amino acids
... ● results in a “backbone” with a repeating pattern of sugar-phosphatesugar-phosphate... ...
... ● results in a “backbone” with a repeating pattern of sugar-phosphatesugar-phosphate... ...
DNA WebQuest
... J. What is Your DNA Alias? (You DO NOT need the computer to do this part!) We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. T ...
... J. What is Your DNA Alias? (You DO NOT need the computer to do this part!) We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. T ...
Evolution of Populations
... • Population genetics: the study of genetic variability within populations • Gene pool: combined aggregate of genes in a population at any one time • Species: a group of populations that have the potential to interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature ...
... • Population genetics: the study of genetic variability within populations • Gene pool: combined aggregate of genes in a population at any one time • Species: a group of populations that have the potential to interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature ...
Jet-swirl nozzle design for producing nanoscale polymer
... How is the information transferred to protein? • The enzyme RNA polymerase reads a specific nucleotide sequence • (gene) from the DNA template while proteins called transcription factors facilitate the copying • Copies are made in the form of Ribonucleic acid (RNA) • RNA resembles DNA except: – -ba ...
... How is the information transferred to protein? • The enzyme RNA polymerase reads a specific nucleotide sequence • (gene) from the DNA template while proteins called transcription factors facilitate the copying • Copies are made in the form of Ribonucleic acid (RNA) • RNA resembles DNA except: – -ba ...
10th Grade Genetics Content - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... Standard 6.4.B The scientific investigation of cellular chemistry enables the biotechnology industry to produce medicines foods and other products for the benefit of society (Essential) Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections ...
... Standard 6.4.B The scientific investigation of cellular chemistry enables the biotechnology industry to produce medicines foods and other products for the benefit of society (Essential) Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections ...
Document
... can they be reunited? If a body is found and the person cannot be identified by looks, how can we identify them? What types of identifiers do we have? ...
... can they be reunited? If a body is found and the person cannot be identified by looks, how can we identify them? What types of identifiers do we have? ...
recBCD
... recBCD Pathway of Homologous Recombination •RecBCD binds an end of linear dsDNA •RecD helicase travels on the strand with a 5' end and RecB on the strand with a 3' end •RecB is slower than RecD, so that a ssDNA loop accumulates ahead of RecB •This produces DNA structures with two ss tails and one s ...
... recBCD Pathway of Homologous Recombination •RecBCD binds an end of linear dsDNA •RecD helicase travels on the strand with a 5' end and RecB on the strand with a 3' end •RecB is slower than RecD, so that a ssDNA loop accumulates ahead of RecB •This produces DNA structures with two ss tails and one s ...
Printable Version
... The general term for the cells in your body that are not directly involved with reproduction. Most cells in multicellular plants and animals are of this type. The general term for the specialized cells in your body that are created for sexual reproduction. These cells are also called gametes. The ce ...
... The general term for the cells in your body that are not directly involved with reproduction. Most cells in multicellular plants and animals are of this type. The general term for the specialized cells in your body that are created for sexual reproduction. These cells are also called gametes. The ce ...
Population genetics as a means to explore
... species not currently in existence Question of origin spawned many hypotheses 1831 voyage of amateur naturalist Charles Darwin along with 1854 exploration of naturalist Alfred Wallace gave enough evidence for both to propose theory of evolution of populations of organisms via natural selection ...
... species not currently in existence Question of origin spawned many hypotheses 1831 voyage of amateur naturalist Charles Darwin along with 1854 exploration of naturalist Alfred Wallace gave enough evidence for both to propose theory of evolution of populations of organisms via natural selection ...
The Genetic Science Glossary - Canadian Council of Churches
... is present to speed up, or catalyze, the reaction. For example, the enzyme called acetylcholinesterase catalyzes (speeds up) the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is released by nerve cells and received by muscle cells, causing the muscle cells to contract. If acetylchol ...
... is present to speed up, or catalyze, the reaction. For example, the enzyme called acetylcholinesterase catalyzes (speeds up) the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is released by nerve cells and received by muscle cells, causing the muscle cells to contract. If acetylchol ...
DNA_Replication 2015
... – Negative supercoiling: double helix is underwound – Positive supercoiling: double helix is overwound ...
... – Negative supercoiling: double helix is underwound – Positive supercoiling: double helix is overwound ...
Document
... DNA: basis of Inheritance & reproduction. Obtain, process, & use energy via metabolism. Sense & respond to changes in environment. Maintain homeostasis: “A state where the internal environment is maintained within a range life can ...
... DNA: basis of Inheritance & reproduction. Obtain, process, & use energy via metabolism. Sense & respond to changes in environment. Maintain homeostasis: “A state where the internal environment is maintained within a range life can ...
Monohybrid Crosses
... Codons, DNA triplets, code for one amino acid. Amino acids link together to form polypeptides-chain containing 2 or more amino acids Polypeptides make up proteins. Genes code for polypeptides. Gene- a specific sequence of nucleotides forming part of a chromosome that codes for a trait (protein) Codo ...
... Codons, DNA triplets, code for one amino acid. Amino acids link together to form polypeptides-chain containing 2 or more amino acids Polypeptides make up proteins. Genes code for polypeptides. Gene- a specific sequence of nucleotides forming part of a chromosome that codes for a trait (protein) Codo ...
Document
... on the hybridization between the nucleotide. Using this technology the presence of one genomic or cDNA sequence in 1,00,000 or more sequences can be screened in a single hybridization. The property of complementary nucleic acid sequences is to specifically pair with each other by forming hydrogen bo ...
... on the hybridization between the nucleotide. Using this technology the presence of one genomic or cDNA sequence in 1,00,000 or more sequences can be screened in a single hybridization. The property of complementary nucleic acid sequences is to specifically pair with each other by forming hydrogen bo ...
Genetic Engineering Genetically
... • Translate DNA into protein • Explain the process of gene expression ...
... • Translate DNA into protein • Explain the process of gene expression ...
evidences for evolution
... -This variation that the parents were born with themselves, can be passed to their offspring...as long as the variation is in the DNA and the DNA is passed in the gametes. Darwin found human’s already picking traits that they wanted in pets (Artificial Selection) and so he ...
... -This variation that the parents were born with themselves, can be passed to their offspring...as long as the variation is in the DNA and the DNA is passed in the gametes. Darwin found human’s already picking traits that they wanted in pets (Artificial Selection) and so he ...
Mrs Single`s Genetics Powerpoint
... It is the chemical substance that codes for the inheritable characteristics of living things, like ...
... It is the chemical substance that codes for the inheritable characteristics of living things, like ...
BACTERIA TRANSFORMATION LAB (ACTIVITY)
... a bacterial plasmid, and then cut these two DNA molecules into fragments using special enzymes called restriction enzymes. The DNA fragments are spliced together with an enzyme called ligase. Finally the engineered plasmid is taken up by a bacterial cell for replication and expression of the inserte ...
... a bacterial plasmid, and then cut these two DNA molecules into fragments using special enzymes called restriction enzymes. The DNA fragments are spliced together with an enzyme called ligase. Finally the engineered plasmid is taken up by a bacterial cell for replication and expression of the inserte ...
Biol 207 Dr. Locke`s section WS9 Page 1 Workshop 9 Biol207
... transformed 0.02 µg of pAT1 into 100 µL of E. coli. Then they added 900 µL of LB and incubated the mixture for 45 min at 37°C. They did a 1/10 dilution three times before a 100 µL aliquot was added to an ampicillin plate. After incubating the plate overnight at 37°C they had 78 colonies. (Helpful no ...
... transformed 0.02 µg of pAT1 into 100 µL of E. coli. Then they added 900 µL of LB and incubated the mixture for 45 min at 37°C. They did a 1/10 dilution three times before a 100 µL aliquot was added to an ampicillin plate. After incubating the plate overnight at 37°C they had 78 colonies. (Helpful no ...
1.5 Page 4 - csfcbiology
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
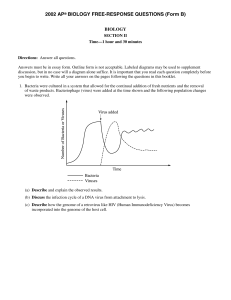
2002 AP Biology Free-Response Questions Form B
... co-existence phase (viruses multiply only in non-resistant/“sensitive” cells or lysogenic situation develops) exceptional description of a particular phase population reaches an equilibrium ...
... co-existence phase (viruses multiply only in non-resistant/“sensitive” cells or lysogenic situation develops) exceptional description of a particular phase population reaches an equilibrium ...
Efficient Restriction Enzyme Digestion of Saliva DNA isolated using
... 35700). Donors simply collect their saliva directly into the ...
... 35700). Donors simply collect their saliva directly into the ...
Transcription
... • The DNA is unwound and becomes single-stranded in the vicinity of the initiation site (defined as +1). • 1st poly reaction catalyzed by RNA pol and transcription initiation complex is formed ...
... • The DNA is unwound and becomes single-stranded in the vicinity of the initiation site (defined as +1). • 1st poly reaction catalyzed by RNA pol and transcription initiation complex is formed ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.