BIOLOGY 212 SI!
... EXPLAIN THE PULSE CHASE EXPERIMENT WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS? ...
... EXPLAIN THE PULSE CHASE EXPERIMENT WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS? ...
Teacher Immunology Project
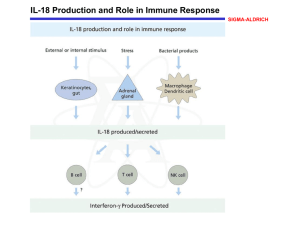
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
Slide 1
... b. inactivates antigens c. allows macrophages to destroy the complex d. changes shape so complement can lysis e. initiates release of mediators ...
... b. inactivates antigens c. allows macrophages to destroy the complex d. changes shape so complement can lysis e. initiates release of mediators ...
immune_07
... b. inactivates antigens c. allows macrophages to destroy the complex d. changes shape so complement can lysis e. initiates release of mediators ...
... b. inactivates antigens c. allows macrophages to destroy the complex d. changes shape so complement can lysis e. initiates release of mediators ...
1. Which one of the following statements is correct ? (A) Peptides of
... (A) Cytokines are large proteins stored in granules and released by exocytotic mechanisms (B) Cytokines bind to cell surface receptors with high affinity (C) Cytokines stimulate macrophages to migrate to an area of inflammation (D) Each cytokine acts independently of other cytokines (E) Cytokines ac ...
... (A) Cytokines are large proteins stored in granules and released by exocytotic mechanisms (B) Cytokines bind to cell surface receptors with high affinity (C) Cytokines stimulate macrophages to migrate to an area of inflammation (D) Each cytokine acts independently of other cytokines (E) Cytokines ac ...
General Pathology: Acute Inflammation
... retained in lymphoid tissues • These cells allow for rapid response to antigens when re-exposed and can secrete small amounts of antibody for years • Vaccinations induce formation of “memory” cells ...
... retained in lymphoid tissues • These cells allow for rapid response to antigens when re-exposed and can secrete small amounts of antibody for years • Vaccinations induce formation of “memory” cells ...
Document
... retrovirus (ERV). DC, responding to `danger' signals through Toll like receptors (TLR), migrate to draining lymph nodes (LN). Inflammatory process leads to upregulation of Class I and Class II MHC molecules. ...
... retrovirus (ERV). DC, responding to `danger' signals through Toll like receptors (TLR), migrate to draining lymph nodes (LN). Inflammatory process leads to upregulation of Class I and Class II MHC molecules. ...
(2) Viral and bacterial superantigens
... retrovirus (ERV). DC, responding to `danger' signals through Toll like receptors (TLR), migrate to draining lymph nodes (LN). Inflammatory process leads to upregulation of Class I and Class II MHC molecules. ...
... retrovirus (ERV). DC, responding to `danger' signals through Toll like receptors (TLR), migrate to draining lymph nodes (LN). Inflammatory process leads to upregulation of Class I and Class II MHC molecules. ...
Intro to Immune System Chpt. 1
... Two Major subsets, TH (CD4) and TC (CD8) Third type TS not as clear Mature T cell expresses TCR TCR cannot recognize antigen on its own MHC I (all nucleated cells) or MHC II (APCs) is required • TH cells secrete cytokines • TC less cytokines, more cytotoxic (virus and tumor survailance) ...
... Two Major subsets, TH (CD4) and TC (CD8) Third type TS not as clear Mature T cell expresses TCR TCR cannot recognize antigen on its own MHC I (all nucleated cells) or MHC II (APCs) is required • TH cells secrete cytokines • TC less cytokines, more cytotoxic (virus and tumor survailance) ...
The integrated view
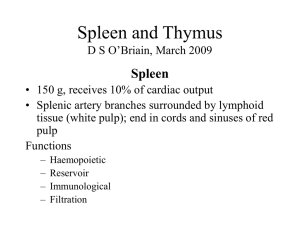
... Red pulp: degradation and consumption of exhausted erythrocytes. White pulp: site of immunological monitoring of blood. Red and white pulp are separated by “marginal zone.” PALS (“periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths) surround blood arteries; arteries deliver blood to sinuses of the marginal zone. Ag’s a ...
... Red pulp: degradation and consumption of exhausted erythrocytes. White pulp: site of immunological monitoring of blood. Red and white pulp are separated by “marginal zone.” PALS (“periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths) surround blood arteries; arteries deliver blood to sinuses of the marginal zone. Ag’s a ...
Time course of immune response
... • Found near epithelial surfaces • Low diversity of TCR specificity • Unknown ligand (something that changes upon infection?) • Recognize Ag directly, not in MHC ...
... • Found near epithelial surfaces • Low diversity of TCR specificity • Unknown ligand (something that changes upon infection?) • Recognize Ag directly, not in MHC ...
Chapter 17: IR to Infectious Disease
... • Starts with TH1 cells – Release of cytokines: • IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF • IL-2/IFN- γ act. NK cells • IL-2 recruits TC cells • Within 7-10 days, most virions are elim; parallels the development of Tc’s vs the virus ...
... • Starts with TH1 cells – Release of cytokines: • IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF • IL-2/IFN- γ act. NK cells • IL-2 recruits TC cells • Within 7-10 days, most virions are elim; parallels the development of Tc’s vs the virus ...
Defense Systems
... plasma cells secrete antibodies which attach to foreign particle marking them for destruction memory cells lie dormant until the next attack 3. Antigens are particles which can stimulate receptors on lymphocytes only part of the foreign invader is antigenic 4. Antibodies are proteins produced ...
... plasma cells secrete antibodies which attach to foreign particle marking them for destruction memory cells lie dormant until the next attack 3. Antigens are particles which can stimulate receptors on lymphocytes only part of the foreign invader is antigenic 4. Antibodies are proteins produced ...
6_Autoimmune_2013
... Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antige ...
... Normal tissue cells do not express MHC class II NO SIGNAL 1. for CD4+ Th activation Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antige ...
Immune System
... • The differences in humoral and cellmediated immunity. • Why Helper T cells are central to immune responses. ...
... • The differences in humoral and cellmediated immunity. • Why Helper T cells are central to immune responses. ...
T cell

T cells or T lymphocytes are a type of lymphocyte (in turn, a type of white blood cell) that plays a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cells and natural killer cells (NK cells), by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on the cell surface. They are called T cells because they mature in the thymus (although some also mature in the tonsils). The several subsets of T cells each have a distinct function. The majority of human T cells rearrange their alpha/beta T cell receptors and are termed alpha beta T cells and are part of adaptive immune system. Specialized gamma delta T cells, which comprise a minority of T cells in the human body (more frequent in ruminants), have invariant TCR (with limited diversity), can effectively present antigens to other T cells and are considered to be part of the innate immune system.