Chapter 8: The Immune Response
... the immune system will produce T lymphocytes that are sensitized to the antigen. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes will destroy the antigen, and T-memory cells will stay in the circulation and will recognize the antigen if the patient is exposed again. The humoral arm of the immune system produces B lymphocyt ...
... the immune system will produce T lymphocytes that are sensitized to the antigen. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes will destroy the antigen, and T-memory cells will stay in the circulation and will recognize the antigen if the patient is exposed again. The humoral arm of the immune system produces B lymphocyt ...
Training Handout for the Immune System
... such as the gut, respiratory tract and urogenital tract. Also found in saliva, tears, and breast milk. They attack microbes and prevents colonization by pathogens before they reach the blood stream so it is most important antibody in local immunity ...
... such as the gut, respiratory tract and urogenital tract. Also found in saliva, tears, and breast milk. They attack microbes and prevents colonization by pathogens before they reach the blood stream so it is most important antibody in local immunity ...
Immune Cells - Morgan Community College
... TH Cells Release Cytokines • Cytokines are chemicals that control the immune response – Inflammatory mediators: cause fever; attract WBCs to the infection ...
... TH Cells Release Cytokines • Cytokines are chemicals that control the immune response – Inflammatory mediators: cause fever; attract WBCs to the infection ...
Affinity and folding properties both influence the selection of
... encoding the w. t. scFv FITC-E2 [7], by the method of Kunkel [20], and confirmed by sequencing. The mutated scFv gene was recloned as a Sfii-Sfii cassette into the expression vector pAK400 [21], and recloned into the SIP vector. 2.3. Expression and purification of scFv fragments The soluble scFv fra ...
... encoding the w. t. scFv FITC-E2 [7], by the method of Kunkel [20], and confirmed by sequencing. The mutated scFv gene was recloned as a Sfii-Sfii cassette into the expression vector pAK400 [21], and recloned into the SIP vector. 2.3. Expression and purification of scFv fragments The soluble scFv fra ...
Unit 12 Chp 43 Animal Immune System Notes
... Thus T cells are alerted to an infectious agent after it has been internalized by a cell (through phagocytosis or receptor-mediated endocytosis), or after it has entered and replicated within a cell (through viral infection). ...
... Thus T cells are alerted to an infectious agent after it has been internalized by a cell (through phagocytosis or receptor-mediated endocytosis), or after it has entered and replicated within a cell (through viral infection). ...
cells of specific (acquired) immunity, after antigen recognition by
... polypeptide chains. H chains contain 1 variable and 3 eventually 4 constant domains (depending on immunoglobulin isotype). L chain possesses 1 variable and 1 constant domain. Variable domains of H and L chain combine together to form an antigen binding site. The heavy chain type (, µ, , , ) dete ...
... polypeptide chains. H chains contain 1 variable and 3 eventually 4 constant domains (depending on immunoglobulin isotype). L chain possesses 1 variable and 1 constant domain. Variable domains of H and L chain combine together to form an antigen binding site. The heavy chain type (, µ, , , ) dete ...
Cancer Immunotherapy-Maria
... interleukin-2 (IL-2), a potent growth factor for T cells; alpha-interferon (IFN-α) ...
... interleukin-2 (IL-2), a potent growth factor for T cells; alpha-interferon (IFN-α) ...
43_DetailLectOut_jkAR
... The immunoglobulin light-chain gene contains a series of 40 variable (V) gene segments separated by a long stretch of DNA from 5 joining (J) gene segments. Beyond the J gene segments is an intron, followed by a single exon that codes for the constant region of the light chain. In this state, t ...
... The immunoglobulin light-chain gene contains a series of 40 variable (V) gene segments separated by a long stretch of DNA from 5 joining (J) gene segments. Beyond the J gene segments is an intron, followed by a single exon that codes for the constant region of the light chain. In this state, t ...
Immunology and Cancer
... Antibody and complement Lymphokines and other cytokines Cell-Mediated Immunity: Cytotoxic T-Cells Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells) Activated Killer Cells Activated macrophages Lymphokine-activated Lymphocytes Granulocytes Combined Humoral and Cell-mediated: Antibody-dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxici ...
... Antibody and complement Lymphokines and other cytokines Cell-Mediated Immunity: Cytotoxic T-Cells Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells) Activated Killer Cells Activated macrophages Lymphokine-activated Lymphocytes Granulocytes Combined Humoral and Cell-mediated: Antibody-dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxici ...
Chapter 43 – The Immune System
... Once V-J rearrangement has occurred, the gene is transcribed and translated into a light chain with a variable and constant region. The light chains combine randomly with the heavy chains that are similarly produced. ...
... Once V-J rearrangement has occurred, the gene is transcribed and translated into a light chain with a variable and constant region. The light chains combine randomly with the heavy chains that are similarly produced. ...
Powerpoint - UCSF Immunology Program
... • They migrate rapidly to lymphoid T zones • They express high levels of costimulatory molecules for provoking activation of T cells • DC influence the differentiation pathway of the T cell in terms of cytokine induction and homing receptor profile ...
... • They migrate rapidly to lymphoid T zones • They express high levels of costimulatory molecules for provoking activation of T cells • DC influence the differentiation pathway of the T cell in terms of cytokine induction and homing receptor profile ...
Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of Tonsil
... Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma is a very rare entity. So far only 12 cases have been reported world wide with involvement of tonsil. We present a new case of follicurlar dendritic cell sarcoma of the tonsil in a 52 years old woman with no evidence of neck node involvement. She had undergone diagn ...
... Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma is a very rare entity. So far only 12 cases have been reported world wide with involvement of tonsil. We present a new case of follicurlar dendritic cell sarcoma of the tonsil in a 52 years old woman with no evidence of neck node involvement. She had undergone diagn ...
Human Pentraxin 3/TSG
... Mature secreted TSG14 contains a pentaxinlike domain at its carboxyterminus that shares 23 28% amino acid (aa) sequence similarity to Creactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid P component (SAP), which belongs to the short pentraxin subfamily. However, the Nterminal sequence of TSG14 does no ...
... Mature secreted TSG14 contains a pentaxinlike domain at its carboxyterminus that shares 23 28% amino acid (aa) sequence similarity to Creactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid P component (SAP), which belongs to the short pentraxin subfamily. However, the Nterminal sequence of TSG14 does no ...
Blood - cloudfront.net
... Occurs in red marrow (myeloid tissue) In adults: flat bones of skull and pelvis, ribs, sternum, proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur After formation, blood cells are sent into blood ...
... Occurs in red marrow (myeloid tissue) In adults: flat bones of skull and pelvis, ribs, sternum, proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur After formation, blood cells are sent into blood ...
Diseases of Immunity
... types. For example, IL-1 and TNF can be produced by any cell. The cytokines can act on many cell types, causing many different effects. For example, IL-2 is a T-cell growth factor; however, it is also regulate the growth and differentiation of B cells and NK cells. Multiple cytokines may induce simi ...
... types. For example, IL-1 and TNF can be produced by any cell. The cytokines can act on many cell types, causing many different effects. For example, IL-2 is a T-cell growth factor; however, it is also regulate the growth and differentiation of B cells and NK cells. Multiple cytokines may induce simi ...
Blood
... During pregnancy with subsequent Rh+ child, anti-Rh IgG can cross placenta and cause hemolytic disease of newborn (less problem if Rhogam is administered during first delivery) Transfusions are typically restricted to matching Rh+ donor to Rh+ recipient. Rh - recipients should not be given Rh+ blood ...
... During pregnancy with subsequent Rh+ child, anti-Rh IgG can cross placenta and cause hemolytic disease of newborn (less problem if Rhogam is administered during first delivery) Transfusions are typically restricted to matching Rh+ donor to Rh+ recipient. Rh - recipients should not be given Rh+ blood ...
CHAPTER 43
... Lecture Outline for Reece et al., Campbell Biology, 10th Edition, Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Lecture Outline for Reece et al., Campbell Biology, 10th Edition, Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Antigen
... of the antigen and production of cellular or humoral response • Antigenicity - ability of raction with products of cellular or humoral response • Specificity – reaction of antibody or specific lymphocytes with epitope ...
... of the antigen and production of cellular or humoral response • Antigenicity - ability of raction with products of cellular or humoral response • Specificity – reaction of antibody or specific lymphocytes with epitope ...
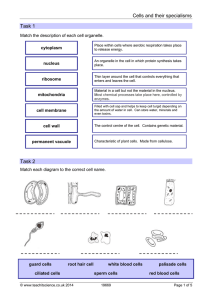
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
SCI 30 UA CH 1.5 TEXT - Fort Saskatchewan High
... reproduce by infecting a host cell and injecting their genetic material into it, turning the host cell into a virus-making factory. Once new viruses are produced, the host cell ruptures and releases virus particles to infect more host cells. Antiviral drugs attempt to stop the infection of cells by ...
... reproduce by infecting a host cell and injecting their genetic material into it, turning the host cell into a virus-making factory. Once new viruses are produced, the host cell ruptures and releases virus particles to infect more host cells. Antiviral drugs attempt to stop the infection of cells by ...
File
... This secreted protein is called an antibody, or immunoglobulin (Ig). o Antibodies have the same Y-shaped organization as B cell antigen receptors, but they are secreted rather than membrane-bound. o It is the antibodies, rather than the B cells themselves, that actually help defend against pathogens ...
... This secreted protein is called an antibody, or immunoglobulin (Ig). o Antibodies have the same Y-shaped organization as B cell antigen receptors, but they are secreted rather than membrane-bound. o It is the antibodies, rather than the B cells themselves, that actually help defend against pathogens ...
File
... This secreted protein is called an antibody, or immunoglobulin (Ig). o Antibodies have the same Y-shaped organization as B cell antigen receptors, but they are secreted rather than membrane-bound. o It is the antibodies, rather than the B cells themselves, that actually help defend against pathogens ...
... This secreted protein is called an antibody, or immunoglobulin (Ig). o Antibodies have the same Y-shaped organization as B cell antigen receptors, but they are secreted rather than membrane-bound. o It is the antibodies, rather than the B cells themselves, that actually help defend against pathogens ...
B-cell receptor signal strength and zinc signaling: unraveling the
... The humoral immune response, alongside cell-mediated immunity, in which B cells play crucial roles, form the primary arms of the adaptive immune system. Resting mature follicular (FO) B cells in the spleen are essential for antibody-mediated immune responses. They recirculate through the blood, and ...
... The humoral immune response, alongside cell-mediated immunity, in which B cells play crucial roles, form the primary arms of the adaptive immune system. Resting mature follicular (FO) B cells in the spleen are essential for antibody-mediated immune responses. They recirculate through the blood, and ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.