Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Read Section 2.1 – Atoms
... 1. __atoms________: The smallest basic unit of matter 2. Atoms consist of three types of smaller particles, called subatomic particles. They are: _____protons_______________ - positive charge _________neutrons__________ - neutral charge __________electrons__________ - negative charge 3. The nucleus ...
... 1. __atoms________: The smallest basic unit of matter 2. Atoms consist of three types of smaller particles, called subatomic particles. They are: _____protons_______________ - positive charge _________neutrons__________ - neutral charge __________electrons__________ - negative charge 3. The nucleus ...
Metagenomics - University of Maryland, College Park
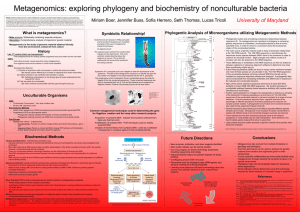
... • RNA recovery is similar to that of DNA except modified to minimize single-stranded polynucleotide degradation of mRNA as well as RNAse activity Genome enrichment: Sample enrichment enhances the screening of metagenomic libraries for a particular gene of interest, the proportion of which is general ...
... • RNA recovery is similar to that of DNA except modified to minimize single-stranded polynucleotide degradation of mRNA as well as RNAse activity Genome enrichment: Sample enrichment enhances the screening of metagenomic libraries for a particular gene of interest, the proportion of which is general ...
Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide and Study Guide
... Autosomal inheritance patterns and characteristics of sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Huntington’s disease Solve and interpret co-dominant crosses involving multiple alleles. A, B, AB and O blood types (alleles: IA, IB, and i). Determine if parentage is possible based on blood types. Some t ...
... Autosomal inheritance patterns and characteristics of sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Huntington’s disease Solve and interpret co-dominant crosses involving multiple alleles. A, B, AB and O blood types (alleles: IA, IB, and i). Determine if parentage is possible based on blood types. Some t ...
CSI Challenge #8
... 3. What system used by the FBI compiles DNA of known violent offenders from all over the nation and can be used to match DNA with a sample found at a crime scene? C. CODIS- The Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) has blood samples of offenders and has solved many cases. CODIS solved a 1993 sexual assa ...
... 3. What system used by the FBI compiles DNA of known violent offenders from all over the nation and can be used to match DNA with a sample found at a crime scene? C. CODIS- The Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) has blood samples of offenders and has solved many cases. CODIS solved a 1993 sexual assa ...
Evolution Study Guide Define the following Keyterms: evolution
... Outline how membranes may have originated in the first cells. (2) ...
... Outline how membranes may have originated in the first cells. (2) ...
Recombinant DNA Lab
... specific nucleotide sequence in DNA molecules, and cuts the backbones of the molecules at that sequence. The result is a set of double-stranded DNA fragments with single-stranded ends, called "sticky ends." Sticky ends are not really sticky; however, the bases on the single stranded ends do easily f ...
... specific nucleotide sequence in DNA molecules, and cuts the backbones of the molecules at that sequence. The result is a set of double-stranded DNA fragments with single-stranded ends, called "sticky ends." Sticky ends are not really sticky; however, the bases on the single stranded ends do easily f ...
mutation
... Loss-of-function mutations - gene product having less or no function. Phenotypes associated with such mutations are most often recessive. Exception is when the reduced dosage of a normal gene product is not enough for a normal phenotye (this is called haploinsufficiency). Dominant negative mutations ...
... Loss-of-function mutations - gene product having less or no function. Phenotypes associated with such mutations are most often recessive. Exception is when the reduced dosage of a normal gene product is not enough for a normal phenotye (this is called haploinsufficiency). Dominant negative mutations ...
Arcturus LCM Instruments and Microgenomics Reagents
... Especially useful when sample needs to be amplified ...
... Especially useful when sample needs to be amplified ...
Protein Synthesis Lab
... make the proteins. • Directions: You need to transcribe the DNA message below into the form of mRNA on your paper. Also write down what Chromosome you are working on. (Click here to review Base ...
... make the proteins. • Directions: You need to transcribe the DNA message below into the form of mRNA on your paper. Also write down what Chromosome you are working on. (Click here to review Base ...
OCR Biology AS and A2 GCE specifications for
... Describe, with the aid of diagrams, the way in which a nucleotide sequence codes for the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide; Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how the sequence of nucleotides within a gene is used to construct a polypeptide, including the roles of messenger RNA, transfer RNA and ...
... Describe, with the aid of diagrams, the way in which a nucleotide sequence codes for the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide; Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how the sequence of nucleotides within a gene is used to construct a polypeptide, including the roles of messenger RNA, transfer RNA and ...
DNA and RNA: Composition and Structure
... • Denaturation or inhibition may change protein structure - will change its function • Coenzyme and co factor may enhance the protein’s structure ...
... • Denaturation or inhibition may change protein structure - will change its function • Coenzyme and co factor may enhance the protein’s structure ...
DATA ENCRYPTION USING BIO MOLECULAR INFORMATION
... messages to make it unreadable[1]. Encryption is a useful tool in protecting confidentiality and integrity of information. It is simply a technique for hiding the true meaning of the information from unauthorised users. The worst case of an attack within communication is complete control of the encr ...
... messages to make it unreadable[1]. Encryption is a useful tool in protecting confidentiality and integrity of information. It is simply a technique for hiding the true meaning of the information from unauthorised users. The worst case of an attack within communication is complete control of the encr ...
Fatma El-Sayed Ibrahim Ali_A Symmetric Encryption Algorithm
... opened the door for researchers to utilize it in many fields especially in security. DNA computing, in the literal sense, is the use of DNA molecules, the molecules which encode genetic information for all living things, in computers. DNA computing is currently one of the fastest growing fields in b ...
... opened the door for researchers to utilize it in many fields especially in security. DNA computing, in the literal sense, is the use of DNA molecules, the molecules which encode genetic information for all living things, in computers. DNA computing is currently one of the fastest growing fields in b ...
Compiling DNA strand displacement reactions using a functional
... Previous work has shown that synthetic DNA circuits can be used to implement computational systems including digital logic circuits [1], neural networks [2] and gameplaying automata [3]. In this setting, DNA is used both as an information carrier and as an engineering material, simultaneously. Furth ...
... Previous work has shown that synthetic DNA circuits can be used to implement computational systems including digital logic circuits [1], neural networks [2] and gameplaying automata [3]. In this setting, DNA is used both as an information carrier and as an engineering material, simultaneously. Furth ...
Figure 5.x3 James Watson and Francis Crick
... needed for that specific job. It is read 3 bases at a time – codon. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – found in ribosomes and helps in the attachment of mRNA and in the assembly of proteins. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transfers the needed amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome so the proteins dictated by the ...
... needed for that specific job. It is read 3 bases at a time – codon. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – found in ribosomes and helps in the attachment of mRNA and in the assembly of proteins. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transfers the needed amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome so the proteins dictated by the ...
Review Guide notes
... traits are indicated by use of superscripts on the X chromosome only (since the Y chromosome does not carry the trait). Ex: Colorblindness is a sex-linked trait (carried on the X chromosome). The possible genotype would be written: XNXN, XNXn, XnXn, XNY, or XnY. The genes for these traits are on the ...
... traits are indicated by use of superscripts on the X chromosome only (since the Y chromosome does not carry the trait). Ex: Colorblindness is a sex-linked trait (carried on the X chromosome). The possible genotype would be written: XNXN, XNXn, XnXn, XNY, or XnY. The genes for these traits are on the ...
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF LIVING SYSTEMS At all levels
... There are intrinsically disordered proteins, for which the disordered state is necessary for the function. Some disordered proteins can participate in several reactions by forming diverse structures when they interact with different partner molecules (moonlighting). Many proteins, however, form well ...
... There are intrinsically disordered proteins, for which the disordered state is necessary for the function. Some disordered proteins can participate in several reactions by forming diverse structures when they interact with different partner molecules (moonlighting). Many proteins, however, form well ...
heredity (b)
... 19. What are the genotypes of the mother and the father? 20. Draw the Punnett square of the cross of the couple 21. What is the genotype and phenotype of the baby? A cross between red-flowered snapdragons and white-flowered snapdragons produces offspring with pink flowers. Let R = red flowers and W ...
... 19. What are the genotypes of the mother and the father? 20. Draw the Punnett square of the cross of the couple 21. What is the genotype and phenotype of the baby? A cross between red-flowered snapdragons and white-flowered snapdragons produces offspring with pink flowers. Let R = red flowers and W ...
Fall06MicrobGenetExamI
... Luria and Delbrück were trying to come up with an experiment to differentiate between the random-mutation hypothesis and the directed-change hypothesis in bacteria. In the experiment they came up with, they utilized the generation of resistance in E.coli to infection by phage T1 as their assay. The ...
... Luria and Delbrück were trying to come up with an experiment to differentiate between the random-mutation hypothesis and the directed-change hypothesis in bacteria. In the experiment they came up with, they utilized the generation of resistance in E.coli to infection by phage T1 as their assay. The ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.