Meiosis - DigitalWebb.com
... o DNA topoisomerase I “unwinds” the DNA by introducing negative supercoils. DNA gyrase also introduces negative supercoils. By this, they relax DNA to form an open complex. Once the DNA is opened, the core enzyme latches onto the DNA. The core enzyme slides upstream and down stream of the DNA but ca ...
... o DNA topoisomerase I “unwinds” the DNA by introducing negative supercoils. DNA gyrase also introduces negative supercoils. By this, they relax DNA to form an open complex. Once the DNA is opened, the core enzyme latches onto the DNA. The core enzyme slides upstream and down stream of the DNA but ca ...
1 Biol 3301 Genetics Exam #2A October 26, 2004
... a) Sigma factor directs RNA polymerase to the promoter by binding the –10 and –35 regions. b) Sigma factor directs RNA polymerase to the promoter by binding the TATA box. c) Rho directs RNA polymerase to the promoter by binding the –10 and –35 regions. d) TFIID directs RNA polymerase to the promoter ...
... a) Sigma factor directs RNA polymerase to the promoter by binding the –10 and –35 regions. b) Sigma factor directs RNA polymerase to the promoter by binding the TATA box. c) Rho directs RNA polymerase to the promoter by binding the –10 and –35 regions. d) TFIID directs RNA polymerase to the promoter ...
JRA1 - Del. 4.3
... Thermal-age.eu is the site for designed to help collections managers and users to quantify the risks associated with destructive analysis of specimens. The website originally to be entitled PrediCtoR was to predict amplification success of PCR, in particular to highlight the importance of sample siz ...
... Thermal-age.eu is the site for designed to help collections managers and users to quantify the risks associated with destructive analysis of specimens. The website originally to be entitled PrediCtoR was to predict amplification success of PCR, in particular to highlight the importance of sample siz ...
Document
... 13. Which statement describes the correct order of events in translation elongation? Answer: e a) The ternary complex binds to the A site, EF-Tu leaves, peptidyl transferase forms a peptide bond, EF-G hydrolyzes ATP to translocate the peptidyl tRNA to the P site, tRNA leaves the E site. b) The terna ...
... 13. Which statement describes the correct order of events in translation elongation? Answer: e a) The ternary complex binds to the A site, EF-Tu leaves, peptidyl transferase forms a peptide bond, EF-G hydrolyzes ATP to translocate the peptidyl tRNA to the P site, tRNA leaves the E site. b) The terna ...
Chem 465 Biochemistry II Hour Exam 2
... C) is the principal DNA polymerase in chromosomal DNA replication. D) represents over 90% of the DNA polymerase activity in E. coli cells. E) requires a free 5'-hydroxyl group as a primer. ...
... C) is the principal DNA polymerase in chromosomal DNA replication. D) represents over 90% of the DNA polymerase activity in E. coli cells. E) requires a free 5'-hydroxyl group as a primer. ...
DNA Mutations
... arteries, thus leading to less heart disease risk. Defective myostatin genes leads to immense muscle strength NTRK1 gene mutation results in loss of all pain and sensations. ...
... arteries, thus leading to less heart disease risk. Defective myostatin genes leads to immense muscle strength NTRK1 gene mutation results in loss of all pain and sensations. ...
Cancer is known as a real threat to human health
... infection by cytomegalovirus gives no symptoms, but in patients with weak immune system, like patient suffering from AIDS, clinical disease is more prevalent. The interaction between virus and host plays a key role for determining the outcome of infection. Viruses, including cytomegalovirus, likely ...
... infection by cytomegalovirus gives no symptoms, but in patients with weak immune system, like patient suffering from AIDS, clinical disease is more prevalent. The interaction between virus and host plays a key role for determining the outcome of infection. Viruses, including cytomegalovirus, likely ...
Protein Synthesis – Level 1
... Protein Synthesis – Level 3 Use the following DNA sequence to answer the questions that follow: ...
... Protein Synthesis – Level 3 Use the following DNA sequence to answer the questions that follow: ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
... Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
Molecular genetics of bacteria
... Simultaneous transcription and translation allows them to synthesize the proteins they need quickly. Wasteful activities are avoided. If there are sufficient amounts of some metabolite, bacteria will avoid making more AND avoid making the enzymes that make the metabolite. Biosynthesis costs! Biochem ...
... Simultaneous transcription and translation allows them to synthesize the proteins they need quickly. Wasteful activities are avoided. If there are sufficient amounts of some metabolite, bacteria will avoid making more AND avoid making the enzymes that make the metabolite. Biosynthesis costs! Biochem ...
Biological Macromolecules
... – Composed of chains of amino acids – There are 20 different amino acids, each with distinctive chemical properties – A protein molecule may contain several hundred amino acids – Each different protein has its own order, or “sequence,” of amino acids – The correct sequence of amino acids is essentia ...
... – Composed of chains of amino acids – There are 20 different amino acids, each with distinctive chemical properties – A protein molecule may contain several hundred amino acids – Each different protein has its own order, or “sequence,” of amino acids – The correct sequence of amino acids is essentia ...
Ei dian otsikkoa
... - In plants, exogenous DNA transfer elicites a wound response which activates nucleases and DNA repair enzymes. The transferred DNA is thus, either degraded or used as a substrate for DNA repair, resulting in its potential rearrangement and incorporation in the genomic DNA (Takano et al. (1997) Plan ...
... - In plants, exogenous DNA transfer elicites a wound response which activates nucleases and DNA repair enzymes. The transferred DNA is thus, either degraded or used as a substrate for DNA repair, resulting in its potential rearrangement and incorporation in the genomic DNA (Takano et al. (1997) Plan ...
Gene7-16
... Alu family is a set of dispersed, related sequences, each ~300 bp long, in the human genome. The individual members have Alu cleavage sites at each end (hence the name). Processed pseudogene is an inactive gene copy that lacks introns, contrasted with the interrupted structure of the active gene. Su ...
... Alu family is a set of dispersed, related sequences, each ~300 bp long, in the human genome. The individual members have Alu cleavage sites at each end (hence the name). Processed pseudogene is an inactive gene copy that lacks introns, contrasted with the interrupted structure of the active gene. Su ...
Origin of Life - stephen fleenor
... into polymers (DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids) These molecules began self-replicating in water ...
... into polymers (DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids) These molecules began self-replicating in water ...
Taxonomy
... - anatomical characteristics - phenotypic characteristics - genetic characteristics - evolutionary links ...
... - anatomical characteristics - phenotypic characteristics - genetic characteristics - evolutionary links ...
here - Triticeae CAP
... example, there are two possibilities (called alleles) for this marker – allele A and allele B. The seed from each individual was also tested for percent protein and is graphed above (allele A individuals in green and allele B in blue). Most of the individuals with the A marker type have lower protei ...
... example, there are two possibilities (called alleles) for this marker – allele A and allele B. The seed from each individual was also tested for percent protein and is graphed above (allele A individuals in green and allele B in blue). Most of the individuals with the A marker type have lower protei ...
Cauliflower mosaic virus: still in the news
... aspects of recent studies on CaMV. The evolution of CaMV and its standing relative to other Caulimoviridae are not discussed. ...
... aspects of recent studies on CaMV. The evolution of CaMV and its standing relative to other Caulimoviridae are not discussed. ...
What is the difference between Autotrophs and heterotrophs?
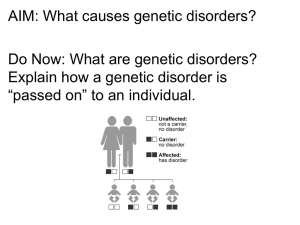
... b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g. gene located on the X or Y chromosome ...
... b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g. gene located on the X or Y chromosome ...
Karina Espinoza - Werner Syndrome
... Sequence Analysis- of WRN coding region to detect mutations Results- 90% of individuals with Werner’s Syndrome showed mutations in the WRN gene Western Blot Analysis- determines the effect of the mutation on the WRN protein Results- majority of affected individuals with WRN mutations absenc ...
... Sequence Analysis- of WRN coding region to detect mutations Results- 90% of individuals with Werner’s Syndrome showed mutations in the WRN gene Western Blot Analysis- determines the effect of the mutation on the WRN protein Results- majority of affected individuals with WRN mutations absenc ...
Session 2 – Origin of Life
... gave us homo-oligomer (all monomers/amino acids are the same) Living organisms are composed on 20 different amino acids, not just one The last problem is that the exclusive ‘lefthandedness’ required for living things is destroyed by heating. They didn’t test this though because they used the simples ...
... gave us homo-oligomer (all monomers/amino acids are the same) Living organisms are composed on 20 different amino acids, not just one The last problem is that the exclusive ‘lefthandedness’ required for living things is destroyed by heating. They didn’t test this though because they used the simples ...
Difference between RNA and DNA
... reading the mRNA code strip in groups of 3 letters called ___________. 7. Each time the ribosome reads 3 letters on the mRNA, it calls for another molecule called a _________, which carries an amino acid. (tRNA stands for ________________ RNA) ...
... reading the mRNA code strip in groups of 3 letters called ___________. 7. Each time the ribosome reads 3 letters on the mRNA, it calls for another molecule called a _________, which carries an amino acid. (tRNA stands for ________________ RNA) ...
Life on Mars
... electric current is passed through the gel, and because the DNA fragments are negatively charged, they are drawn towards the positive electrode. The smaller the DNA fragment, the faster it travels along the gel. This results in DNA separation by size, with the smaller fragments migrating further tha ...
... electric current is passed through the gel, and because the DNA fragments are negatively charged, they are drawn towards the positive electrode. The smaller the DNA fragment, the faster it travels along the gel. This results in DNA separation by size, with the smaller fragments migrating further tha ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.