PDF of PowerPoint
... The potential of stem cells capable of self-renewal-- can divide and renew themselves for long periods unspecialized cells that can differentiate into other types of cells ...
... The potential of stem cells capable of self-renewal-- can divide and renew themselves for long periods unspecialized cells that can differentiate into other types of cells ...
Igs and the Immune System
... immune system is thus presented with the shell of the invader, and can start producing antibodies against those antigens. Because we are exposed to millions of different antigens, the immune system has a method to distinguish occasional threats from persistent threats. If the immune system wasted al ...
... immune system is thus presented with the shell of the invader, and can start producing antibodies against those antigens. Because we are exposed to millions of different antigens, the immune system has a method to distinguish occasional threats from persistent threats. If the immune system wasted al ...
David Emerine Immune system Supplemental Instruction Nov 17
... It is similar to blood, but does not contain red blood cells and it does not contain many of the “plasma proteins” Lymph does contain white blood cells. Some large fats and proteins that can’t get into blood capillaries can enter lymph ...
... It is similar to blood, but does not contain red blood cells and it does not contain many of the “plasma proteins” Lymph does contain white blood cells. Some large fats and proteins that can’t get into blood capillaries can enter lymph ...
chapter 13 t-cell/b-cell cooperation in humoral immunity
... One unusual feature which has been recognized since ancient times is that the thymus starts out as a fairly large organ in very young animals (including humans) which continues to grow through early life, but then undergoes a process of involution or progressive degeneration and decrease in size, be ...
... One unusual feature which has been recognized since ancient times is that the thymus starts out as a fairly large organ in very young animals (including humans) which continues to grow through early life, but then undergoes a process of involution or progressive degeneration and decrease in size, be ...
acquired immunity
... • Cytokines stimulate aforementioned cells and also recruit new cells to the area, activate them ...
... • Cytokines stimulate aforementioned cells and also recruit new cells to the area, activate them ...
Ch46
... T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes target specific invaders. Antigen recognition and clonal selection. An antibody is specific for an antigen. Antibodies to many antigens can be produced. The clonal selection theory states that... 1. Lymphocytes have unique receptors on their surfaces that recognize th ...
... T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes target specific invaders. Antigen recognition and clonal selection. An antibody is specific for an antigen. Antibodies to many antigens can be produced. The clonal selection theory states that... 1. Lymphocytes have unique receptors on their surfaces that recognize th ...
Tolerance
... receptors that bind some self ligand with low avidity are selected to survive and mature further •Developing B cells receive survival signals simply because of expression of complete antigen receptors, without recognition of a self antigen. •However, as in T cells, self antigen of different affiniti ...
... receptors that bind some self ligand with low avidity are selected to survive and mature further •Developing B cells receive survival signals simply because of expression of complete antigen receptors, without recognition of a self antigen. •However, as in T cells, self antigen of different affiniti ...
Immunology Study of the components and function of the immune
... Following exposure to previously encountered antigen, there is a rapid rise in IgG and slow or no rise in IgM Memory or anamnestic response ...
... Following exposure to previously encountered antigen, there is a rapid rise in IgG and slow or no rise in IgM Memory or anamnestic response ...
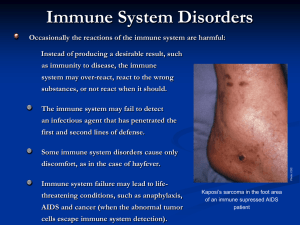
Immune System Disorders
... vigorous overreaction of the immune system to a previously encountered antigen. Mast cells are immune cells involved in allergic responses, they are non- motile, found around blood vessels, in connective tissue and in the lungs. Mast cells release active agents such as Histamine, which cause contrac ...
... vigorous overreaction of the immune system to a previously encountered antigen. Mast cells are immune cells involved in allergic responses, they are non- motile, found around blood vessels, in connective tissue and in the lungs. Mast cells release active agents such as Histamine, which cause contrac ...
Stem Cell Notes
... • Cells that form tissues communicate with one another to maintain the tissue by telling when and how to differentiate • These are often protein messengers • They must be identified and proliferated to help differentiate cells in vitro ...
... • Cells that form tissues communicate with one another to maintain the tissue by telling when and how to differentiate • These are often protein messengers • They must be identified and proliferated to help differentiate cells in vitro ...
4th Lecture
... The precursors of the macrophage and PMN develop from pluripotent stem cells that have become committed to the myeloid lineage Differentiation into macrophage or PMN is dependent on the interaction with specific colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) such as macrophage-CSF (M-CSF), granulocyte-CSF (G ...
... The precursors of the macrophage and PMN develop from pluripotent stem cells that have become committed to the myeloid lineage Differentiation into macrophage or PMN is dependent on the interaction with specific colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) such as macrophage-CSF (M-CSF), granulocyte-CSF (G ...
antigen processing and presentation
... T cells recognize peptide fragments which have been processed and presented by MHC molecules on APC. The MHC class I and class II molecules present peptides derived from endogenous and exogenous antigens, respectively. CD4 cells recognize antigen plus class II MHC molecules while CD8 cells recognize ...
... T cells recognize peptide fragments which have been processed and presented by MHC molecules on APC. The MHC class I and class II molecules present peptides derived from endogenous and exogenous antigens, respectively. CD4 cells recognize antigen plus class II MHC molecules while CD8 cells recognize ...
Nr - MWM-Vermittlung
... (iPS) cells, which are similar in many properties to natural stem cells. "Besides the fact that here ethical issues and political debates are less important than for embryonic stem (ES) cells, iPS cells have the advantage that they are tailored to the particular patient and therefore – unlike ES cel ...
... (iPS) cells, which are similar in many properties to natural stem cells. "Besides the fact that here ethical issues and political debates are less important than for embryonic stem (ES) cells, iPS cells have the advantage that they are tailored to the particular patient and therefore – unlike ES cel ...
ANTIGEN PROCESSING AND PRESENTATION
... T cells recognize peptide fragments which have been processed and presented by MHC molecules on APC. The MHC class I and class II molecules present peptides derived from endogenous and exogenous antigens, respectively. CD4 cells recognize antigen plus class II MHC molecules while CD8 cells recognize ...
... T cells recognize peptide fragments which have been processed and presented by MHC molecules on APC. The MHC class I and class II molecules present peptides derived from endogenous and exogenous antigens, respectively. CD4 cells recognize antigen plus class II MHC molecules while CD8 cells recognize ...
Exam Key 3 2008
... tumors (cancers) can undergo a transition from epithelial to mesenchymal (fibroblast like) where they downregulate epithelial markers and upregulate mesenchymal genes. As mesenchymal cells, they can move from primary site to secondary sites (metastasis). Thus, the mesenchymal cells are the ones that ...
... tumors (cancers) can undergo a transition from epithelial to mesenchymal (fibroblast like) where they downregulate epithelial markers and upregulate mesenchymal genes. As mesenchymal cells, they can move from primary site to secondary sites (metastasis). Thus, the mesenchymal cells are the ones that ...
Hematopoiesis: New ways to make a blood cell | eLife
... emerged in which a small number of selfrenewing stem cells give rise to multipotent progenitor cells, from which successive generations of progenitor cells can develop, each progressively more restricted in the types of cell they can develop into. Eventually the progenitor cells give rise to the dif ...
... emerged in which a small number of selfrenewing stem cells give rise to multipotent progenitor cells, from which successive generations of progenitor cells can develop, each progressively more restricted in the types of cell they can develop into. Eventually the progenitor cells give rise to the dif ...
the immune system - lpvec
... • nonspecific - the same response works against many pathogens • this type of response is the same no matter how often it is triggered • the types of cells involved are macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells, and mast cells • a soluble factor, complement, is also involved ...
... • nonspecific - the same response works against many pathogens • this type of response is the same no matter how often it is triggered • the types of cells involved are macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells, and mast cells • a soluble factor, complement, is also involved ...
insights - The Journal of Experimental Medicine
... et al. suggests that high levels of resolvins in the lung parenchyma have an important role to play, and the outcome of other infectious pneumonias may also depend on the appearance, or lack thereof, of resolvins and related lipids. However, unless tightly regulated, excessive activation of the inna ...
... et al. suggests that high levels of resolvins in the lung parenchyma have an important role to play, and the outcome of other infectious pneumonias may also depend on the appearance, or lack thereof, of resolvins and related lipids. However, unless tightly regulated, excessive activation of the inna ...
DEFENSE - Immune 15-16
... • skin – body’s first line of defense (also part of integumentary system) • white blood cells – recognize disease agents (antigens) and create antibodies to tag and remove these antigens. Macrophages are the white blood cell type that actually eat and destroy these antigens. Macrophage of a mouse ...
... • skin – body’s first line of defense (also part of integumentary system) • white blood cells – recognize disease agents (antigens) and create antibodies to tag and remove these antigens. Macrophages are the white blood cell type that actually eat and destroy these antigens. Macrophage of a mouse ...
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.Pathosis in lymphopoiesis leads to any of various lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias.