planets in orbit around it, they would not be visible even using the most powerful ...
... by direct visual observation. This is because of their relatively small size and the tremendous distances from one star to another. Proxima Centauri, the closest star to the Sun, is 4.5 light-years away, so if it has planets in orbit around it, they would not be visible even using the most powerful ...
NASA-TV Highlights
... to Vega for dim little Corona Borealis, the Northern Crown, with its one modestly bright star, Alphecca or Gemma. Two thirds of the way from Arcturus to Vega glimmers the dim Keystone of Hercules. Continue on down past Vega, and you hit Cygnus. Sunday, May 18 Look south after dark for Mars at its hi ...
... to Vega for dim little Corona Borealis, the Northern Crown, with its one modestly bright star, Alphecca or Gemma. Two thirds of the way from Arcturus to Vega glimmers the dim Keystone of Hercules. Continue on down past Vega, and you hit Cygnus. Sunday, May 18 Look south after dark for Mars at its hi ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/solution-manual-geosystems-7th-edition-christopherson ...
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/solution-manual-geosystems-7th-edition-christopherson ...
pompton lakes high school - Pompton Lakes School District
... used in astronomical telescopes. Explain the particular advantages of reflecting telescopes for astronomical use, and specify why very large telescopes are needed for most astronomical studies. Describe how Earth’s atmosphere affects astronomical observations, and discuss some of the current eff ...
... used in astronomical telescopes. Explain the particular advantages of reflecting telescopes for astronomical use, and specify why very large telescopes are needed for most astronomical studies. Describe how Earth’s atmosphere affects astronomical observations, and discuss some of the current eff ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 6
... The Big Dipper asterism within the constellation Ursa Major is one of the most wellknown patterns in the sky. But the Big Bear boasts more delights than those within the dipper. Lets go Owl hunting. Messier 97 is a faint (mag. 9.9) planetary nebula found just below the bowl of the dipper. At a dista ...
... The Big Dipper asterism within the constellation Ursa Major is one of the most wellknown patterns in the sky. But the Big Bear boasts more delights than those within the dipper. Lets go Owl hunting. Messier 97 is a faint (mag. 9.9) planetary nebula found just below the bowl of the dipper. At a dista ...
pompton lakes high school - Pompton Lakes School District
... used in astronomical telescopes. Explain the particular advantages of reflecting telescopes for astronomical use, and specify why very large telescopes are needed for most astronomical studies. Describe how Earth’s atmosphere affects astronomical observations, and discuss some of the current eff ...
... used in astronomical telescopes. Explain the particular advantages of reflecting telescopes for astronomical use, and specify why very large telescopes are needed for most astronomical studies. Describe how Earth’s atmosphere affects astronomical observations, and discuss some of the current eff ...
Pluto and the Kuiper Belt
... Surprisingly, many Kuiper belt objects are in 3:2 resonance with Neptune: They make 2 orbits around the Sun while Neptune makes 3 orbits. Pluto is in the same resonance. These objects are called “Plutinos” (“little Plutos”). It is sensible to think of Pluto as the biggest Plutino, not than the small ...
... Surprisingly, many Kuiper belt objects are in 3:2 resonance with Neptune: They make 2 orbits around the Sun while Neptune makes 3 orbits. Pluto is in the same resonance. These objects are called “Plutinos” (“little Plutos”). It is sensible to think of Pluto as the biggest Plutino, not than the small ...
The Earth in the Solar System
... thermal structure of the solar nebula. Time scales for the condensation of gas to dust, of accumulation of dust to planetesimals, and of accretion of planetesimals to planets and moons are also not well constrained. If cooling occurred slowly in comparison to other processes then planets would have ...
... thermal structure of the solar nebula. Time scales for the condensation of gas to dust, of accumulation of dust to planetesimals, and of accretion of planetesimals to planets and moons are also not well constrained. If cooling occurred slowly in comparison to other processes then planets would have ...
History
... Johann Bode (1747-1826) – Popularized a relationship between the planets and their relative distances from the sun. • Begin with a series of 4’s – one for each planet • add to each 4 the corresponding number in the sequence 0, 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, 96..., then divide the result by ten. ...
... Johann Bode (1747-1826) – Popularized a relationship between the planets and their relative distances from the sun. • Begin with a series of 4’s – one for each planet • add to each 4 the corresponding number in the sequence 0, 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, 96..., then divide the result by ten. ...
Lecture 21: Planet formation III. Planet
... Core formation: A solid protoplanet (“core”) grows via a succession of twobody collisions until it becomes massive enough to retain a significant gaseous atmosphere or envelope (similar to terrestrial planet formation). Hydrostatic growth: Initially the envelope surrounding the solid core is in hydr ...
... Core formation: A solid protoplanet (“core”) grows via a succession of twobody collisions until it becomes massive enough to retain a significant gaseous atmosphere or envelope (similar to terrestrial planet formation). Hydrostatic growth: Initially the envelope surrounding the solid core is in hydr ...
Jovian Planets Notes
... c) Io’s surface has been transformed by the volcanoes and is by far the youngest surface we have observed in our Solar System d) Gravitational forces from the other Galilean satellites distort Io’s orbit slightly, which changes the tidal force on it from Jupiter in a varying fashion i) This changing ...
... c) Io’s surface has been transformed by the volcanoes and is by far the youngest surface we have observed in our Solar System d) Gravitational forces from the other Galilean satellites distort Io’s orbit slightly, which changes the tidal force on it from Jupiter in a varying fashion i) This changing ...
Geosystems-7th-Edition-Christopherson-Solution
... • Distinguish among galaxies, stars, and planets, and locate Earth. 1. Describe the Sun’s status among stars in the Milky Way Galaxy. Describe the Sun’s location, size, and relationship to its planets. Our Sun is both unique to us and commonplace in our galaxy. It is only average in temperature, siz ...
... • Distinguish among galaxies, stars, and planets, and locate Earth. 1. Describe the Sun’s status among stars in the Milky Way Galaxy. Describe the Sun’s location, size, and relationship to its planets. Our Sun is both unique to us and commonplace in our galaxy. It is only average in temperature, siz ...
Celebrating the centennial of a celestial yardstick
... platinum. The planet has also had abundant volcanic activity (and may have some ongoing activity today), which is involved in concentrating such elements. Yet the amounts of these elements, their distribution, and many other factors are completely unknown. The MESSENGER spacecraft is studying Mercur ...
... platinum. The planet has also had abundant volcanic activity (and may have some ongoing activity today), which is involved in concentrating such elements. Yet the amounts of these elements, their distribution, and many other factors are completely unknown. The MESSENGER spacecraft is studying Mercur ...
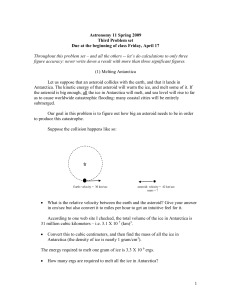
Third problem set
... R = flux from Alpha Centauri / flux from its planet. [Now you can see why finding such planets is so hard: they would be very much fainter than their stars, and they would lie very close to them as seen from here. Any planets that exist would be overwhelmed by the far brighter glare from their stars ...
... R = flux from Alpha Centauri / flux from its planet. [Now you can see why finding such planets is so hard: they would be very much fainter than their stars, and they would lie very close to them as seen from here. Any planets that exist would be overwhelmed by the far brighter glare from their stars ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe
... — Earth is part of the Solar System, which is the Milky Way Galaxy, which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster. ...
... — Earth is part of the Solar System, which is the Milky Way Galaxy, which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster. ...
Seeing another Earth: Detecting and Characterizing Rocky Planets
... further out, and thus cooler, would likely be undetectable. However, planets closer to their star, with equilibrium temperatures correspondingly higher, could very well be bright enough to study. An Earthsize planet at an equilibrium temperature of T=600 K would be roughly four times closer than a t ...
... further out, and thus cooler, would likely be undetectable. However, planets closer to their star, with equilibrium temperatures correspondingly higher, could very well be bright enough to study. An Earthsize planet at an equilibrium temperature of T=600 K would be roughly four times closer than a t ...
Hubble Offers a Dazzling View of Necklace Nebula
... ring is actually two stars orbiting close together. One of the stars is near the end of its life and created the planetary nebula. The estimated age of the ring is around 5,000 years. The nebula is 15,000 light-years from Earth. Astronomers discovered the nebula in November 2005 with the Isaac Newto ...
... ring is actually two stars orbiting close together. One of the stars is near the end of its life and created the planetary nebula. The estimated age of the ring is around 5,000 years. The nebula is 15,000 light-years from Earth. Astronomers discovered the nebula in November 2005 with the Isaac Newto ...
How to Use This Presentation
... • In the late 1500s, Pope Gregory XIII formed a committee to create a calendar that would keep the calendar aligned with the seasons. We use this calendar today. • In this Gregorian calendar, century years, such as 1800 and 1900, are not leap years unless the century years are exactly divisible by 4 ...
... • In the late 1500s, Pope Gregory XIII formed a committee to create a calendar that would keep the calendar aligned with the seasons. We use this calendar today. • In this Gregorian calendar, century years, such as 1800 and 1900, are not leap years unless the century years are exactly divisible by 4 ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.