No Slide Title - The Robinson Group – University of Nottingham
... of non-, non- conformation Loops – larger stretches with no secondary structure. Often disordered. • “Random coil” • Sequences vary much more than secondary structure regions ...
... of non-, non- conformation Loops – larger stretches with no secondary structure. Often disordered. • “Random coil” • Sequences vary much more than secondary structure regions ...
How are protein products made from a gene?
... generated. There are 20 amino acids used to make proteins (more details about DNA, RNA and amino acids can be found in “What is some basic information about DNA?”, “What is transcription?” and “What is translation?”). ...
... generated. There are 20 amino acids used to make proteins (more details about DNA, RNA and amino acids can be found in “What is some basic information about DNA?”, “What is transcription?” and “What is translation?”). ...
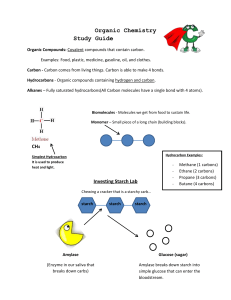
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... Organic Compounds: Covalent compounds that contain carbon. Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons( ...
... Organic Compounds: Covalent compounds that contain carbon. Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons( ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... There are four classes of macromolecules -carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon ...
... There are four classes of macromolecules -carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon ...
1 Food intake regulation
... A simplified version of homeostatic regulation of food intake; focus on signals from the digestive system (ghrelin, CCK, PYY), adipose tissue (leptin) and the pancreas (insulin) ...
... A simplified version of homeostatic regulation of food intake; focus on signals from the digestive system (ghrelin, CCK, PYY), adipose tissue (leptin) and the pancreas (insulin) ...
Reading - Science with Ms. Wang
... through peptide bonds. The type of protein, and thus its function, is determined by the kind of amino acids joined together and the order in which those amino acids are arranged. Some proteins are very large molecules, containing hundreds of amino acids. Often these long proteins are bent and folded ...
... through peptide bonds. The type of protein, and thus its function, is determined by the kind of amino acids joined together and the order in which those amino acids are arranged. Some proteins are very large molecules, containing hundreds of amino acids. Often these long proteins are bent and folded ...
ch_6_-_the_proteins2
... The nitrogen atoms give the name amino (nitrogen containing) to amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of protein The amino acids in a strand of protein are different from on another – can contain 20 different kinds of amino acids Amino Acids All amino acids have a chemical backbone ...
... The nitrogen atoms give the name amino (nitrogen containing) to amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of protein The amino acids in a strand of protein are different from on another – can contain 20 different kinds of amino acids Amino Acids All amino acids have a chemical backbone ...
POWERPOINT NOTES SHEET 2.3 Carbon Compounds
... All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. ...
... All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. ...
BIOL103 Review Questions for Midterm 2 SP16
... 1. What are proteins made up of? What are the differences among essential, non-‐ essential and conditionally essential amino acids (AAs)? 2. Which type of bonds link AAs? 3. What are functions of body protei ...
... 1. What are proteins made up of? What are the differences among essential, non-‐ essential and conditionally essential amino acids (AAs)? 2. Which type of bonds link AAs? 3. What are functions of body protei ...
File - Edgeley Family and consumer sciences
... Dietary Protein The National Academy of Sciences has created a method of scoring proteins. They are assessed and given a number value. Those proteins that contain an adequate content of all 9 essential amino acids are given a high score and are called complete proteins. Those that are missing one o ...
... Dietary Protein The National Academy of Sciences has created a method of scoring proteins. They are assessed and given a number value. Those proteins that contain an adequate content of all 9 essential amino acids are given a high score and are called complete proteins. Those that are missing one o ...
Introduction
... Impact of recombinant DNA technology on the production of proteins • Overcomes the problem of source availability : allows the manufacture of any protein in whatever quantity it is required • Overcomes the problem of product safety: Avoiding transmission of blood-born pathogens such as hepatitis B, ...
... Impact of recombinant DNA technology on the production of proteins • Overcomes the problem of source availability : allows the manufacture of any protein in whatever quantity it is required • Overcomes the problem of product safety: Avoiding transmission of blood-born pathogens such as hepatitis B, ...
2 Biochemistry
... Proteins = hemoglobin (in blood), collagen (in skin), elastin (structure), myosin & actin (muscles), keratin (hair & nails), enzymes (catalysts), hormones* ...
... Proteins = hemoglobin (in blood), collagen (in skin), elastin (structure), myosin & actin (muscles), keratin (hair & nails), enzymes (catalysts), hormones* ...
Binding Kinetics of Protein Lipid Interactions Using OpenSPR
... OpenSPR. Tests were run at 20 µL/min using HBS running buffer. LIP-1 Sensors were first cleaned with 40 mM Octyl βD-glucopyranoside and 20 mM CHAPS. 3. Liposomes (0.17 µg/mL) were run over the chip surface until 1 nm of immobilization was observed. An injection of 1% w/v bovine serum albumin (BSA) i ...
... OpenSPR. Tests were run at 20 µL/min using HBS running buffer. LIP-1 Sensors were first cleaned with 40 mM Octyl βD-glucopyranoside and 20 mM CHAPS. 3. Liposomes (0.17 µg/mL) were run over the chip surface until 1 nm of immobilization was observed. An injection of 1% w/v bovine serum albumin (BSA) i ...
Chapter 5 Overview: The Molecules of Life • All living things are
... • A slight change in primary structure can affect a protein’s structure and ability to function • Sickle-cell disease, an inherited blood disorder, results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin What Determines Protein Structure? • In addition to primary structure, physical ...
... • A slight change in primary structure can affect a protein’s structure and ability to function • Sickle-cell disease, an inherited blood disorder, results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin What Determines Protein Structure? • In addition to primary structure, physical ...
The Ubiquitin Proteosome pathway
... Ubiquitin system is considered to be involved in brain development. Defective synthesis of gene coding for E3 ligase E6-AP Characteristic symptoms involve mental retardation, seizures, out of context frequent smiling and laughter. Brain proteins that could be stabilized by mutation have not ...
... Ubiquitin system is considered to be involved in brain development. Defective synthesis of gene coding for E3 ligase E6-AP Characteristic symptoms involve mental retardation, seizures, out of context frequent smiling and laughter. Brain proteins that could be stabilized by mutation have not ...
What observations did Darwin make that lead him to the Theory of
... 6. List the bonds formed by molecules used by organisms. Which can hold a molecule together? Which ionize in solution? Which yield polar molecules? Which from at bonds between molecules? 7. Summarize the basic design pattern(s) of the macromolecules. Lipids are an exception – explain. 8. Compare & c ...
... 6. List the bonds formed by molecules used by organisms. Which can hold a molecule together? Which ionize in solution? Which yield polar molecules? Which from at bonds between molecules? 7. Summarize the basic design pattern(s) of the macromolecules. Lipids are an exception – explain. 8. Compare & c ...
The Protein Folding Problem When will it be solved?
... • Critical Assessment of Techniques for Structure Prediction (Moult, 1994) • Social experiment • Prediction of native state from amino-acid sequence alone • Approaches are homology modeling and protein threading ...
... • Critical Assessment of Techniques for Structure Prediction (Moult, 1994) • Social experiment • Prediction of native state from amino-acid sequence alone • Approaches are homology modeling and protein threading ...
Lecture 10/09
... The molecules here are used in all kinds of ways depending on what you want to look at. For example, if you want to know where a protein is in the cytoplasm, then perhaps using phalloidin conjugated with a flourescent molecule in ADDITION to your tagged protein (use a different flourescent molecule ...
... The molecules here are used in all kinds of ways depending on what you want to look at. For example, if you want to know where a protein is in the cytoplasm, then perhaps using phalloidin conjugated with a flourescent molecule in ADDITION to your tagged protein (use a different flourescent molecule ...
Lecture 5: The Chemistry of Life III
... • In straight structures, H atoms on one strand can bond with OH groups on other strands • Parallel cellulose molecules held together this way are grouped into microfibrils, which form strong building materials for plants ...
... • In straight structures, H atoms on one strand can bond with OH groups on other strands • Parallel cellulose molecules held together this way are grouped into microfibrils, which form strong building materials for plants ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.