Chapter-by-Chapter Guide - We can offer most test bank and
... 1.496 108 kilometers. Light-year: the distance that light travels in 1 year, which is about 9.46 trillion kilometers. Because light travels at a fixed speed, it takes time for it to go between two points in space. Although light travels very quickly, the distances in the universe are so large that ...
... 1.496 108 kilometers. Light-year: the distance that light travels in 1 year, which is about 9.46 trillion kilometers. Because light travels at a fixed speed, it takes time for it to go between two points in space. Although light travels very quickly, the distances in the universe are so large that ...
Kepler`s Search for Exoplanets
... Here we’ve marked stars with confirmed exoplanets. There are over nearly 2000 confirmed exoplanets [update as needed], and we’re still just getting started! Results from Kepler indicate that it’s likely every star we see in the night sky has planets. And it’s just a matter of time before we find ano ...
... Here we’ve marked stars with confirmed exoplanets. There are over nearly 2000 confirmed exoplanets [update as needed], and we’re still just getting started! Results from Kepler indicate that it’s likely every star we see in the night sky has planets. And it’s just a matter of time before we find ano ...
Chapter 13 Power Point Lecture
... massive planets can eject one planet while flinging the other into a highly elliptical orbit. • Multiple close encounters with smaller planetesimals can also cause inward migration. ...
... massive planets can eject one planet while flinging the other into a highly elliptical orbit. • Multiple close encounters with smaller planetesimals can also cause inward migration. ...
Astronomy Puzzle-1
... Answers of puzzle are hidden in the box. The answers are either vertical, horizontal, diagonal or in reverse order. Sample answer is shown in the puzzle. Clues 1. The Astronomy research institute set up by the University Grant Commission. 2. The research institution set up by the Department of Spac ...
... Answers of puzzle are hidden in the box. The answers are either vertical, horizontal, diagonal or in reverse order. Sample answer is shown in the puzzle. Clues 1. The Astronomy research institute set up by the University Grant Commission. 2. The research institution set up by the Department of Spac ...
SCA/Endeavour Complete Ferry Flight at LAX
... star cluster M11. Ever since 1844, deep-sky observers have known M11 as the Wild Duck Cluster. But where, exactly, are the ducks? We unpack the mystery in the September Sky & Telescope, page 53. Yes, you can see them. ...
... star cluster M11. Ever since 1844, deep-sky observers have known M11 as the Wild Duck Cluster. But where, exactly, are the ducks? We unpack the mystery in the September Sky & Telescope, page 53. Yes, you can see them. ...
The Astrophysics of Planetary Habitability
... P2.7. Stellar prominence oscillations and eruptions: The cases of HK Aqr and PZ Tel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P2.8. First Results from the MUSCLES Treasury Survey of the UV and X-ray Emission from K and M Dwarf Stars that Host Exoplanets . P2.9. The variations of tidal ...
... P2.7. Stellar prominence oscillations and eruptions: The cases of HK Aqr and PZ Tel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P2.8. First Results from the MUSCLES Treasury Survey of the UV and X-ray Emission from K and M Dwarf Stars that Host Exoplanets . P2.9. The variations of tidal ...
The Anglo-Australian Planet Search – XXI. A Gas-Giant
... years it has been observed regularly in observations of 450-900s (depending on observing conditions) giving a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of ≈200 per spectral pixel in the iodine region. The root-mean-square (rms) scatter about the mean velocity of all AAPS data for HD 38283 is 8.5 m s−1 , which is ...
... years it has been observed regularly in observations of 450-900s (depending on observing conditions) giving a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of ≈200 per spectral pixel in the iodine region. The root-mean-square (rms) scatter about the mean velocity of all AAPS data for HD 38283 is 8.5 m s−1 , which is ...
Astronomy - Great Smoky Mountains Institute at Tremont
... lamp, of course, is the sun. Have each student stand with his or her back to the lamp and hold the moon ball up at arm’s length so that some light shines on it. Explain that just like the Earth has day and night, so does the moon. Ask them to point to where it is night on their moons. Why is it nigh ...
... lamp, of course, is the sun. Have each student stand with his or her back to the lamp and hold the moon ball up at arm’s length so that some light shines on it. Explain that just like the Earth has day and night, so does the moon. Ask them to point to where it is night on their moons. Why is it nigh ...
THE REASON FOR THE SEASONS OVERVIEW Program
... sun receives more direct solar radiation, thus it is warmer. Now ask the student holding Earth to orbit the sun, making sure to hold the tilt in the same direction until the tilt of the Earth is positioned so that the sun is directly overhead of the pushpin/person in the Southern Hemisphere. Ask: Is ...
... sun receives more direct solar radiation, thus it is warmer. Now ask the student holding Earth to orbit the sun, making sure to hold the tilt in the same direction until the tilt of the Earth is positioned so that the sun is directly overhead of the pushpin/person in the Southern Hemisphere. Ask: Is ...
FREE Sample Here
... imagine a raisin cake rising, we can see that every raisin will move away from every other raisin. So each raisin will see all of the others moving away from it, with more distant ones moving faster—just as Hubble observed galaxies to be moving. Thus, just as the raisin observations can be explained ...
... imagine a raisin cake rising, we can see that every raisin will move away from every other raisin. So each raisin will see all of the others moving away from it, with more distant ones moving faster—just as Hubble observed galaxies to be moving. Thus, just as the raisin observations can be explained ...
Biosignatures and Planetary Properties to be
... Beyond the Earth yet within our Solar System, our search for life and evidence about the origin of life will likely be confined to Mars, Europa, and Titan, along with small bodies such as comets, asteroids, and meteorite fragments derived therefrom. These objects present a wonderful opportunity for ...
... Beyond the Earth yet within our Solar System, our search for life and evidence about the origin of life will likely be confined to Mars, Europa, and Titan, along with small bodies such as comets, asteroids, and meteorite fragments derived therefrom. These objects present a wonderful opportunity for ...
Venus
... Venus is the __________________________ planet from the Sun in our Solar System. It is the _________________________ planet in our Solar System. This planet is covered with fastmoving sulphuric acid clouds which trap __________________________ from the Sun. Its thick atmosphere is mostly carbon diox ...
... Venus is the __________________________ planet from the Sun in our Solar System. It is the _________________________ planet in our Solar System. This planet is covered with fastmoving sulphuric acid clouds which trap __________________________ from the Sun. Its thick atmosphere is mostly carbon diox ...
Earth Chakras - Sophia Foundation
... Rudolf Steiner considered Southeast Asia separately from the rest of Asia, bringing the number back to seven. Southeast Asia he correlated with Venus, and the rest of Asia—at least, that part of Asia comprising the natural habitat of the “Mongolian peoples”—he brought into connection with Mars. Thu ...
... Rudolf Steiner considered Southeast Asia separately from the rest of Asia, bringing the number back to seven. Southeast Asia he correlated with Venus, and the rest of Asia—at least, that part of Asia comprising the natural habitat of the “Mongolian peoples”—he brought into connection with Mars. Thu ...
Pluto
... At least two smaller, colorful pictures showing what the astronomical object does (or may) look like. These should be color photos, or pictures from the computer. (10 pts) ...
... At least two smaller, colorful pictures showing what the astronomical object does (or may) look like. These should be color photos, or pictures from the computer. (10 pts) ...
Young Astronomers Digest
... you are), this month’s issue is on the Myths and Urban Legends of Astronomy. For the younger minds, we’ve laid out myths like the phases and the spinning of the moon (yes it does spin!) as well as why stars actually don’t come in only the colour white and why Polaris may not be as bright as you thin ...
... you are), this month’s issue is on the Myths and Urban Legends of Astronomy. For the younger minds, we’ve laid out myths like the phases and the spinning of the moon (yes it does spin!) as well as why stars actually don’t come in only the colour white and why Polaris may not be as bright as you thin ...
No. 54 - Institute for Astronomy
... out as a result of passing through a narrow aperture or across an edge. PLANETS’ mirror will also be polished to be very smooth to minimize diffuse scattered light from mirror roughness, a major source of light scattering. PLANETS will also have a stellar coronagraph to block out the blinding glare ...
... out as a result of passing through a narrow aperture or across an edge. PLANETS’ mirror will also be polished to be very smooth to minimize diffuse scattered light from mirror roughness, a major source of light scattering. PLANETS will also have a stellar coronagraph to block out the blinding glare ...
February 2015 - astronomy for beginners
... bright. Jupiter always displays an almost full disc but can lose a tiny amount from the edge when it is at greatest elongation (at about 90° from the Sun as we view it from Earth). However Jupiter will appear absolutely full to the untrained eye. For these reasons Jupiter will be as good as it gets ...
... bright. Jupiter always displays an almost full disc but can lose a tiny amount from the edge when it is at greatest elongation (at about 90° from the Sun as we view it from Earth). However Jupiter will appear absolutely full to the untrained eye. For these reasons Jupiter will be as good as it gets ...
Lecture 10 - Lick Observatory
... Now drop the rocks on the moon. Is the acceleration of the rocks larger or smaller than it was on earth? smaller Do the rocks fall faster or slower than they ...
... Now drop the rocks on the moon. Is the acceleration of the rocks larger or smaller than it was on earth? smaller Do the rocks fall faster or slower than they ...
Document
... day – to explain why the planets move as they do. To solve this problem he developed … • the three laws of motion, • the theory of universal gravitation, • calculus, a branch of mathematics. Newton quote: “If I have been able to see farther than others it is because I stood on the shoulders of giant ...
... day – to explain why the planets move as they do. To solve this problem he developed … • the three laws of motion, • the theory of universal gravitation, • calculus, a branch of mathematics. Newton quote: “If I have been able to see farther than others it is because I stood on the shoulders of giant ...
13_Lecture_Outline
... Revisiting the Nebular Theory • The nebular theory predicts that massive Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © ...
... Revisiting the Nebular Theory • The nebular theory predicts that massive Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of hot Jupiters has forced reexamination of nebular theory. • Planetary migration or gravitational encounters may explain hot Jupiters. © ...
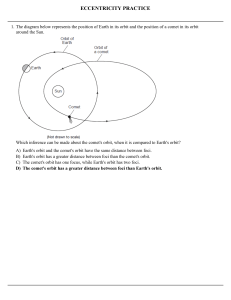
ECCENTRICITY PRACTICE
... Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cyclic decrease in the brightness of Ogle-Tr-3 every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the r ...
... Scientists studying a Sun-like star named Ogle-Tr-3 discovered a planet that is, on the average, 3.5 million kilometers away from the star’s surface. The planet was discovered as a result of observing a cyclic decrease in the brightness of Ogle-Tr-3 every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the r ...
Chapter 5 Gravitational fields - crypt
... 5 Draw a straight line of best fit. The gradient of the graph is equal to G. 6 Determine the value of G from the graph. What is the percentage uncertainty in your value? ...
... 5 Draw a straight line of best fit. The gradient of the graph is equal to G. 6 Determine the value of G from the graph. What is the percentage uncertainty in your value? ...
introduction to astronomy
... This course meets the lecture portion of the lab/science general studies requirement for graduation when taken with the lab course (AST 102). This course is provided for students who cannot take the lecture and lab during the same semester. The combination of AST 101-102 is equivalent to AST 103. ...
... This course meets the lecture portion of the lab/science general studies requirement for graduation when taken with the lab course (AST 102). This course is provided for students who cannot take the lecture and lab during the same semester. The combination of AST 101-102 is equivalent to AST 103. ...
Grade 5 Unit 6
... brightness of stars. They also collect and analyze data in order to describe patterns of daily changes in length and direction of shadows, day and night, and the seasonal appearance of some stars in the night sky. To begin the progression of learning in this unit, students explore the effects of gra ...
... brightness of stars. They also collect and analyze data in order to describe patterns of daily changes in length and direction of shadows, day and night, and the seasonal appearance of some stars in the night sky. To begin the progression of learning in this unit, students explore the effects of gra ...
Newfoundland Sky in Summer
... are much fainter because they are so far away. Some stars look brighter than others, but these are not necessarily the biggest, and many of the largest stars cannot be seen at all. One of the larger stars is Antares, in the constellation of Scorpius. This is a supergiant star; if we could put i t wh ...
... are much fainter because they are so far away. Some stars look brighter than others, but these are not necessarily the biggest, and many of the largest stars cannot be seen at all. One of the larger stars is Antares, in the constellation of Scorpius. This is a supergiant star; if we could put i t wh ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.