Respiratory tract defense mechanisms Mechanical lung host
... Humoral immune functions of the lung • Lymphocytes in the lung are found in submucosal collections known as bronchial associated lymphoid tissue (BALT); Ig may also diffuse into the lung • IgG, IgA, and IgE are all present in measurable amounts in the lung • IgA, IgG3 and IgG4 are present in greate ...
... Humoral immune functions of the lung • Lymphocytes in the lung are found in submucosal collections known as bronchial associated lymphoid tissue (BALT); Ig may also diffuse into the lung • IgG, IgA, and IgE are all present in measurable amounts in the lung • IgA, IgG3 and IgG4 are present in greate ...
Question 1 (1 point)
... e. Immediate hypersensitivity typically leads to granuloma formation. Save answer Question 19 (1 point) Mast cell degradulation and Eosinophil activation are associated with a. Th1 cells b. Th2 cells c. IgG d. INF-gamma e. macrophage activation Save answer Question 20 (1 point) A 22-year-old man who ...
... e. Immediate hypersensitivity typically leads to granuloma formation. Save answer Question 19 (1 point) Mast cell degradulation and Eosinophil activation are associated with a. Th1 cells b. Th2 cells c. IgG d. INF-gamma e. macrophage activation Save answer Question 20 (1 point) A 22-year-old man who ...
Chapter 7
... system that have V (variable) region(s) and those that don't cannot be overemphasized. Specific interactions typically take place via a V region, while non-specific interactions take place via non-variable molecules. Adaptive immunity is the ability of the immune system to learn and exhibit memory, ...
... system that have V (variable) region(s) and those that don't cannot be overemphasized. Specific interactions typically take place via a V region, while non-specific interactions take place via non-variable molecules. Adaptive immunity is the ability of the immune system to learn and exhibit memory, ...
Connective tissue mast cells
... One subunit binds cytokine, other are associated with cytoplasmic signaling molecules (protein kinases) Signaling subunit is shared by several different cytokine receptors - called receptor family ...
... One subunit binds cytokine, other are associated with cytoplasmic signaling molecules (protein kinases) Signaling subunit is shared by several different cytokine receptors - called receptor family ...
chapter 22 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... External Barriers to Invasion 1. The ________ is an inhospitable environment for ______________ growth 2. ________, _________ _________, and _____________ defend mucous membranes against microbes (Figure 22-2) B. ___________________ Internal Defenses Combat ____________ 1. __________________ cells a ...
... External Barriers to Invasion 1. The ________ is an inhospitable environment for ______________ growth 2. ________, _________ _________, and _____________ defend mucous membranes against microbes (Figure 22-2) B. ___________________ Internal Defenses Combat ____________ 1. __________________ cells a ...
The Adaptive Immune Response - Emmanuel Biology 12
... Small, bean-shaped lymph nodes sit along the lymphatic vessels, with clusters in the neck, armpits, abdomen, and groin. Each lymph node contains specialized compartments where immune cells congregate and encounter antigens. Immune cells and foreign particles enter the lymph nodes via incoming lympha ...
... Small, bean-shaped lymph nodes sit along the lymphatic vessels, with clusters in the neck, armpits, abdomen, and groin. Each lymph node contains specialized compartments where immune cells congregate and encounter antigens. Immune cells and foreign particles enter the lymph nodes via incoming lympha ...
Immune System Reading Guide
... When a microbe enters the body via a break in the skin, what is the body’s first line of defense? Include the term phagocytosis in your answer. Phagocytes are examples of a non-specific, cell mediated immune response. Outline the mechanism of how these cells work in your defense. Four types of leuko ...
... When a microbe enters the body via a break in the skin, what is the body’s first line of defense? Include the term phagocytosis in your answer. Phagocytes are examples of a non-specific, cell mediated immune response. Outline the mechanism of how these cells work in your defense. Four types of leuko ...
Chap 40 Immune Syst
... C. Vaccines prevent the body from responding to disease agents. D. Vaccines cause the body to create memory cells that are prepared to fight any future encounters with the disease organism. ...
... C. Vaccines prevent the body from responding to disease agents. D. Vaccines cause the body to create memory cells that are prepared to fight any future encounters with the disease organism. ...
1. T cells
... cells and virus-infected cells are destroyed. Tc is important in transplantation immunity, tumor immunity and viral infections. Recently, the presence of another subtype – regulatory T cell (Treg) – has been identified. Treg is considered to be involved in immune control, including suppression of au ...
... cells and virus-infected cells are destroyed. Tc is important in transplantation immunity, tumor immunity and viral infections. Recently, the presence of another subtype – regulatory T cell (Treg) – has been identified. Treg is considered to be involved in immune control, including suppression of au ...
3D Tumorscreening - Bayer research Magazine
... be transferred to humans. Only after the researchers have tested these aspects sufficiently can they send their active substances on the long road through clinical development. It will take at least ten years before these discoveries in the laboratory can be turned into a drug, but Steigemann is opt ...
... be transferred to humans. Only after the researchers have tested these aspects sufficiently can they send their active substances on the long road through clinical development. It will take at least ten years before these discoveries in the laboratory can be turned into a drug, but Steigemann is opt ...
Cells
... Macrophages are phagocytes that are constitutively present in tissues and respond rapidly to microbes that enter these tissues. Neutrophils, an abundant type of phagocyte, and monocytes, the precursors of tissue macrophages, are always present in the blood and can be quickly delivered anywhere in th ...
... Macrophages are phagocytes that are constitutively present in tissues and respond rapidly to microbes that enter these tissues. Neutrophils, an abundant type of phagocyte, and monocytes, the precursors of tissue macrophages, are always present in the blood and can be quickly delivered anywhere in th ...
Lymphocytes
... including; macrophages, lymphocytes and dendritic cells. T cells also can turn still other cells into auxiliary APC's by secreting gamma interferon (e.g. endothelial cells). 3. Subtypes of T cells carry out individual functions. Subtypes of T cells used to be named for their particular functions (“h ...
... including; macrophages, lymphocytes and dendritic cells. T cells also can turn still other cells into auxiliary APC's by secreting gamma interferon (e.g. endothelial cells). 3. Subtypes of T cells carry out individual functions. Subtypes of T cells used to be named for their particular functions (“h ...
Receptors
... • Recognition of self – cell recognise environmental cells., important for appropriate functions • Identification of lack of self – can start reaction (Ca decrease amount of MHC I molecules, that enable Natural Killers – NK cells – to destroy self cells) • Recognition of foreign – via 2 types of rec ...
... • Recognition of self – cell recognise environmental cells., important for appropriate functions • Identification of lack of self – can start reaction (Ca decrease amount of MHC I molecules, that enable Natural Killers – NK cells – to destroy self cells) • Recognition of foreign – via 2 types of rec ...
Antigen Presentation by B cells
... lymphocytes. (2) Lymph fluid percolates through the lymph nodes; the fluid is channeled to them from peripheral tissues, where dendritic cells collect antigenic material. In inflamed tissues, dendritic cells are mobilized to carry antigen to lymph nodes, where they stimulate antigen-specific T cells ...
... lymphocytes. (2) Lymph fluid percolates through the lymph nodes; the fluid is channeled to them from peripheral tissues, where dendritic cells collect antigenic material. In inflamed tissues, dendritic cells are mobilized to carry antigen to lymph nodes, where they stimulate antigen-specific T cells ...
Eman Mohamed Ali Hassan_Pathogenesis2
... multiple-step process that requires both stimulation of the TCR and several accessory signals delivered through other cell surface receptors. The sequence of activation events can be termed primary stimulation, costimulation, and mitotic stimulation (diagramed as steps 1, 2, and 3).The initial inter ...
... multiple-step process that requires both stimulation of the TCR and several accessory signals delivered through other cell surface receptors. The sequence of activation events can be termed primary stimulation, costimulation, and mitotic stimulation (diagramed as steps 1, 2, and 3).The initial inter ...
Specific Defenses of the Host - Suffolk County Community College
... -chemical messengers used within immune system (proteins or glycoproteins) -many kinds, each has specific message Cells = T cells -originate from stem cells in bone marrow but mature in thymus, travel to blood & lymph -each only recognizes one antigen -when it binds to antigen, will undergo clonal s ...
... -chemical messengers used within immune system (proteins or glycoproteins) -many kinds, each has specific message Cells = T cells -originate from stem cells in bone marrow but mature in thymus, travel to blood & lymph -each only recognizes one antigen -when it binds to antigen, will undergo clonal s ...
Static
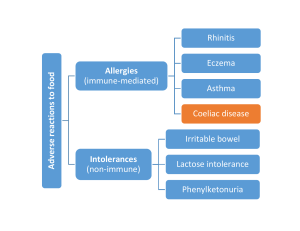
... Most people have no problem with gluten Thus disease attributable mainly to host factors ...
... Most people have no problem with gluten Thus disease attributable mainly to host factors ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. Explain the different types of antibody classes. 12. Describe cytosolic pathway involved in antigen presentation. 13. Define allograft. Describe the different types of transplantation rejection. 14. Bring out the role of tumour antigens in tumour immunology. 15. Explain the characteristic featur ...
... 11. Explain the different types of antibody classes. 12. Describe cytosolic pathway involved in antigen presentation. 13. Define allograft. Describe the different types of transplantation rejection. 14. Bring out the role of tumour antigens in tumour immunology. 15. Explain the characteristic featur ...
Cells and Organs of the Immune System
... All answers are correct. Loss of a spleen would be more detrimental to a child than an adult, primarily due to a pre-established immune response (B cells and their ability to produce specific antibodies) to bacterial antigens in the adult. In the adult, preexisting memory B cells surviving in other ...
... All answers are correct. Loss of a spleen would be more detrimental to a child than an adult, primarily due to a pre-established immune response (B cells and their ability to produce specific antibodies) to bacterial antigens in the adult. In the adult, preexisting memory B cells surviving in other ...
Innate immunity - Fadel Muhammad Garishah, MD
... Neutrophils and monocytes are recruited from the blood to sites of infection by binding to adhesion molecules on endothelial cells and by chemoattractants produced in response to the infection. ...
... Neutrophils and monocytes are recruited from the blood to sites of infection by binding to adhesion molecules on endothelial cells and by chemoattractants produced in response to the infection. ...
B cell - immunology.unideb.hu
... The maturation of CD4 T cells in the thymus depends on the interaction of thymocytes with MHC class II molecules on thymic epithelial cells. When the MHC class II genes are deleted genetically in mice, the mice also exhibit a deficiency of CD4 T lymphocytes. 2. Why did Helen have a low level of immu ...
... The maturation of CD4 T cells in the thymus depends on the interaction of thymocytes with MHC class II molecules on thymic epithelial cells. When the MHC class II genes are deleted genetically in mice, the mice also exhibit a deficiency of CD4 T lymphocytes. 2. Why did Helen have a low level of immu ...
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.Pathosis in lymphopoiesis leads to any of various lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias.