Organic Molecules
... – Active site: location where substrate binds to enzyme – Enzymes are unique: • Never change shape or form! • Only fit one substrate! • Can be reused! ...
... – Active site: location where substrate binds to enzyme – Enzymes are unique: • Never change shape or form! • Only fit one substrate! • Can be reused! ...
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.2
... DNA REPLICATION Knowledge of DNA’s structure helped scientists understand how DNA replicates. DNA replication is the process in which DNA is copied. It occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle. DNA replication begins when an enzyme breaks the bonds between complementary bas ...
... DNA REPLICATION Knowledge of DNA’s structure helped scientists understand how DNA replicates. DNA replication is the process in which DNA is copied. It occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle. DNA replication begins when an enzyme breaks the bonds between complementary bas ...
Kids Building Bricks - Johnston County Schools
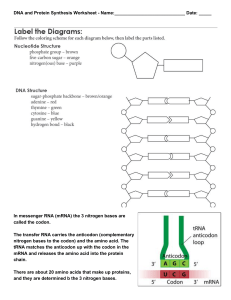
... • From DNA to mRNA • Occurs in the nucleus • Enzymes make a RNA copy of a segment of DNA –Just like DNA replication except A pairs with U, not with T ...
... • From DNA to mRNA • Occurs in the nucleus • Enzymes make a RNA copy of a segment of DNA –Just like DNA replication except A pairs with U, not with T ...
Longest Common Subsequence Assignment
... Computers execute machine code, a series of 0’s and 1’s. The machine code for living organisms is DNA, a sequence of four nucleotides: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Machine code and DNA are very similar in theoretical structure. Thus, a technique that is useful in computer science can als ...
... Computers execute machine code, a series of 0’s and 1’s. The machine code for living organisms is DNA, a sequence of four nucleotides: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Machine code and DNA are very similar in theoretical structure. Thus, a technique that is useful in computer science can als ...
Section 3 Vocabulary Vocabulary Term Definition heritable
... are packages of DNA that classify and categorize the instructions for making each individual organism are uninterrupted segments of DNA which carry specific instructions for specific characteristics for an organism ...
... are packages of DNA that classify and categorize the instructions for making each individual organism are uninterrupted segments of DNA which carry specific instructions for specific characteristics for an organism ...
Big Ideas - Fort Bend ISD
... Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. Evolution is a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time, with natural selection its major driving mechanism. Darwin’s theory, which is supported by evidence from many scientific disciplines, states that inheri ...
... Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. Evolution is a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time, with natural selection its major driving mechanism. Darwin’s theory, which is supported by evidence from many scientific disciplines, states that inheri ...
Phylogenetic DNA profiling : a tool for the investigation of poaching
... mutations is dependant upon the function of the mutated DNA sequence; sequences that are involved in critical life processes accumulate mutations at a slower rate than those with less important function. In many ways the science behind phylogenetics is akin to the basic principles of photography. To ...
... mutations is dependant upon the function of the mutated DNA sequence; sequences that are involved in critical life processes accumulate mutations at a slower rate than those with less important function. In many ways the science behind phylogenetics is akin to the basic principles of photography. To ...
CHAPTER 4 Principles of Laboratory Diagnosis
... 2. A probe is a cloned DNA fragment which has been labeled so it can be detected if it hybridizes to complementary sequences in such a test system 3. A probe derived from the gene for a known protein detects that gene 4. A variant in which the DNA is separated by agarose gel electrophoresis before b ...
... 2. A probe is a cloned DNA fragment which has been labeled so it can be detected if it hybridizes to complementary sequences in such a test system 3. A probe derived from the gene for a known protein detects that gene 4. A variant in which the DNA is separated by agarose gel electrophoresis before b ...
Effects of 6-Thioguanine on RNA Biosynthesis in Regenerating Rat
... the specific mRNA molecules for these proteins or by affect ing the synthesis of the specific mRNA's themselves. The punine antimetabolite has been shown to be incorporated into both RNA and DNA (8, 9, 15, 17), but it is the incorpora tion into DNA to which cytotoxicity has been attributed (see, INT ...
... the specific mRNA molecules for these proteins or by affect ing the synthesis of the specific mRNA's themselves. The punine antimetabolite has been shown to be incorporated into both RNA and DNA (8, 9, 15, 17), but it is the incorpora tion into DNA to which cytotoxicity has been attributed (see, INT ...
Section E: Variation and Selection
... In substitution, Figure 16.7 (c), a different nucleotide is used. The triplet of bases in which the mutation occurs is changed and it may code for a different amino acid. If it does, the structure of the protein molecule will be different. This may be enough to produce a significant alteration in th ...
... In substitution, Figure 16.7 (c), a different nucleotide is used. The triplet of bases in which the mutation occurs is changed and it may code for a different amino acid. If it does, the structure of the protein molecule will be different. This may be enough to produce a significant alteration in th ...
2007/2008 Biology Curriculum Calendar and Testing
... succession (primary and secondary) pioneer species primary productivity trophic levels producers, consumers carnivores, omnivores, detritivores, decomposers energy pyramid/cycling acid rain, CFC’s global warming/ozone layer greenhouse effect biological magnification Explain the difference between ex ...
... succession (primary and secondary) pioneer species primary productivity trophic levels producers, consumers carnivores, omnivores, detritivores, decomposers energy pyramid/cycling acid rain, CFC’s global warming/ozone layer greenhouse effect biological magnification Explain the difference between ex ...
BIOL290
... A. Understand the changes that can occur in chromosomes, such as translocation, inversion, deletion, duplication, and loss/gain of genetic material. B. Review the terms euploidy and aneuploidy and be able to recognize examples of each. C. Understand the correlation between chromosome sets and size o ...
... A. Understand the changes that can occur in chromosomes, such as translocation, inversion, deletion, duplication, and loss/gain of genetic material. B. Review the terms euploidy and aneuploidy and be able to recognize examples of each. C. Understand the correlation between chromosome sets and size o ...
Genetic engineering
... Selective Breeding – Allowing only those organisms with desired characteristics to produce the next generation Hybridization – Breeding together dissimilar individuals to bring together desired characteristics from both organisms Recombinant DNA - a chromosome, plasmid or other segment of DNA ...
... Selective Breeding – Allowing only those organisms with desired characteristics to produce the next generation Hybridization – Breeding together dissimilar individuals to bring together desired characteristics from both organisms Recombinant DNA - a chromosome, plasmid or other segment of DNA ...
Enzymes
... ENZYMES ARE SPECIFIC • Every enzyme can only be used for one reaction. Each one can only bond with one substrate • So every time you have a new substrate, you need a new enzyme • This is called being SUBSTRATE SPECIFIC ...
... ENZYMES ARE SPECIFIC • Every enzyme can only be used for one reaction. Each one can only bond with one substrate • So every time you have a new substrate, you need a new enzyme • This is called being SUBSTRATE SPECIFIC ...
Chem 150: Review for Ch
... What bases are used in RNA, and those in DNA? What sugar is used in RNA, and the one in DNA? Can you distinguish between a polynucleotide that is from DNA versus one that is from RNA? (How can you tell? What do you look for?) III. DNA structure Primary structure, secondary structure and tertiary str ...
... What bases are used in RNA, and those in DNA? What sugar is used in RNA, and the one in DNA? Can you distinguish between a polynucleotide that is from DNA versus one that is from RNA? (How can you tell? What do you look for?) III. DNA structure Primary structure, secondary structure and tertiary str ...
Biotechnology Webquest
... Science involving the understanding and use of DNA has evolved at a revolutionary pace. From the point in which Watson and Crick announced the fundamental double helical structure of DNA great advances have been made in the application and understanding of this remarkable molecule for all walks of l ...
... Science involving the understanding and use of DNA has evolved at a revolutionary pace. From the point in which Watson and Crick announced the fundamental double helical structure of DNA great advances have been made in the application and understanding of this remarkable molecule for all walks of l ...
Basic molecular genetics for epidemiologists
... Mutation that does not change the genetic information, either because it lies in a non-coding region, or because it changes a codon into another coding for the same aminoacid. The second case is called a synonymous mutation. Somatic mutation Mutation happening in any non-germ line cell and affecting ...
... Mutation that does not change the genetic information, either because it lies in a non-coding region, or because it changes a codon into another coding for the same aminoacid. The second case is called a synonymous mutation. Somatic mutation Mutation happening in any non-germ line cell and affecting ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.