chapter 5 - SWR Global History
... B. Early Rome: according to legend, founded in 753 B.C.E. by Romulus and Remus 1. Pastoral people, spoke Latin (the language of Latium) 2. Were influenced, and probably directly ruled, by the Etruscans, who urbanized Rome a. Romans adopted Etruscan toga, fasces insignia for magistrates, and alphabet ...
... B. Early Rome: according to legend, founded in 753 B.C.E. by Romulus and Remus 1. Pastoral people, spoke Latin (the language of Latium) 2. Were influenced, and probably directly ruled, by the Etruscans, who urbanized Rome a. Romans adopted Etruscan toga, fasces insignia for magistrates, and alphabet ...
The Fall of the Roman Empire
... things by force. It was the first time in centuries that nomadic invaders had entered Rome. After looting the city for three days, the Goths left. The city of Rome tried to recover and go on, but it was seriously weakened. Germanic peoples also invaded what is now France, Spain, and northern Africa. ...
... things by force. It was the first time in centuries that nomadic invaders had entered Rome. After looting the city for three days, the Goths left. The city of Rome tried to recover and go on, but it was seriously weakened. Germanic peoples also invaded what is now France, Spain, and northern Africa. ...
Chapter 5 The Roman World
... took the Egyptian throne for himself and did not make Egypt a province. Also after Actium, Augustus personally completed the conquest of Spain and between 19 B.C.E. and 9 B.C.E. Illyricum, Pannonia, and Rhaetia were subjugated. Rome expanded into Germany in 15 B.C.E when its forces crossed the Rhine ...
... took the Egyptian throne for himself and did not make Egypt a province. Also after Actium, Augustus personally completed the conquest of Spain and between 19 B.C.E. and 9 B.C.E. Illyricum, Pannonia, and Rhaetia were subjugated. Rome expanded into Germany in 15 B.C.E when its forces crossed the Rhine ...
1.1 The Legacy of the Roman Empire Introduction
... The emperors in Rome soon found themselves threatened by invading Germanic tribes. In 410 C.E., one of these tribes attacked and looted Rome itself. Finally, in 476, the last emperor in the west was driven from his throne. The western half of the empire began to dissolve into separate kingdoms. In t ...
... The emperors in Rome soon found themselves threatened by invading Germanic tribes. In 410 C.E., one of these tribes attacked and looted Rome itself. Finally, in 476, the last emperor in the west was driven from his throne. The western half of the empire began to dissolve into separate kingdoms. In t ...
File
... the races, including Rome's poor. There were races every day. It was the height of success to race in the Circus Maximus. ...
... the races, including Rome's poor. There were races every day. It was the height of success to race in the Circus Maximus. ...
Essential Question: –What factors led to the collapse of the Roman
... Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The was divided But,empire the empire The East was far wealthier than between was also Greek-speaking divided the West because it had most of & Latin-speaking halves by wealth the great cities & trade centers ...
... Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The was divided But,empire the empire The East was far wealthier than between was also Greek-speaking divided the West because it had most of & Latin-speaking halves by wealth the great cities & trade centers ...
Historical information / Variant / Development notes - PD
... a widespread system of alliances during several wars in Mid-Italy. New colonies were founded at locations that were strategically important. From these times Rome emerged as a strong state with a powerful army and thus was prepared for its further rise to become a world power. Perilous opponents wer ...
... a widespread system of alliances during several wars in Mid-Italy. New colonies were founded at locations that were strategically important. From these times Rome emerged as a strong state with a powerful army and thus was prepared for its further rise to become a world power. Perilous opponents wer ...
30 - News.com.au
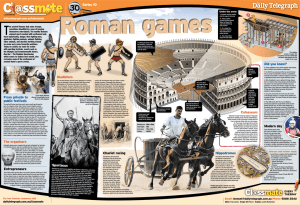
... The earliest Roman sporting events were usually performed as part of a religious ritual. Even chariot races probably evolved from the Greek practice of holding funerary games, the earliest mention of which is in Homer’s epic poem The Iliad (from about the 9th or 8th century BC). Rather like the sain ...
... The earliest Roman sporting events were usually performed as part of a religious ritual. Even chariot races probably evolved from the Greek practice of holding funerary games, the earliest mention of which is in Homer’s epic poem The Iliad (from about the 9th or 8th century BC). Rather like the sain ...
2013RBAdapted 6196KB Sep 04 2013 12:03:13 PM
... In AD 43, the Roman conquest of Britain began. Vespasian's subsequent campaign to conquer the tribes of the Atrebates, Dumnonii, and Durotriges in the southwest of Britain took place in AD 43–47. Based on the discovery of a group of bodies in the Late Iron Age formal cemetery that had met a violent ...
... In AD 43, the Roman conquest of Britain began. Vespasian's subsequent campaign to conquer the tribes of the Atrebates, Dumnonii, and Durotriges in the southwest of Britain took place in AD 43–47. Based on the discovery of a group of bodies in the Late Iron Age formal cemetery that had met a violent ...
Pre-Roman Hispania
... The Carthaginians entered into conflict with Rome over control of the Peninsula ...
... The Carthaginians entered into conflict with Rome over control of the Peninsula ...
Augustus and the Family at the Birth qfthe Roman Empire. By Beth
... domain of men from dominant aristocratic famil ies. The next chapter explores the last half of Augustus' reign (12 BC - AD 14) and shows how private family worship of household divinities, including the father's genius (protective spirit), was used as the model upon which to base the public cult of ...
... domain of men from dominant aristocratic famil ies. The next chapter explores the last half of Augustus' reign (12 BC - AD 14) and shows how private family worship of household divinities, including the father's genius (protective spirit), was used as the model upon which to base the public cult of ...
File - world history
... THE EMPEROR AUGUSTUS & PAX ROMANA: Augustus paved the way for 200 years of peace and prosperity in Rome, THE emperors who followed him were not all good rulers, but they helped the Roman Empire reach its peak. For centuries, the Mediterranean region had been filled with conflict. Under Augustus and ...
... THE EMPEROR AUGUSTUS & PAX ROMANA: Augustus paved the way for 200 years of peace and prosperity in Rome, THE emperors who followed him were not all good rulers, but they helped the Roman Empire reach its peak. For centuries, the Mediterranean region had been filled with conflict. Under Augustus and ...
Georgraphy Ancient Names
... of the Pannonia province within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found today inBudapest, the capital city of Hungary. It is believed that Marcus Aurelius may have written at least part of his book Meditations at Aquincum ...
... of the Pannonia province within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found today inBudapest, the capital city of Hungary. It is believed that Marcus Aurelius may have written at least part of his book Meditations at Aquincum ...
Roman Daily Life
... fairly common for Romans to have one main meal in the late afternoon, from around four in the afternoon to six in the evening. Breakfast and lunch were typically very light, usually consisting of bread or fruit. If you were part of the lower class, you could expect to eat mostly cereal grains, often ...
... fairly common for Romans to have one main meal in the late afternoon, from around four in the afternoon to six in the evening. Breakfast and lunch were typically very light, usually consisting of bread or fruit. If you were part of the lower class, you could expect to eat mostly cereal grains, often ...
hui216_10_v7
... the Roman Empire: the reaction of the Romans • The Romans did none of these things • At a time when the entire Roman army had a total of only 29 legions to garrison the entire empire, one legion was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a h ...
... the Roman Empire: the reaction of the Romans • The Romans did none of these things • At a time when the entire Roman army had a total of only 29 legions to garrison the entire empire, one legion was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a h ...
Chapter 5
... Augustus believed that Roman morals had been corrupted during the late republic – Created social legislation to slow/halt decline – Luxury had undermined roman morality – easy divorce, declining birthrate in upper class, hedonistic behavior ...
... Augustus believed that Roman morals had been corrupted during the late republic – Created social legislation to slow/halt decline – Luxury had undermined roman morality – easy divorce, declining birthrate in upper class, hedonistic behavior ...
Pax Romana
... east to the newly built city of Constantinople in present-day Turkey. Neither Diocletian nor Constantine I succeeded to save the Roman Empire. In 378 A.D., a Germanic group defeated Roman legions at the Battle of Adrianople. In 410 A.D., the Germanic chief Alaric and his soldiers invaded Rome, burni ...
... east to the newly built city of Constantinople in present-day Turkey. Neither Diocletian nor Constantine I succeeded to save the Roman Empire. In 378 A.D., a Germanic group defeated Roman legions at the Battle of Adrianople. In 410 A.D., the Germanic chief Alaric and his soldiers invaded Rome, burni ...
roman power point
... • Eastern emperors held greater power as they were considered head of the church and state. • Eastern societies did not have profitable trading routes while western societies had many trade routes. • Western societies provided large mosaics. Eastern societies built churches. ...
... • Eastern emperors held greater power as they were considered head of the church and state. • Eastern societies did not have profitable trading routes while western societies had many trade routes. • Western societies provided large mosaics. Eastern societies built churches. ...
Chapter 4 - Cloudfront.net
... • Sparta: Singularly militaristic aristocracy • Other city states were aristocratic, but not necessarily bent on the impact of the military • Aristocracy comes from Greek terms, meaning “rule of the best” ...
... • Sparta: Singularly militaristic aristocracy • Other city states were aristocratic, but not necessarily bent on the impact of the military • Aristocracy comes from Greek terms, meaning “rule of the best” ...
Decline and Fall of Roman Empire
... Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The was divided But,empire the empire The East was far wealthier than between was also Greek-speaking divided the West because it had most of & Latin-speaking halves by wealth the great cities & trade centers ...
... Rome was too large & dividing the empire into the Western Eastern Roman Empires The was divided But,empire the empire The East was far wealthier than between was also Greek-speaking divided the West because it had most of & Latin-speaking halves by wealth the great cities & trade centers ...
Romans in Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia
... invaded the kingdom of Armenia, allied to the Romans. After gaining (60) and losing (62) Armenia, the Romans under Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo, legate of Syria entered (63) into an agreement of Vologases I of Parthia, which confirmed Tiridates I as king of Armenia, thus founding the Arshakuni Dynasty. A ...
... invaded the kingdom of Armenia, allied to the Romans. After gaining (60) and losing (62) Armenia, the Romans under Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo, legate of Syria entered (63) into an agreement of Vologases I of Parthia, which confirmed Tiridates I as king of Armenia, thus founding the Arshakuni Dynasty. A ...
Rome at War AD 293-696
... cumulatively they contributed to diminishing imperial authority, undermining the fiscal and military structures which permitted the imperial machine to function. By the late fifth century an emperor had become irrelevant in the western Mediterranean, although the eastern ruler was accepted as a figu ...
... cumulatively they contributed to diminishing imperial authority, undermining the fiscal and military structures which permitted the imperial machine to function. By the late fifth century an emperor had become irrelevant in the western Mediterranean, although the eastern ruler was accepted as a figu ...