How was the Solar System Formed?
... Sun and Planets formed at about the same time out of a cloud of rotating gas and dust called a nebula. Matter from the Universe gathers into cloud 5 bya: Cloud forms when a supernova explodes. Under intense gravity and pressure caused the center of the solar nebula to become hotter and denser. At 10 ...
... Sun and Planets formed at about the same time out of a cloud of rotating gas and dust called a nebula. Matter from the Universe gathers into cloud 5 bya: Cloud forms when a supernova explodes. Under intense gravity and pressure caused the center of the solar nebula to become hotter and denser. At 10 ...
Transcript - Cheap Astronomy
... There’s no doubt Copernicus was a polymath and a jolly-clever fellow, but did it all really start with him? For example, there was Aristarchus of Samos who lived around 300 BC. No writings by Aristarchus remain, his proposal is described by Aristotle – who relayed that Aristarchus thought the Sun th ...
... There’s no doubt Copernicus was a polymath and a jolly-clever fellow, but did it all really start with him? For example, there was Aristarchus of Samos who lived around 300 BC. No writings by Aristarchus remain, his proposal is described by Aristotle – who relayed that Aristarchus thought the Sun th ...
lecture9 Solar System1
... Grow into planetesimals some still survive today asteroids comets ...
... Grow into planetesimals some still survive today asteroids comets ...
write the scientific term
... Because, the earth rotates around itself once every 24 hours. Because, the earth revolves around the sun once every 1 year. Because, carbon dioxide gas produced during blowing in the lime water changes it into turbid (milky). 8. Because, it doesn’t help in burning. ...
... Because, the earth rotates around itself once every 24 hours. Because, the earth revolves around the sun once every 1 year. Because, carbon dioxide gas produced during blowing in the lime water changes it into turbid (milky). 8. Because, it doesn’t help in burning. ...
Why Is the Sun a Star
... The Sun is the center of our Solar System. It is so massive that its strong gravity attracts all the planets and their moons, comets, asteroids and meteors into orbit around it. Its light provides Earth with 99% of all the energy used on our planet and we see its reflected light on all the planets a ...
... The Sun is the center of our Solar System. It is so massive that its strong gravity attracts all the planets and their moons, comets, asteroids and meteors into orbit around it. Its light provides Earth with 99% of all the energy used on our planet and we see its reflected light on all the planets a ...
PDF only
... the search for life elsewhere, such as in the most Earth-like regions of Mars or Jupiter’s watery moon Europa. Now, however, discoveries of potentially habitable planets orbiting stars other than our sun – exoplanets, that is – are challenging that geocentric approach. Over the past two decades astr ...
... the search for life elsewhere, such as in the most Earth-like regions of Mars or Jupiter’s watery moon Europa. Now, however, discoveries of potentially habitable planets orbiting stars other than our sun – exoplanets, that is – are challenging that geocentric approach. Over the past two decades astr ...
The Scientific Revolution - Online
... challenged Aristotle's universe and its theological-philosophical worldview,34and laid the foundations for dynamics (how objects move on the earth) and gravity. ...
... challenged Aristotle's universe and its theological-philosophical worldview,34and laid the foundations for dynamics (how objects move on the earth) and gravity. ...
2015-16 Space Week 1 and 2 ppt
... 17.What two states are involved in the transmission of information to and from Hubble Space Telescope? 18.Stephen Hawking originally intended to study what field? 19.The first words uttered by Neil Armstrong as Eagle touched down on the Moon's surface can be heard in a movie about the Apollo 11 land ...
... 17.What two states are involved in the transmission of information to and from Hubble Space Telescope? 18.Stephen Hawking originally intended to study what field? 19.The first words uttered by Neil Armstrong as Eagle touched down on the Moon's surface can be heard in a movie about the Apollo 11 land ...
Station 1 - Fall River Public Schools
... Centauri. Light travels 9,460,000,000,000 kilometers in one year, or 300,000 kilometers per second. Even if you traveled at the speed of light, it would take you 4.3 years to reach Proxima Centauri. What Makes Up the Universe? The universe contains billions of galaxies, more than any person can coun ...
... Centauri. Light travels 9,460,000,000,000 kilometers in one year, or 300,000 kilometers per second. Even if you traveled at the speed of light, it would take you 4.3 years to reach Proxima Centauri. What Makes Up the Universe? The universe contains billions of galaxies, more than any person can coun ...
Chapter-08
... Sun’s mass is 2x1030 kg. Earth’s mass is 6x1024 kg. Thus, Sun is nearly a million times more massive than Earth. Which object “feels” a larger gravitational force? (Assume a two-body system.) ...
... Sun’s mass is 2x1030 kg. Earth’s mass is 6x1024 kg. Thus, Sun is nearly a million times more massive than Earth. Which object “feels” a larger gravitational force? (Assume a two-body system.) ...
Introduction to Space
... with beautiful sunrises and sunsets ~The moon is the brightest and most recognizable object in the sky at night, and it the closest celestial body (any object beyond the Earth and visible in the sky) to the Earth ~From a dark site away from city lights, we can see nearly 3000 stars (compared to the ...
... with beautiful sunrises and sunsets ~The moon is the brightest and most recognizable object in the sky at night, and it the closest celestial body (any object beyond the Earth and visible in the sky) to the Earth ~From a dark site away from city lights, we can see nearly 3000 stars (compared to the ...
3 Habitable Zones in Extrasolar Planetary Systems
... solar system [6], the Martian orbit position was within the HZ up to about 500 million years ago. Jovian-type planets do not have a solid or liquid surface, covered by an atmosphere, near which organisms may exist. Therefore, usually they are considered as inhabitable. But there is the possibility t ...
... solar system [6], the Martian orbit position was within the HZ up to about 500 million years ago. Jovian-type planets do not have a solid or liquid surface, covered by an atmosphere, near which organisms may exist. Therefore, usually they are considered as inhabitable. But there is the possibility t ...
Astronomy that falls from the sky
... 1. Our Sun is an average star and the closest star to Earth in the Milky Way galaxy containing billions of stars. (Q&A: Which is the next closest star?) 2. Our solar system includes all the planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, dust, ice, and gas orbiting the Sun. 3. What are referred to as ...
... 1. Our Sun is an average star and the closest star to Earth in the Milky Way galaxy containing billions of stars. (Q&A: Which is the next closest star?) 2. Our solar system includes all the planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, dust, ice, and gas orbiting the Sun. 3. What are referred to as ...
Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... We weren't there (it was 5 billion years ago). We need a good theory. We can try to check it against other forming solar systems. What must it explain? - Solar system is very flat. - Almost all moons and planets (and Sun) rotate and revolve in the same direction. - Planets are isolated in space. - T ...
... We weren't there (it was 5 billion years ago). We need a good theory. We can try to check it against other forming solar systems. What must it explain? - Solar system is very flat. - Almost all moons and planets (and Sun) rotate and revolve in the same direction. - Planets are isolated in space. - T ...
Chapter 17 Solar system.pmd
... upwards. The ball would (a) directly fall down from the point it is released. (b) hang in space. (c) go up and then come back to the surface of the moon. (d) keep going up never to come back. ...
... upwards. The ball would (a) directly fall down from the point it is released. (b) hang in space. (c) go up and then come back to the surface of the moon. (d) keep going up never to come back. ...
File
... Galaxies will collide, creating a high-energy, high-density mass – the opposite of the big bang. ...
... Galaxies will collide, creating a high-energy, high-density mass – the opposite of the big bang. ...
Detection and Properties of Planetary Systems
... • How do planetary systems form? • Is this a common or an infrequent event? • How unique are the properties of our own solar system? • Are these qualities important for life to form? Up until now we have had only one laboratory to test planet formation theories. We need more! ...
... • How do planetary systems form? • Is this a common or an infrequent event? • How unique are the properties of our own solar system? • Are these qualities important for life to form? Up until now we have had only one laboratory to test planet formation theories. We need more! ...
5th Grade - IUSD.org
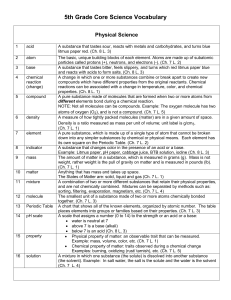
... A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemical reaction. NOTE: Not all molecules can be compounds. Example: The oxygen molecule has two atoms of oxygen (O2), and is not a compound. (Ch. 7 L. 5) A measure of how tightly packed ...
... A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemical reaction. NOTE: Not all molecules can be compounds. Example: The oxygen molecule has two atoms of oxygen (O2), and is not a compound. (Ch. 7 L. 5) A measure of how tightly packed ...
On a New Primary Planet of our Solar System, Long Suspected
... [Mars], casts out too little light from its surface, on account of which it has hitherto eluded our sharpened eyes. Who knows of what quality its surface is? We know heavenly bodies that twincle between color shades of red and green, as e.g. Mars, and the double star in Andromeda, who’s light decrea ...
... [Mars], casts out too little light from its surface, on account of which it has hitherto eluded our sharpened eyes. Who knows of what quality its surface is? We know heavenly bodies that twincle between color shades of red and green, as e.g. Mars, and the double star in Andromeda, who’s light decrea ...
The Solar System: Unit 3 Review/Study Guide
... been ionized by the sun). The ion tail only shows up as the comet nears the sun, and it always points away from the sun. The dust tail of a comet is different from the ion tail, and it can be millions of km long! The Oort Cloud is a spherical region that surrounds the solar system and extends almost ...
... been ionized by the sun). The ion tail only shows up as the comet nears the sun, and it always points away from the sun. The dust tail of a comet is different from the ion tail, and it can be millions of km long! The Oort Cloud is a spherical region that surrounds the solar system and extends almost ...
Lecture powerpoint
... is rather difficult, so we will restrict most of our analysis to the limiting case in which an ellipse becomes a circle. Most planetary orbits differ only very slightly from being circular. If a satellite has a circular orbit, its speed is ...
... is rather difficult, so we will restrict most of our analysis to the limiting case in which an ellipse becomes a circle. Most planetary orbits differ only very slightly from being circular. If a satellite has a circular orbit, its speed is ...
the planets - St John Brebeuf
... It also contains at least one dwarf planet - Pluto. Pluto is indeed now considered to be a member of the Kuiper Belt - the largest object belonging to it, in fact! Like other members of the Belt, it is composed primarily of rock and ice and is relatively small.. The Kuiper Belt is also believed to b ...
... It also contains at least one dwarf planet - Pluto. Pluto is indeed now considered to be a member of the Kuiper Belt - the largest object belonging to it, in fact! Like other members of the Belt, it is composed primarily of rock and ice and is relatively small.. The Kuiper Belt is also believed to b ...
Name
... 35. While looking through a telescope, you see a galaxy with lots of main sequence stars in the outer regions and lots of white dwarfs and red giants near the center. What kind of galaxy do you think it is and why? Explain. ...
... 35. While looking through a telescope, you see a galaxy with lots of main sequence stars in the outer regions and lots of white dwarfs and red giants near the center. What kind of galaxy do you think it is and why? Explain. ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.