Functional characterization of LePGT1, a membrane
... the enzymatic activity. A detailed kinetic analysis of mutant enzymes revealed the amino acid residues responsible for substrate binding were also identified. Contrary to ubiquinone biosynthetic PPTs, such as UBIA in Escherichia coli which accepts many prenyl substrates of different chain lengths, L ...
... the enzymatic activity. A detailed kinetic analysis of mutant enzymes revealed the amino acid residues responsible for substrate binding were also identified. Contrary to ubiquinone biosynthetic PPTs, such as UBIA in Escherichia coli which accepts many prenyl substrates of different chain lengths, L ...
An extreme cytoplasmic bottleneck in the modern European
... We have used the polymorphic chloroplast (cp) and nuclear simple sequence repeats (SSRs) to analyse levels of cytoplasmic and nuclear diversity in the gene pool of the European cultivated potato (Solanum tuberosum ssp. tuberosum). Primers designed from the complete chloroplast sequence of tobacco (N ...
... We have used the polymorphic chloroplast (cp) and nuclear simple sequence repeats (SSRs) to analyse levels of cytoplasmic and nuclear diversity in the gene pool of the European cultivated potato (Solanum tuberosum ssp. tuberosum). Primers designed from the complete chloroplast sequence of tobacco (N ...
Chapter 11
... animal farming is in the addition of human genes to the genes of farm animals in order to get the farm animals to produce human proteins in their milk. • The animals are called transgenic animals because they have foreign DNA in their cells. ...
... animal farming is in the addition of human genes to the genes of farm animals in order to get the farm animals to produce human proteins in their milk. • The animals are called transgenic animals because they have foreign DNA in their cells. ...
Natural Selection and the Origin of Modules
... unresolved. In principle selection for evolvability is possible, in particular in asexual species. The mechanism is a simple Darwinian selection process based on a differential in mean fitness between clones caused by differences in the rate of adaptation among clones (Wagner, 1981). Experimentally ...
... unresolved. In principle selection for evolvability is possible, in particular in asexual species. The mechanism is a simple Darwinian selection process based on a differential in mean fitness between clones caused by differences in the rate of adaptation among clones (Wagner, 1981). Experimentally ...
XIST
... Models of Tsix-mediated repression of Xist. (A) Tsix DNA sequence itself could function as a long-range silencer to repress or block the transcription of the Xist gene. (B) Transcription of Xist may be prohibited by the processivity of RNA polymerase in the antisense orientation. As RNA polymerase ...
... Models of Tsix-mediated repression of Xist. (A) Tsix DNA sequence itself could function as a long-range silencer to repress or block the transcription of the Xist gene. (B) Transcription of Xist may be prohibited by the processivity of RNA polymerase in the antisense orientation. As RNA polymerase ...
Conformational Changes in HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Induced
... 11-Cyclopropyl-4-methyl-5,11-dihydro-6H-dipyrido[3,2-b:2', 3'-e][1,4]diazepin-6-one (nevirapine; Fig. (1a)); 1-[3-[(1methylethyl)amino]-2-pyridinyl]-4-[[5-[(methylsulfonyl) amino]-1H-indol-2-yl]carbonyl]-piperazine (delavirdine; Fig. (1 b )); and (4S)-6-chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4trifluoromethyl-1 ...
... 11-Cyclopropyl-4-methyl-5,11-dihydro-6H-dipyrido[3,2-b:2', 3'-e][1,4]diazepin-6-one (nevirapine; Fig. (1a)); 1-[3-[(1methylethyl)amino]-2-pyridinyl]-4-[[5-[(methylsulfonyl) amino]-1H-indol-2-yl]carbonyl]-piperazine (delavirdine; Fig. (1 b )); and (4S)-6-chloro-4-cyclopropylethynyl-4trifluoromethyl-1 ...
... b) Regulation of glycolysis d) Regulation of mRNA synthesis. 1. Allosteric effects refer to the fact that a protein/enzyme has two structures. 2. One structure is “active” (R-state) the other structure is “inactive” (T-state). 3. The two states are in equilibrium with each other, so the system can b ...
ExamView - Test 2 Ch 5-9 Take Home Exam DUE IN CLASS NO
... a. increasing the amount of free energy of the reaction. b. lowering the activation energy of the reaction. c. decreasing the equilibrium constant of the reaction. d. supplying energy to speed up the reaction. e. changing the shape of the active site. ____ 23. The statement “enzymes are highly speci ...
... a. increasing the amount of free energy of the reaction. b. lowering the activation energy of the reaction. c. decreasing the equilibrium constant of the reaction. d. supplying energy to speed up the reaction. e. changing the shape of the active site. ____ 23. The statement “enzymes are highly speci ...
Resume - TILT - Colorado State University
... We extended our methodologies for the synthesis of -substituted -amino acids and substituted -amino acids which is being given more importance in recent years. This process also involves the conjugate addition of N-benzylhydroxylamine to the respective substituted and unsaturated imides using ca ...
... We extended our methodologies for the synthesis of -substituted -amino acids and substituted -amino acids which is being given more importance in recent years. This process also involves the conjugate addition of N-benzylhydroxylamine to the respective substituted and unsaturated imides using ca ...
Polymorphism of Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Gene among Chicken
... chicken breeds clearly demonstrated that the Cobb 500 breed was the fastest growing one with the best feed conversion rate (FCR) among the studied breeds, whereas the Sasso breed was the slowest growing one as shown in Table I. Amplicons of the expected sizes were obtained from RT-PCR of different a ...
... chicken breeds clearly demonstrated that the Cobb 500 breed was the fastest growing one with the best feed conversion rate (FCR) among the studied breeds, whereas the Sasso breed was the slowest growing one as shown in Table I. Amplicons of the expected sizes were obtained from RT-PCR of different a ...
- Philsci-Archive
... believe this relationship to possess which leads them to think of it as specific -- and only secondarily with the complicated and controversial question of whether the relationship in fact possesses these features. For example, some will hold that it is more accurate to think of the causal specifici ...
... believe this relationship to possess which leads them to think of it as specific -- and only secondarily with the complicated and controversial question of whether the relationship in fact possesses these features. For example, some will hold that it is more accurate to think of the causal specifici ...
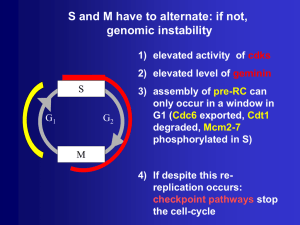
No Slide Title
... • Use in prognosis: e.g. tumors with high S phase fraction detected by flow cytometry have poorer prognosis • Use in predicting responsiveness to a particular type of therapy: e.g. high S phase fraction and loss of p53 will make cells more suceptible to DNA damaging agents ...
... • Use in prognosis: e.g. tumors with high S phase fraction detected by flow cytometry have poorer prognosis • Use in predicting responsiveness to a particular type of therapy: e.g. high S phase fraction and loss of p53 will make cells more suceptible to DNA damaging agents ...
Core promoter
... Many INR-promoters have activating sites for Sp1 when an Inr is inserted into a synthetic promoter downstream of six binding sites for transcription factor Sp1, the Inr supports high levels of transcription that initiate at a specific start site within the Inr. act synergistically when separated by ...
... Many INR-promoters have activating sites for Sp1 when an Inr is inserted into a synthetic promoter downstream of six binding sites for transcription factor Sp1, the Inr supports high levels of transcription that initiate at a specific start site within the Inr. act synergistically when separated by ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 5 Notes
... Inhibitor competes with substrates for binding to active site Inhibitor is similar in structure to substrate binds more strongly reacts more slowly Increasing [I] increases [EI] and reduces [E] that is available for substrate binding Need to constantly keep [I] high for effective inhibition (cannot ...
... Inhibitor competes with substrates for binding to active site Inhibitor is similar in structure to substrate binds more strongly reacts more slowly Increasing [I] increases [EI] and reduces [E] that is available for substrate binding Need to constantly keep [I] high for effective inhibition (cannot ...
Structure of a Plasmodium yoelii gene
... contain stretches of very conserved amino acid sequences; the site of phosphorylation (James et al. 1987), the FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate)-binding region (believed to be a part of ATP binding region) (Filoteo et al. 1987) and the FSBA (5'-p-fluorosulfonyl-benzoyladenosine; an analog of ATP)-bi ...
... contain stretches of very conserved amino acid sequences; the site of phosphorylation (James et al. 1987), the FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate)-binding region (believed to be a part of ATP binding region) (Filoteo et al. 1987) and the FSBA (5'-p-fluorosulfonyl-benzoyladenosine; an analog of ATP)-bi ...
Genetic mapping of mutations using phenotypic pools and
... in Fig. 2C. For example, at an amplification potential of 0.025, median window size decreases smoothly as pool size increases from 5 to 20 individuals. However, when pool size increases by 1 more, to 21 individuals, median window size jumps abruptly from 5 to 10 recombination units. There are simila ...
... in Fig. 2C. For example, at an amplification potential of 0.025, median window size decreases smoothly as pool size increases from 5 to 20 individuals. However, when pool size increases by 1 more, to 21 individuals, median window size jumps abruptly from 5 to 10 recombination units. There are simila ...
Distinguishing Different DNA Heterozygotes by
... These are not identical because such curves are skewed at low temperatures from heteroduplex contributions. In either case, the Tm is only one point on the melting curve. Use of the complete melting curve, conveniently displayed as difference plots, allows differentiation of most heterozygotes (21 o ...
... These are not identical because such curves are skewed at low temperatures from heteroduplex contributions. In either case, the Tm is only one point on the melting curve. Use of the complete melting curve, conveniently displayed as difference plots, allows differentiation of most heterozygotes (21 o ...
MECHANISTIC STUDIES ON THE MONOAMINE OXIDASE B
... from the active site, and the proximity of an appropriate nucleophile, radical or electrophile on the enzyme for covalent bond formation. Mechanism based inactivators have proven to be useful in the study of enzyme mechanisms. The value of these inactivators in the study of enzyme mechanisms is deri ...
... from the active site, and the proximity of an appropriate nucleophile, radical or electrophile on the enzyme for covalent bond formation. Mechanism based inactivators have proven to be useful in the study of enzyme mechanisms. The value of these inactivators in the study of enzyme mechanisms is deri ...
arXiv:0708.2724v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Aug 2007
... chemical techniques and physical differences of strands of DNA. Most importantly, these proposals challenge our understanding of, and ability to manipulate and probe, physical processes at the interface between solids, liquids, and biomolecules down to the nanometer scale regime (Di Ventra et al., 2 ...
... chemical techniques and physical differences of strands of DNA. Most importantly, these proposals challenge our understanding of, and ability to manipulate and probe, physical processes at the interface between solids, liquids, and biomolecules down to the nanometer scale regime (Di Ventra et al., 2 ...
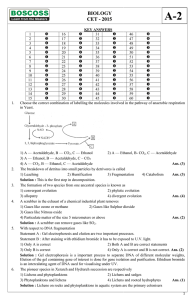
Bio CET 2015 Key Answers
... 1) a polypeptide of 24 amino acids is formed. 2) a polypeptide of 124 amino acids is formed. 3) No polypeptides are formed. 4) a polypeptide of 25 amino acids is formed. Ans. (1) th Solution : 24 amino acids are coded the 25 UAA is a termination rmination sequence with no amino acid. Three copies of ...
... 1) a polypeptide of 24 amino acids is formed. 2) a polypeptide of 124 amino acids is formed. 3) No polypeptides are formed. 4) a polypeptide of 25 amino acids is formed. Ans. (1) th Solution : 24 amino acids are coded the 25 UAA is a termination rmination sequence with no amino acid. Three copies of ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.


















![arXiv:0708.2724v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Aug 2007](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014946021_1-c477dba1add7a260e278ca181f537c79-300x300.png)