Innate Immunity - microbiology and immunology on-line
... malignant cells identified by the presence of CD56 & CD16 and absence of CD3 activated by IL2 and IFN-γ to become LAK cells ...
... malignant cells identified by the presence of CD56 & CD16 and absence of CD3 activated by IL2 and IFN-γ to become LAK cells ...
Immunity to infection
... • Defensins are antimicrobial proteins produced by macrophages and mucosal cells. Their production is upregulated by proinflammatory cytokines. • The secretory immune system protects the external ...
... • Defensins are antimicrobial proteins produced by macrophages and mucosal cells. Their production is upregulated by proinflammatory cytokines. • The secretory immune system protects the external ...
Immune Worksheet Key Session 26
... 1) Name and describe the four steps for phagocyte mobilization (how does the phagocyte reach the pathogen in the first place?): Step 1: Leukocytosis: Neutrophils enter blood from bone marrow Step 2: Margination: Neutrophils cling to the capillary wall Step 3: Diapedesis: Neutrophils flatten and sque ...
... 1) Name and describe the four steps for phagocyte mobilization (how does the phagocyte reach the pathogen in the first place?): Step 1: Leukocytosis: Neutrophils enter blood from bone marrow Step 2: Margination: Neutrophils cling to the capillary wall Step 3: Diapedesis: Neutrophils flatten and sque ...
Immune System Disorders
... Genes encoding histocompatibility antigens Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex: MHC genes in humans ...
... Genes encoding histocompatibility antigens Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex: MHC genes in humans ...
AMA 180 powerpoint
... Thrombocytes: platelets; clotting cells that are formed in bone marrow from giant cells called megakaryocytes. ...
... Thrombocytes: platelets; clotting cells that are formed in bone marrow from giant cells called megakaryocytes. ...
activate B cells
... 2) Role of Th cells in humoral immune response to TD-Ag For a protein Ag to stimulate Ab response, B cells and Th cells specific for that Ag must come together in lymphoid organs and interact in a way that stimulates B cell proliferation and differentiation. ...
... 2) Role of Th cells in humoral immune response to TD-Ag For a protein Ag to stimulate Ab response, B cells and Th cells specific for that Ag must come together in lymphoid organs and interact in a way that stimulates B cell proliferation and differentiation. ...
Hygiene III The Hugiene Hypothesis
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
... – Each produces a different receptor in the cell membrane – Each receptor is composed of 1 molecule each of two different proteins – Each receptor binds a specific antigen but has only one binding site – Receptor only recognizes antigens which are "presented" to it within another membrane protein of ...
2nd seminar - Innate immunity, inflammation 2015
... Symbiotic, non-pathogenic microbes, living in „peaceful” commensalisms Beneficial features: • Digesting non absorbable food compounds e.g. cellulose • Producing vitamines, antimicrobial molecules, regulating pH • Compete with pathogenic microbes – survival of the fittest • Providing constant low-dos ...
... Symbiotic, non-pathogenic microbes, living in „peaceful” commensalisms Beneficial features: • Digesting non absorbable food compounds e.g. cellulose • Producing vitamines, antimicrobial molecules, regulating pH • Compete with pathogenic microbes – survival of the fittest • Providing constant low-dos ...
REGULATION OF THE IMMUNE RESPONSE
... • T cells in elderly people have significantly shorter telomeres than young ones, • People with some premature ageing syndromes have short telomeres and usually have low life expectancy ...
... • T cells in elderly people have significantly shorter telomeres than young ones, • People with some premature ageing syndromes have short telomeres and usually have low life expectancy ...
B CELL
... lymphocytes are produced in waves to ensure protective immune responses •A sustained loss of tissue mass, cellularity and functionality of the thymus starts after puberty and lasts to middle age followed by a slower rate of involution extending to old age •DN cells do not proliferate and differentia ...
... lymphocytes are produced in waves to ensure protective immune responses •A sustained loss of tissue mass, cellularity and functionality of the thymus starts after puberty and lasts to middle age followed by a slower rate of involution extending to old age •DN cells do not proliferate and differentia ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM:
... 1. Barriers like your skin keep pathogens from getting into your body. Pathogens cause disease. 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and dest ...
... 1. Barriers like your skin keep pathogens from getting into your body. Pathogens cause disease. 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and dest ...
Week 9: Today`s Program
... Vertebrate lymphocytes take on specialized roles Circulate through blood & lymph, concentrated in spleen & lymph nodes B & T cells bear ~100K antigen receptors (all the same) Antigenbinding sites ...
... Vertebrate lymphocytes take on specialized roles Circulate through blood & lymph, concentrated in spleen & lymph nodes B & T cells bear ~100K antigen receptors (all the same) Antigenbinding sites ...
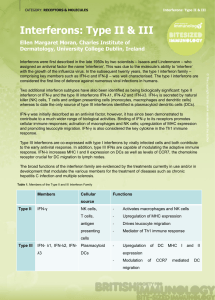
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
Poietics™ human immune system cells
... hepatitis C virus. Where donor testing is not possible, cell products are tested for the presence of viral nucleic acid from HIV, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus. Testing can not offer complete assurance that HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus are absent. All human sourced prod ...
... hepatitis C virus. Where donor testing is not possible, cell products are tested for the presence of viral nucleic acid from HIV, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus. Testing can not offer complete assurance that HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus are absent. All human sourced prod ...
Immunol-mol-med-3
... Signal 1 - TCR, MHC, antigen Signal 2 - CD28 binding to B7 Both signals must be from the same APC ONLY now can T cell proliferation start ...
... Signal 1 - TCR, MHC, antigen Signal 2 - CD28 binding to B7 Both signals must be from the same APC ONLY now can T cell proliferation start ...
No Slide Title - Pegasus @ UCF
... Development of the T-cell System Lymphocyte precursors originate in the yolk sac and migrate into the fetus. The lymphoid stem cells then migrate to the thymus under the influence of an “attraction factor.” The cells then become “programmed” and become immunocompetent. PUTATIVE PROCESS: 1. Thymic h ...
... Development of the T-cell System Lymphocyte precursors originate in the yolk sac and migrate into the fetus. The lymphoid stem cells then migrate to the thymus under the influence of an “attraction factor.” The cells then become “programmed” and become immunocompetent. PUTATIVE PROCESS: 1. Thymic h ...
Chapter 3 Review Answers
... 3. The stomach produces gastric juice, which is very acidic and can destroy bacteria. 4. The innate immune response is quick and general. The immune system does not have to recognize a particular antigen in order to respond. Since phagocytes are already in the blood or tissues, the response time is ...
... 3. The stomach produces gastric juice, which is very acidic and can destroy bacteria. 4. The innate immune response is quick and general. The immune system does not have to recognize a particular antigen in order to respond. Since phagocytes are already in the blood or tissues, the response time is ...
BIOL 495: Introduction to Immunology
... *Protective adaptations in higher organisms to rid the body of foreign particles (microbial and otherwise) and abnormal cells Our Immune system involves the interplay between our Non-specific and our Specific Immune responses Non-specific immunities collectively referred to as our Innate immunity ...
... *Protective adaptations in higher organisms to rid the body of foreign particles (microbial and otherwise) and abnormal cells Our Immune system involves the interplay between our Non-specific and our Specific Immune responses Non-specific immunities collectively referred to as our Innate immunity ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM How Do We Keep Our Bodies Healthy?
... biotoxins/detection/images/AntibodyMolecule.jpg ...
... biotoxins/detection/images/AntibodyMolecule.jpg ...
T cell

T cells or T lymphocytes are a type of lymphocyte (in turn, a type of white blood cell) that plays a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cells and natural killer cells (NK cells), by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on the cell surface. They are called T cells because they mature in the thymus (although some also mature in the tonsils). The several subsets of T cells each have a distinct function. The majority of human T cells rearrange their alpha/beta T cell receptors and are termed alpha beta T cells and are part of adaptive immune system. Specialized gamma delta T cells, which comprise a minority of T cells in the human body (more frequent in ruminants), have invariant TCR (with limited diversity), can effectively present antigens to other T cells and are considered to be part of the innate immune system.