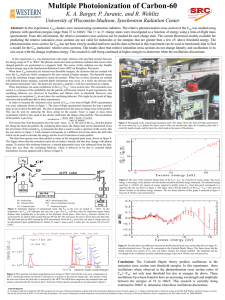
Sodium: A Charge-Transfer Insulator at High Pressures
... case the role of the anion is played by the interstitially confined electron gas. In this sense, transparent sodium behaves as an unconventional inorganic electride [19], characterized by the simplest possible anion: an electronic charge without an ionic core. The strong enhancement of the peak at a ...
... case the role of the anion is played by the interstitially confined electron gas. In this sense, transparent sodium behaves as an unconventional inorganic electride [19], characterized by the simplest possible anion: an electronic charge without an ionic core. The strong enhancement of the peak at a ...
Molecular Geometry
... the octets of the outer atoms first (H only requires 2 electrons), then place any remaining e–’s on the central atom. 4. If there are too few valence electrons to give each atom an octet, multiple bond(s) may be required. In this case, convert outer atom lone pairs to bond pairs to form multiple bon ...
... the octets of the outer atoms first (H only requires 2 electrons), then place any remaining e–’s on the central atom. 4. If there are too few valence electrons to give each atom an octet, multiple bond(s) may be required. In this case, convert outer atom lone pairs to bond pairs to form multiple bon ...
1. Structure of Matter
... • As the electron moves to orbits of increasing radius, it does so in opposition to the restoring force due to the positive nucleus, and its potential energy is thereby raised. This is entirely analogous to the increase in potential energy that occurs when any mechanical system moves against a rest ...
... • As the electron moves to orbits of increasing radius, it does so in opposition to the restoring force due to the positive nucleus, and its potential energy is thereby raised. This is entirely analogous to the increase in potential energy that occurs when any mechanical system moves against a rest ...
Snectra of Cs-137 and Co-60 Using Nal Detector lJçI Abstract
... A sample of Cs collect data for a period of fifteen minutes. This collection time was used to filter out as much background noise as possible and to get a sufficient count for the known 0.667 MeV Cesium line and the two undetermined Cobalt lines. The count for specific photons was plotted against th ...
... A sample of Cs collect data for a period of fifteen minutes. This collection time was used to filter out as much background noise as possible and to get a sufficient count for the known 0.667 MeV Cesium line and the two undetermined Cobalt lines. The count for specific photons was plotted against th ...
-Atomic Bonding in Solids
... In covalent bonding, stable electron configurations are assumed by the sharing of electrons between adjacent atoms. Two atoms that are covalently bonded will each contribute at least one electron to the bond, and the shared electrons may be considered to belong to both atoms. Covalent bonding is sch ...
... In covalent bonding, stable electron configurations are assumed by the sharing of electrons between adjacent atoms. Two atoms that are covalently bonded will each contribute at least one electron to the bond, and the shared electrons may be considered to belong to both atoms. Covalent bonding is sch ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... electronegativity between atoms, the greater the polarity/dipole moment. The higher the dipole moment, the stronger the intermolecular forces. The stronger the IMF’s the higher the melting and boiling point. ...
... electronegativity between atoms, the greater the polarity/dipole moment. The higher the dipole moment, the stronger the intermolecular forces. The stronger the IMF’s the higher the melting and boiling point. ...
ON POSSIBILITY OF MEASUREMENT OF THE
... static and uniform magnetic field B [2, 3] which allows us to find out the new additional aspects. In particular, it is found that the kinematical restrictions on the photon absorption process lead to interesting selection effects in angles of propagation of photons which can be absorbed by electron ...
... static and uniform magnetic field B [2, 3] which allows us to find out the new additional aspects. In particular, it is found that the kinematical restrictions on the photon absorption process lead to interesting selection effects in angles of propagation of photons which can be absorbed by electron ...
Electron Scattering - Department of Physics, HKU
... 1960s and were the first to find out about the charge distribution of protons in the nucleus – using high energy electron scattering. c ...
... 1960s and were the first to find out about the charge distribution of protons in the nucleus – using high energy electron scattering. c ...
Electron dynamics in the carbon atom induced by spin
... ML = +1 and MS = −1/2. This change in orbital magnetic quantum number can have a noticeable effect on the atomic dynamics: For example, in harmonic generation of noble-gas ions Ne+ and Ar+ , the harmonic yields for ML = 0 were reduced by a factor 2-4 compared to ML = ±1 [7, 8]. Recently, pump-probe ...
... ML = +1 and MS = −1/2. This change in orbital magnetic quantum number can have a noticeable effect on the atomic dynamics: For example, in harmonic generation of noble-gas ions Ne+ and Ar+ , the harmonic yields for ML = 0 were reduced by a factor 2-4 compared to ML = ±1 [7, 8]. Recently, pump-probe ...
Electron domain and molecular geometry of bro2-
... Molecular Structure Calculations.. Molecular Structure Calculations A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of ClO3- including a description of the ClO3- bond angles. Looking at the ClO3- Lewis structure we can see. A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of SO2 including a description o ...
... Molecular Structure Calculations.. Molecular Structure Calculations A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of ClO3- including a description of the ClO3- bond angles. Looking at the ClO3- Lewis structure we can see. A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of SO2 including a description o ...
Exam #3
... questions. For questions involving calculations, show all of your work -- HOW you arrived at a particular answer is MORE important than the answer itself! Circle your final answer to numerical questions. The entire exam is worth a total of 150 points. Attached are a periodic table and a formula shee ...
... questions. For questions involving calculations, show all of your work -- HOW you arrived at a particular answer is MORE important than the answer itself! Circle your final answer to numerical questions. The entire exam is worth a total of 150 points. Attached are a periodic table and a formula shee ...
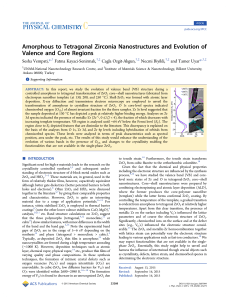
Amorphous to Tetragonal Zirconia
... to any specific ionic state, due to the finite uncertainty involved in deconvolution in the background of complex envelop of density of states. Hence, these peaks are referred to Zr+ζ, 0 ≤ |ζ| < 4, with varying (2.8−3.2 eV) spin orbit splitting. From Table 1, it is also noted that the relative area ra ...
... to any specific ionic state, due to the finite uncertainty involved in deconvolution in the background of complex envelop of density of states. Hence, these peaks are referred to Zr+ζ, 0 ≤ |ζ| < 4, with varying (2.8−3.2 eV) spin orbit splitting. From Table 1, it is also noted that the relative area ra ...
Chemical bond - Physical Science
... • Recall that all elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons (electrons in their outermost energy levels) • Thus, they must gain or lose the same number of electrons to achieve a full outer energy level in a bond • Oxidation number: the charge of an ion • For ionic compound ...
... • Recall that all elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons (electrons in their outermost energy levels) • Thus, they must gain or lose the same number of electrons to achieve a full outer energy level in a bond • Oxidation number: the charge of an ion • For ionic compound ...
Electronic Structure - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Angular Quantum Number, l. This quantum number describes the shape of an orbital. l = 0, 1, 2, and 3 (4 shapes) but we use letters for l (s, p, d and f). Usually we refer to the s, p, d and f-orbitals Magnetic Quantum Number, ml. This quantum number describes the orientation of orbitals of the same ...
... Angular Quantum Number, l. This quantum number describes the shape of an orbital. l = 0, 1, 2, and 3 (4 shapes) but we use letters for l (s, p, d and f). Usually we refer to the s, p, d and f-orbitals Magnetic Quantum Number, ml. This quantum number describes the orientation of orbitals of the same ...
Hybridization Theory Review Review
... full valency - a term often employed when an atom has gained electrons to become isoelectronic with a noble element; usually adhering to the octet or duet rule. geometric isomers - have the same gross connectivity but differ only how the groups are oriented in space due to hindered rotation about th ...
... full valency - a term often employed when an atom has gained electrons to become isoelectronic with a noble element; usually adhering to the octet or duet rule. geometric isomers - have the same gross connectivity but differ only how the groups are oriented in space due to hindered rotation about th ...
The quantum atom
... consequences of doing so are extremely important to us. Once the form of is known, the allowed energies E of an atom can be predicted from the above equation. Soon after Schrödinger's proposal, his equation was solved for several atoms, and in each case the predicted energy levels agreed exactly wit ...
... consequences of doing so are extremely important to us. Once the form of is known, the allowed energies E of an atom can be predicted from the above equation. Soon after Schrödinger's proposal, his equation was solved for several atoms, and in each case the predicted energy levels agreed exactly wit ...
Review for Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
... hybrid orbitals are employed. The inclusion of the d orbital enables “expanded octets” to occur. For octahedral molecules in which six pairs of electrons are arranged around a central atom, sp3d2 hybrid orbitals are used. 10. Sigma bonds are covalent bonds formed by orbitals overlapping end-to-end, ...
... hybrid orbitals are employed. The inclusion of the d orbital enables “expanded octets” to occur. For octahedral molecules in which six pairs of electrons are arranged around a central atom, sp3d2 hybrid orbitals are used. 10. Sigma bonds are covalent bonds formed by orbitals overlapping end-to-end, ...
Major 02
... In the hydrogen atom, the energies of the orbitals for a given principal quantum level increase as follows: Es < Ep < Ed < Ef This is certainly false, because from Bohr's model follows that in any 1-electron system like H all orbitals with the same n are degenerate, i.e. have the same energies, B) m ...
... In the hydrogen atom, the energies of the orbitals for a given principal quantum level increase as follows: Es < Ep < Ed < Ef This is certainly false, because from Bohr's model follows that in any 1-electron system like H all orbitals with the same n are degenerate, i.e. have the same energies, B) m ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.